When dealing with tension or conflict around the world, several different parties are usually involved. These include non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and international organizations (IO). Some international organizations, such as the United Nations (UN) and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), are well known. These organizations are well known in Quebec because they are involved in the part of the world in which we live. But other important organizations include the Arab League and the African Union.

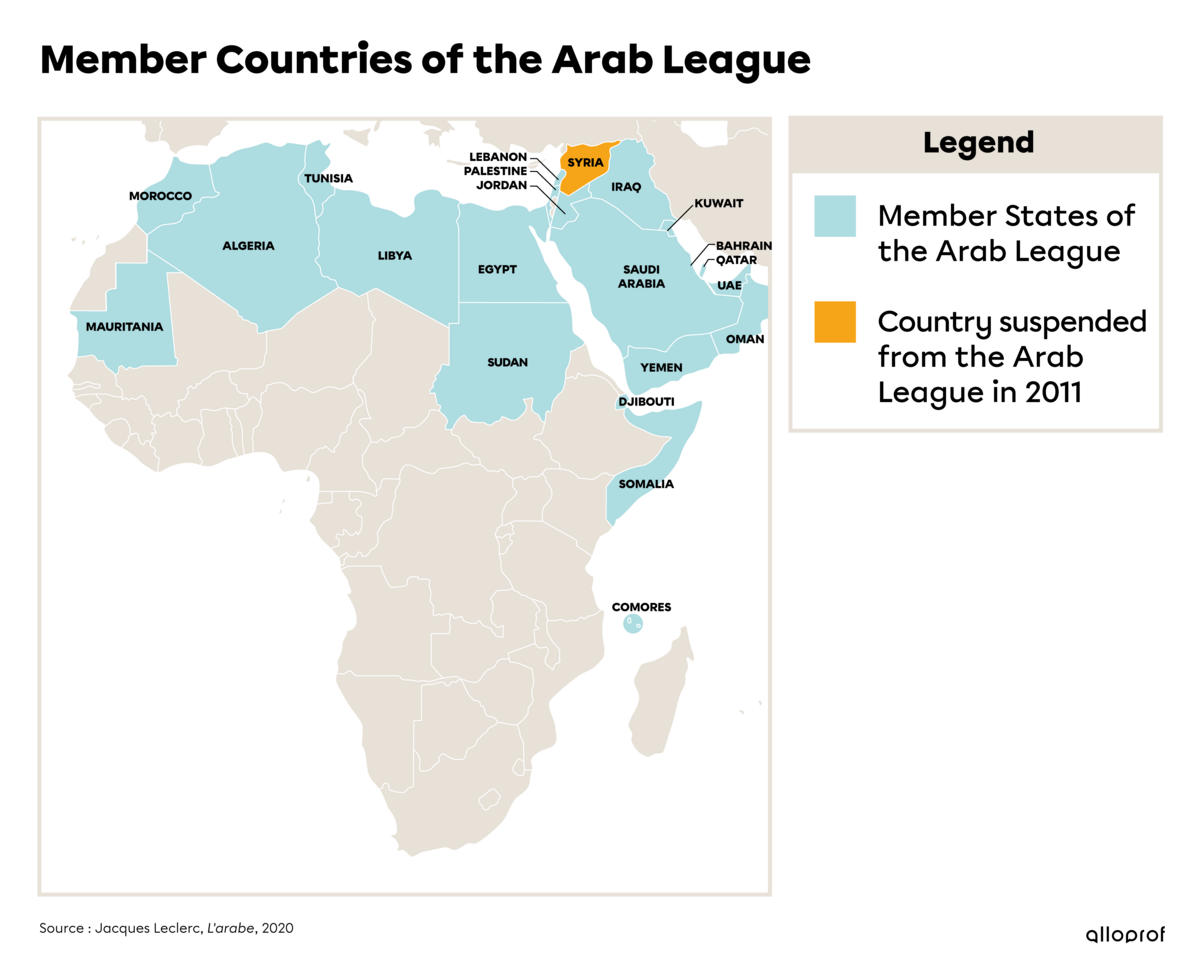
| Founded | 1945. Its primary aim is to strengthen political and economic ties between Arab countries. Today, it mainly settles disputes between Member States. |
|---|---|
| Member countries | There are 22 member countries (which once included Syria, a country suspended since 2011). |
| Means used to reduce tension and conflict | Since it was founded, the Arab League has excluded the use of force from its means of resolving issues. It focuses on organizing negotiations and acting as a mediator (i.e. proposing a peace plan) between opposing countries or groups. It can also pressure governments to implement economic sanctions against a certain country to resolve a conflict. |
A mediator is a person or organization acting as an intermediary to help resolve a conflict. A mediator is a neutral and impartial party that should not be directly involved in the conflict.
