This Crash Course focuses on the main states of matter, the changes of state and the phase change diagrams. You can use the interactive video, recap and practice questions to review this topic.
The terms state of matter and phase of matter, as well as the terms change of state and phase change are interchangeable.
-
Matter is any substance that makes up something with a mass. All matter is made up of particles.
-
The state or the phase of matter refers to the organization of its particles.
-
A change of state, or phase change, is a transformation of matter from one state to another.
-
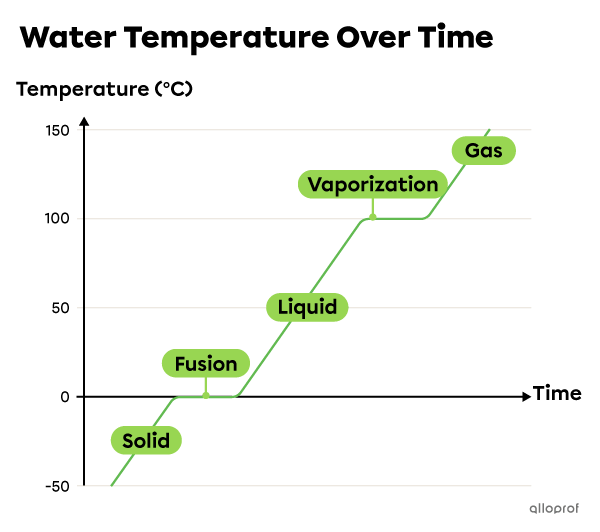
A phase change diagram is a graph showing how the temperature of a substance changes over time.
The main characteristics of the three states of matter are described in the following table.
|
State of matter |
Particle behaviour |
Shape and volume retention |
Diagram of water particles |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Solid |
|
|
 |
|
Liquid |
|
|
 |
|
Gaseous |
|
|
 |
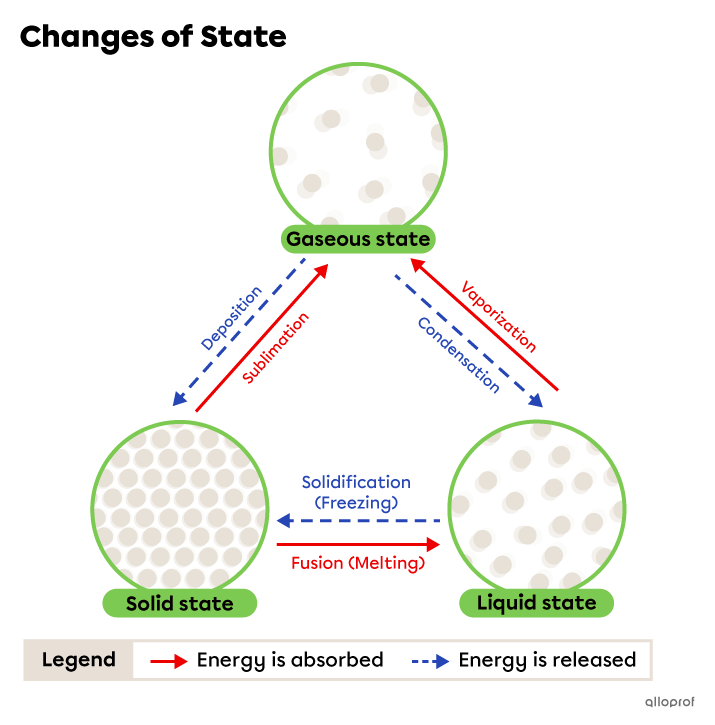
A change of state, or phase change, occurs when a substance passes from one state of matter to another due to a temperature change. The temperature change affects the behaviour of the particles but not their nature.
-
When the temperature increases, energy is absorbed. Particles move faster and further away from each other.
-
When the temperature decreases, energy is released. The particles slow down and move closer to each other.
The six phase changes are shown in the following diagram.
The phase changes can be represented as a graph, called the phase change diagram. The temperature remains the same during the plateaus which correspond to phase changes. The following phase change diagram of water indicates that it passes from solid to liquid to gaseous state, as the temperature increases.