The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is an important international player. It is a military power that works to provide security, democracy and peace.
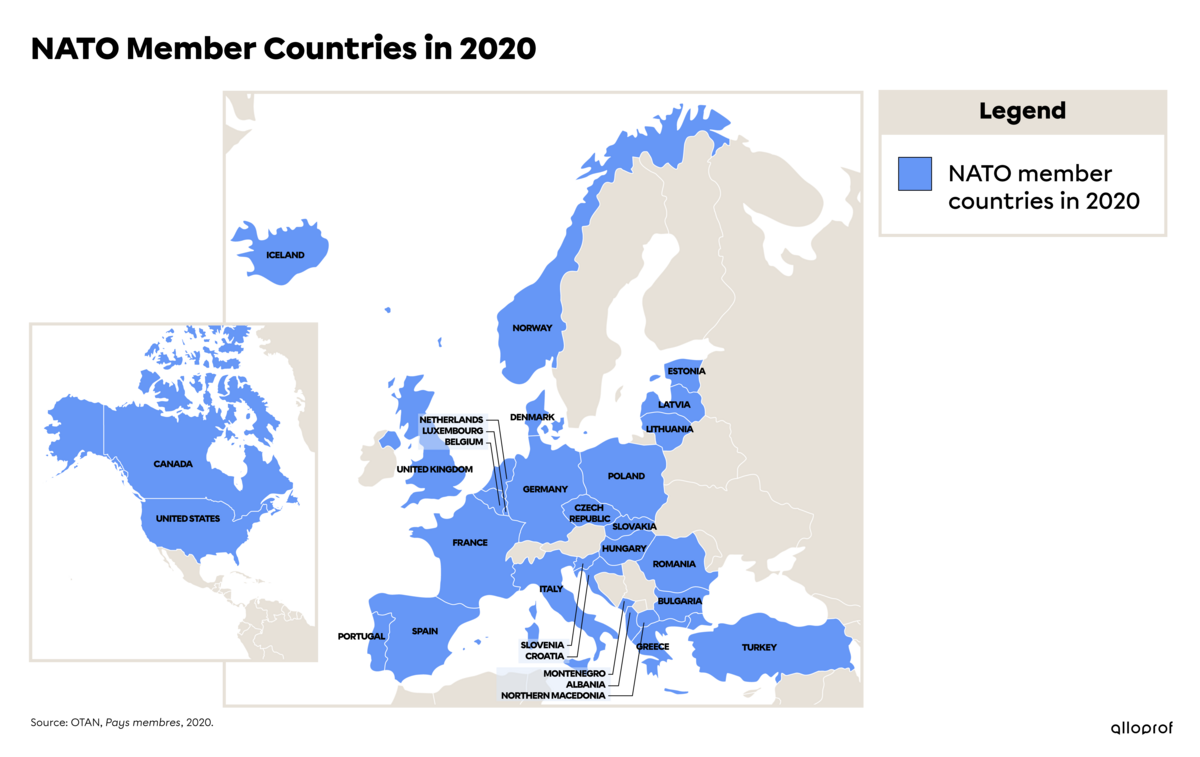
NATO was founded in 1949. It includes several Western countries such as the United States, Canada and European countries. In 2020, NATO had 30 members. The name North Atlantic refers to the fact that this organization is open to countries located near the northern part of the Atlantic Ocean, namely Western Europe and North America.