Why is it called the Palestinian Authority? Because Palestine’s statehood is not recognized by the entire international community. Consequently, it cannot sign agreements on behalf of a country that does not exist in the eyes of the entire international community.
The Arab League is heavily involved in the conflict in Syria. In 2011, Syria was suspended from the Arab League, even though it was one of the five founding countries. In 2020, Syria was still suspended from the Arab League. This shows the League’s opposition to the regime of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad, in office since 2000. But what happened in 2011? During the Arab Spring, several protests were organized to denounce President Bashar al-Assad’s authoritarian regime and to demand democracy. These protests were violently repressed by the government. At that time, the Arab League organized diplomatic negotiations to propose a peace plan. The Syrian government rejected this proposal, which resulted in its suspension from the Arab League.
The protest movement turned into an armed rebellion. The conflict has continued and new parties (such as the Islamic State) took advantage of the situation to get involved. The Syrian conflict has become much more complex. The Syrian government has been accused of war crimes and crimes against humanity, including aerial bombings of civilians, political torture, executions by hanging and people being falsely imprisoned and then reported missing.
Repression is intended to end movements of revolt or protest by using force and violence. These actions do not respect human rights.

| Founded | The African Union, which was created in 2002, supports the development of democracy and respect for human rights to promote Africa’s growth and economic development. |
|---|---|
| Member countries | There are 55 Member States representing all of Africa. |