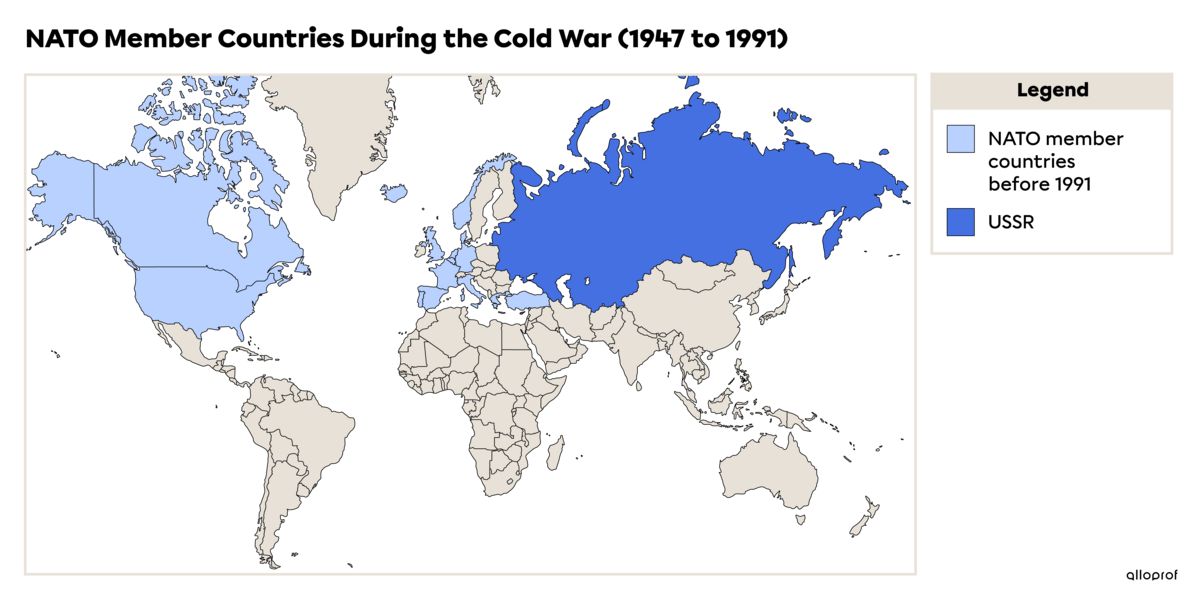
This organization was created during the Cold War, when the USA opposed the USSR (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics). This conflict divided the world in 2: capitalist countries versus communist countries. NATO was created to protect Western (capitalist) countries from attacks by the USSR (communist). Its goals have changed slightly since the USSR collapsed in 1991.
NATO is still a strategic and military alliance whose mission is to protect the freedom and security of all its members by military and political means.
-
Political role: NATO promotes democratic values and facilitates discussion and cooperation among its members to resolve defence and security issues. The long-term goal is to avoid potential conflicts.
-
Military role: NATO always advocates for peaceful conflict resolution. However, if diplomacy and negotiation efforts fail, it has the military power to conduct armed operations. NATO can act under its internal treaty or under the mandate of the United Nations (UN). It may also request help from non-member countries or other international organizations.
NATO’s specific details and rules are laid out in the North Atlantic Treaty. Article 5 stipulates that an armed attack against one of the member countries is considered an attack against them all. If one member is attacked, all member states must retaliate. NATO is a strong military alliance with a high strike capability since it brings together the armed forces from all its members.
An international organization (IO) is an organization that brings together representatives of different states to achieve common objectives on global issues.
NATO has redefined its mission and operations since 1991. These days, it can intervene in non-member countries. When it intervenes in a sovereign state, it does so with the following goals in mind:
-
to help governments ensure the security of their country
-
to participate in the creation of a favourable environment for the establishment of democratic institutions
It is also more involved in supporting other international organizations such as the UN (supporting peace missions) or the African Union. It provides direct humanitarian aid to countries in crisis. In addition, the member countries have combined their military forces to, among other things, fight terrorism following the attack on the United States on September 11, 2001.
-
Sovereignty is the absolute power of a state to govern itself by making its own laws and enforcing them within its territory. A sovereign state is independent, meaning that it cannot be controlled by any other state or institution.
To better understand what sovereignty is, you can watch the video Sovereignty and Interference.
-
An institution is an organization governed by rules and laws that plays a specific role in society. Its role may be political, social, economic, religious, etc.
To better understand what an institution is, you can watch the video What is… an institution?.
As of August 2019, NATO was conducting operations in Afghanistan, Kosovo and the Mediterranean.
NATO has had more than one mission in Afghanistan. In 2001, Afghan authorities requested US assistance, which led to the creation of the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) in Afghanistan. NATO directed this mission from 2003 to 2014. The goal was to train Afghan security forces to effectively protect the country. It was also an attempt to create a situation conducive to establishing democracy. Force was used when necessary to prevent the country from falling into the hands of terrorists. Forces from 51 countries have contributed to the ISAF.
In 2015, NATO launched Operation Resolute Support. It provided training, advice and assistance to Afghan security forces and security institutions. This time, force was not used by NATO soldiers.
NATO conducts operations in more than just conflict zones. Since September 11, 2001, NATO has begun to take steps toward combating international terrorism. Launched in 2001, the Active Endeavour surveillance mission aims to detect and stop terrorist activities in the Mediterranean, including the Strait of Gibraltar (kamikaze operations by ship, taking ships hostage, transporting weapons and explosives, etc.). In 2016, this mission was replaced by Operation Sea Guardian, which aims to secure the maritime environment through various tasks.
Kosovo is a country that is not yet recognized by the entire international community and is in conflict with Serbia. In 2019, 3500 soldiers from NATO member countries and partner countries were operating in Kosovo as part of the Kosovo Force (KFOR). KFOR has been deployed there since 1999. When Kosovo declared its independence in 2008, the UN Security Council asked KFOR to maintain its presence there. Its mission is to handle security tasks that are not handled by the police and to help create a professional security force in Kosovo. It also supports dialogue between Kosovo and Serbia.
Below are examples of other countries where NATO has conducted operations:
Iraq, from 2004 to 2011: This was a mission to train, mentor and assist Iraqi security forces. In 2018, NATO was still conducting operations in Iraq as part of the NATO Mission Iraq. The aim was to strengthen Iraqi security and military forces to prevent the return of the Islamic State (a terrorist, military and political organization also called Daesh).
Libya, in 2011: This was a mission to support the Libyan people. NATO conducted the UN-mandated Operation Unified Protector, which aimed to stop the transport of weapons and mercenaries into Libya, establish a no-fly zone (territory over which no airplanes are allowed to fly) to prevent bombing of civilians and coordinate air and naval strikes against attacks targeting civilians.
Darfur (Sudan) 2005 to 2007: NATO assisted the African Union in its efforts to end the violence and the catastrophic humanitarian crisis that had been happening since 2003 when the War in Darfur started, which was still raging in 2020.
Pakistan, from 2005 to 2006: NATO provided emergency humanitarian aid after an earthquake.
Southern United States, 2005, after Hurricane Katrina: NATO helped with reconstruction and humanitarian relief operations.
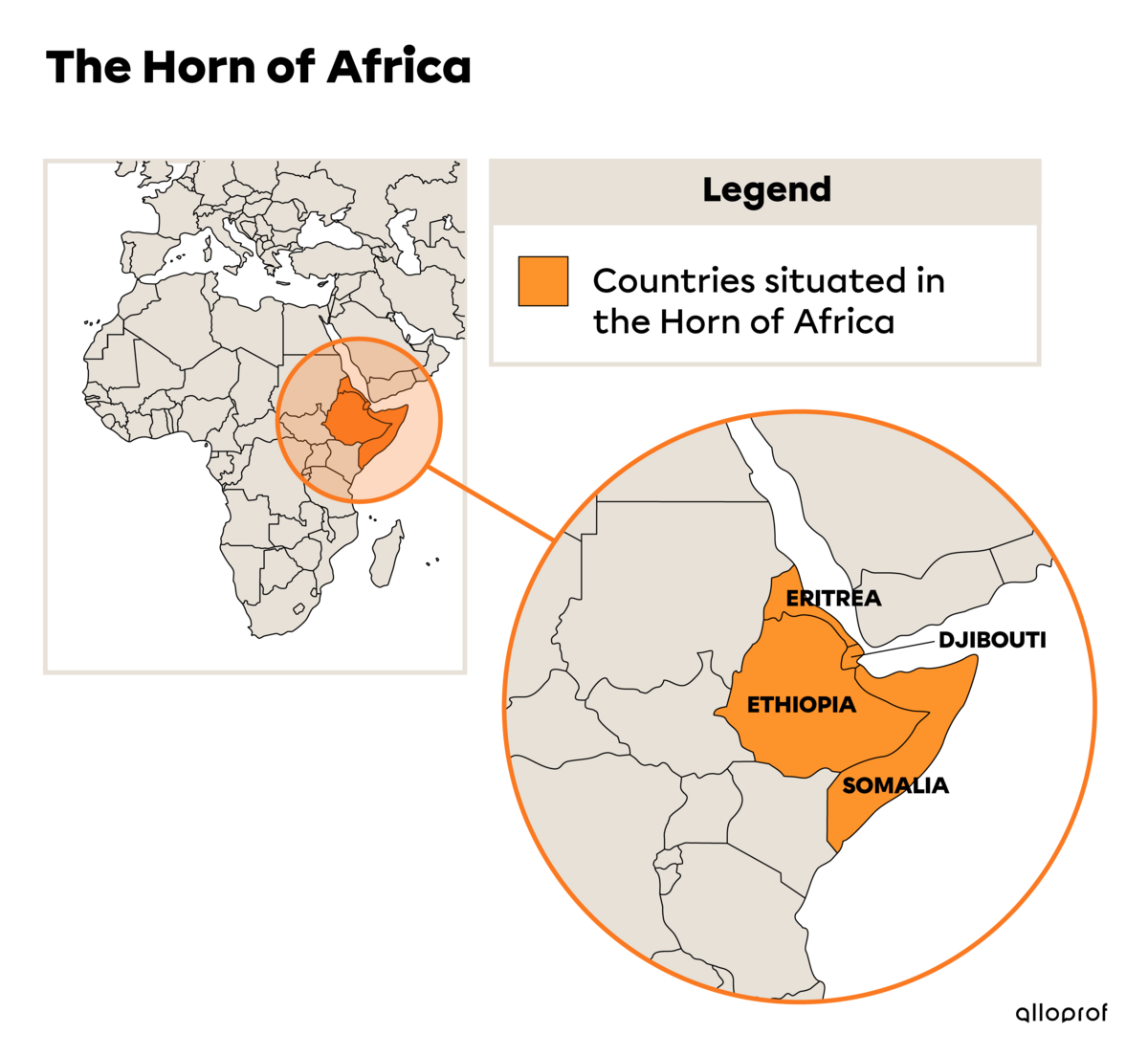
Gulf of Aden and off the Horn of Africa, between 2008 and 2016: NATO led the fight against pirates. It protected ships from piracy and helped improve security around the Horn of Africa. It was assisted by several other countries including India, China, Malaysia and Russia. Foreign navies played a major role in eradicating piracy in Somali waters.
The Horn of Africa is a nickname for the East African peninsula. It includes Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia and Somalia.