| Means used to reduce tension and conflict | The AU has established institutions that allow it to intervene within its Member States. The AU Peace and Security Council gets involved when there is tension or conflict. It tries to anticipate and prevent conflicts by conducting observation missions in areas of tension, organizing peace meetings between opposing parties and conducting peacemaking and peacekeeping missions. It also has a military force that member countries can call on. The AU also participates in peace missions with other international organizations such as the UN and NATO. |
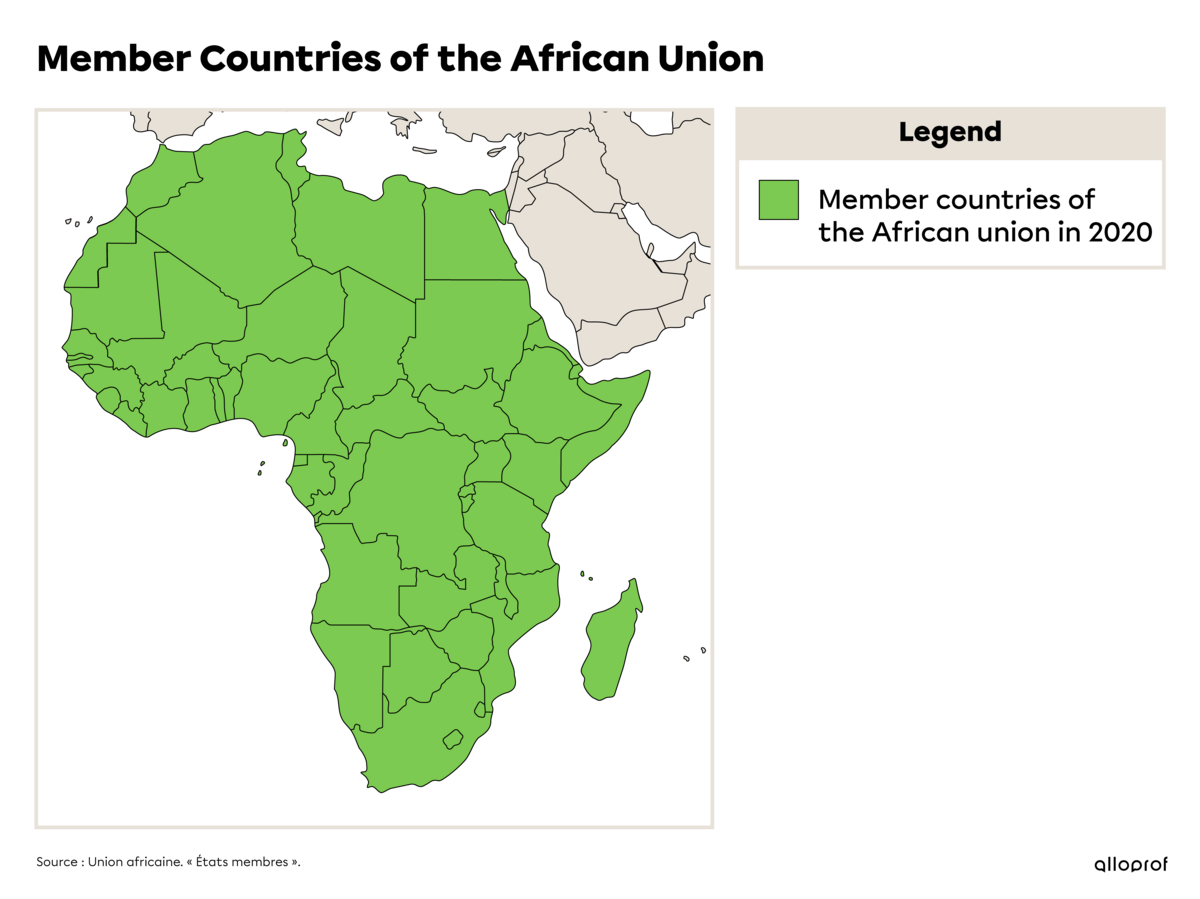
The African Union (AU) has 55 African Member States, but Africa officially has only 54 countries. This is because the AU includes the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR), which is not recognized by all countries. The UN defines it as a territory that is not self-governing and that has not yet been fully decolonized. However, the AU recognizes the SADR as a sovereign nation. The SADR is located on the territory of Western Sahara and Morocco.
A civil war has been raging in Somalia since 1991, when President Siad Barre was overthrown, causing Somalia’s government and economy to collapse. The country has yet to recover. A stable government cannot be established because several groups are fighting for power. In 2007, the AU Peace and Security Council established the African Union Mission in Somalia (AMISOM). After being authorized by the UN, it was deployed. The EU has also greatly assisted in funding AMISOM. Soldiers from AU member countries are being sent to Somalia to fight the jihadist group al-Shabaab.
However, the AU soldiers in Somalia did not have a good reputation. Human Rights Watch reported that some soldiers allegedly sexually abused women seeking medical help or water at AU military bases.
For more information, visit their official website: https://au.int/en

The European Union is an economic, political and military union of 27 European countries.
|
Founded |
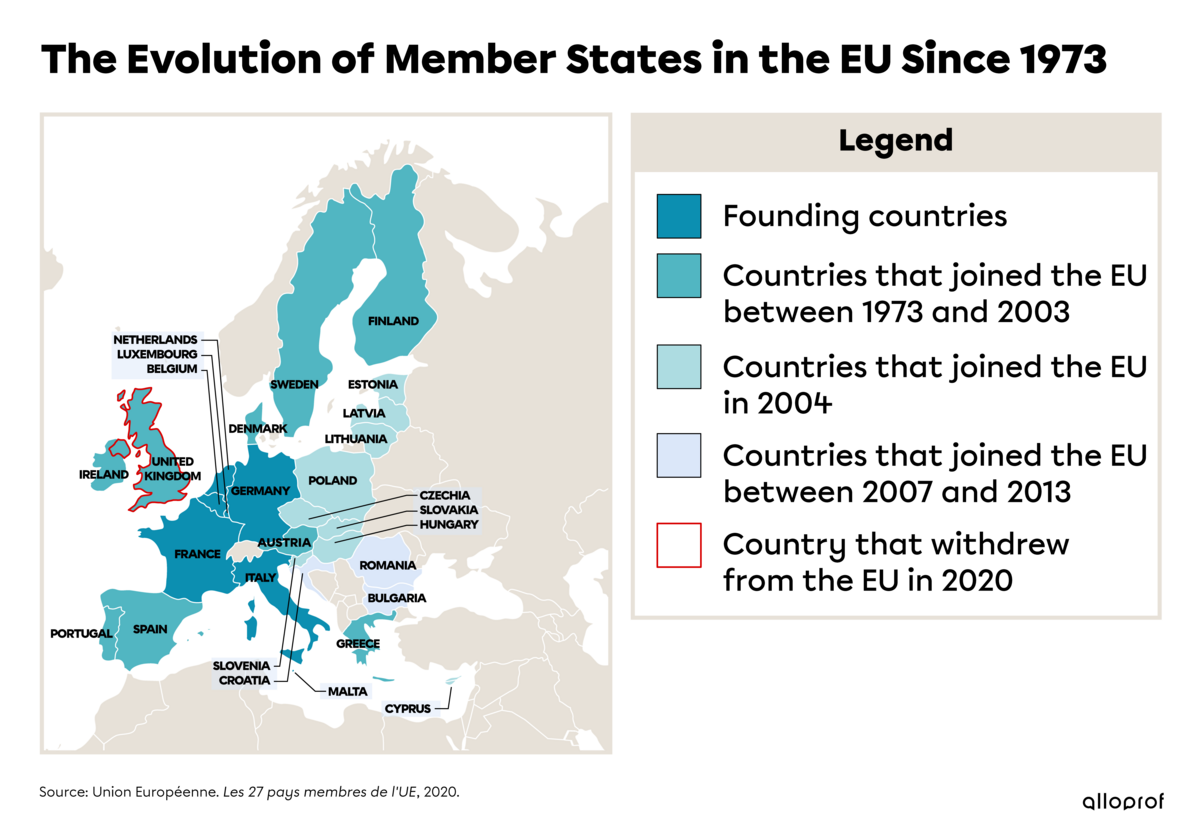
The European Union was founded in 1951, when six European countries decided to join together to create genuine economic cooperation. The organization was officially named the European Economic Community in 1958 followed by the European Union in 1993. Over time, several other countries have joined. |
|---|---|
|
Member countries |
As of March 2020, the EU had 27 member countries after the United Kingdom withdrew on January 31, 2020. These are: Germany, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Croatia, Denmark, Spain, Estonia, Finland, France, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Sweden and the Czech Republic (Czechia). |
|
Goals |
The EU has a foreign and security policy aimed at resolving conflicts and promoting understanding between countries, giving priority to diplomatic agreements. The four main goals of this policy are to:
|
|
Means used to reduce tension and conflict |
The EU does not have a standing army but can call on military forces provided by member countries as needed. It sends missions to conflict areas to uphold law and order, participate in peacekeeping or provide assistance to civilians. It also helps manage international relations. |
The rule of law refers to the idea that all individuals, even those with political or military power (governments, leaders, etc.) are accountable under the same laws. In other words, no one is above the law. Laws and their application must be independent of any other authority so as not to be influenced or corrupted. The laws must also be compatible with international human rights.
To find out more about the EU’s international missions in other areas (environment, migration, fighting disinformation, etc.), visit the following site: About the European External Action Service. To view a map and find out more about current EU missions, visit this site.