NATO has faced a lot of criticism. One complaint is that it essentially serves US military and strategic ambitions around the world. This would make it a tool for increasing American hegemony. French leaders, for example, have already aimed strong criticism at NATO.
Hegemony is the political or military dominance of one group or state over others.
Some people argue that NATO is gradually crumbling, that it is no longer useful and that the US is moving away from it. Why does it still exist when it was originally created to counter the threat posed by the Soviet Union, which no longer exists? Some people say that NATO still exists to increase US power.
American hegemony began to rise near the end of World War II and the beginning of the Cold War. The United States has tried to spread its hegemony around the world and assert its influence in several areas. On a cultural level, the influence of American films, music and even lifestyle has spread to Western countries and many Eastern countries.
From a military standpoint, the US established military bases in several countries. Its military gets involved in many conflicts, which boosts the US economy. A large part of the US economy depends on the production of military hardware. Weapons companies, among others, can put a lot of pressure on the government. Politics and military companies are closely tied in the United States. In 2019, US military spending was $732 billion, or 38% of global military spending.
From an economic standpoint, the United States has developed a global economy. It:
-
owns many industries and companies abroad;
-
has successfully integrated capitalism into most countries;
-
has lent money to several countries to help them develop, leaving these countries indebted to it.
Interesting fact: Since money around the world has different values, one way of comparing the purchasing power (the amount of goods and services that can be bought with a certain amount of money) of different countries is the Big Mac index. It lists the price of a Big Mac in different McDonald’s across the globe. This demonstrates the cultural influence and economic presence that the United States has around the world.
However, some people believe that American hegemony has been declining for several years. The US may lose the upper hand to new global powers such as China.
Finally, some NATO operations, such as the one in Kosovo in 1999, have been widely criticized. In 1999, NATO intervened in Kosovo under the pretence that the conflict between Kosovo and Serbia threatened the security of several European countries. NATO ended up bombing Yugoslavia, where Kosovo was located, several times before being mandated by the UN. However, international law stipulates that only the UN Security Council can sanction an attack on a sovereign country.