|
Founded |
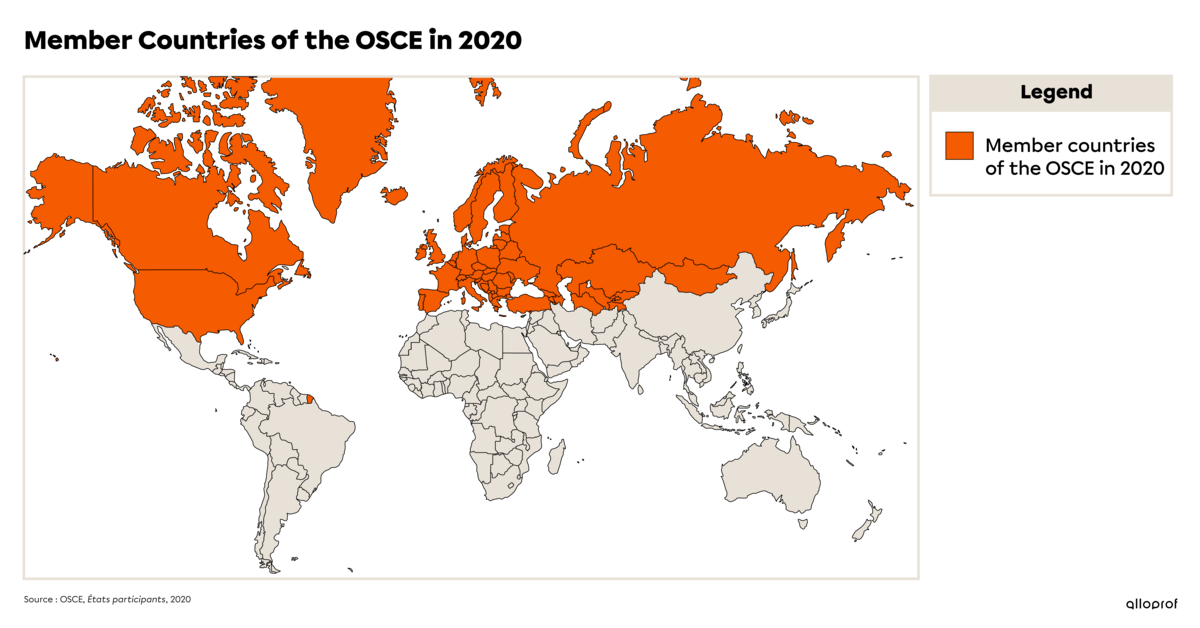
The OSCE was founded in 1995. It replaces the Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe (CSCE), first established in 1975. |
|---|---|
|
Member countries |
The OSCE is made up of 57 countries from North America, Europe and Central Asia. Click here to see the list of 57 member countries. |
|
Goals |
The OSCE works to promote stability, peace and democracy.
|
|
Means used to reduce tension and conflict |
It provides a space for dialogue between its different members. Based on this dialogue, operations and missions are sometimes launched in the field. However, this can only take place with permission from the country where these operations and missions are conducted. |
The OSCE conducts projects to help with arms control and to fight human trafficking and corruption (such as reporting on violations during democratic elections). During the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, the OSCE adapted its work to help Albania deal with the pandemic.
The OSCE conducts projects to strengthen democracy and promote human rights.
The OSCE has been conducting an observation mission (unarmed) since 2014 in all regions of Ukraine to observe and report on what is happening and to help establish dialogue between the different conflicting parties.
For more information on Ukraine’s conflict with Russia, which began in 2014, visit the following site: Conflict Tracker: Ukraine.
The OSCE is also conducting missions in Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia and Moldova.
If the organization is called the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, why are Canada and the United States members when they are not European countries?
This organization was created due to the fallout from the Cold War and the repercussions on all of Europe. NATO was also established as a result of the Cold War. The OSCE welcomed NATO member countries within its organization, which included Canada and the USA.
Ladouceur, Maude, and collabs. Globe, 2014.