To access the rest of the unit, consult the Tools in Geography concept sheet.
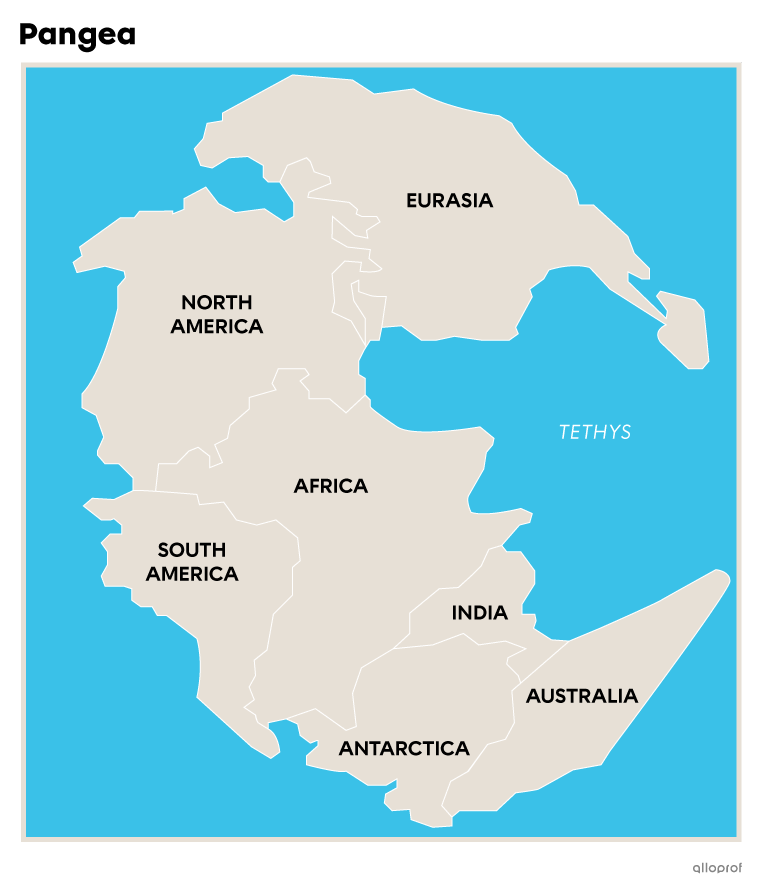
The shape and location of continents and oceans have been evolving for 3 billion years. Over these many years, the tectonic plates on which the continents rest have detached, moved and separated until reaching their current shape and location.
Plate tectonics is the theory that the tectonic plates on which the continents rest are slowly moving towards or away from each other. According to this theory, these movements began over 3 billion years ago.
Here are some continents and their evolution over time:
-
Rodinia: plates shifted and clung together to form Rodinia, 1100 million years ago. It was a megacontinent that brought together almost all of today's continents. It began to come apart around 700 million years ago.
-
Laurentia and Siberia: these two continents separated from Rodinia around 560 million years ago. Laurentia corresponds to part of today's North America, while Siberia represents today's Siberian Shield, located in Russia.
-
Baltica: around 540 million years ago, this continent separated from what remains of Rodinia. Baltica contains the following present-day regions: Scandinavia, Russia, Poland and part of Germany.
-
Gondwana: this is the name given to the remaining part of the former megacontinent Rodinia.
These continents moved for several million years. They began to move closer together 500 million years ago to form Pangea. This newly formed megacontinent remained in place for almost 100 million years before it began to move apart, quietly leading to today's formation of continents.
A continent is a large expanse of land surrounded by one or more oceans.
There are 7 continents on the planet.
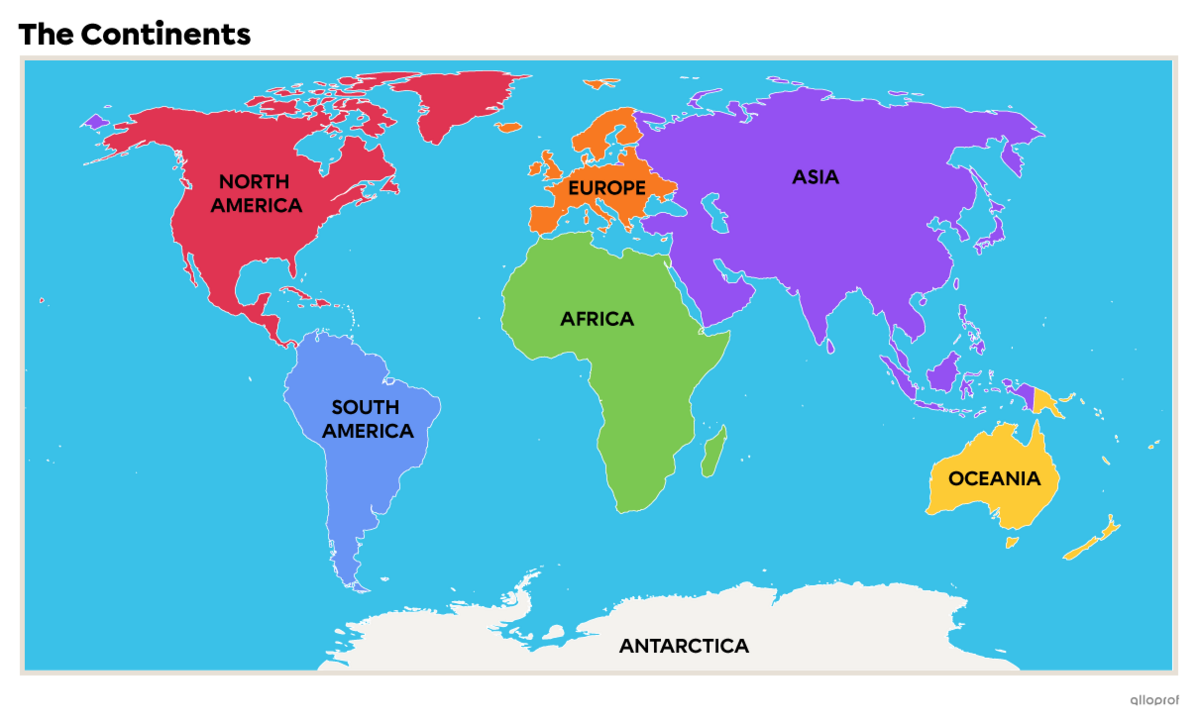
Here is the surface area in km2 of each continent.
| Continent | Surface (km2) |
|---|---|
|
44 000 000 km2 |
|
|
30 300 000 km2 |
|
|
24 700 000 km2 |
|
|
17 800 000 km2 |
|
|
12 200 000 km2 |
|
|
10 500 000 km2 |
|
|
9 000 000 km2 |
|
Data source: Bergevin, Charette, and Méthé, 2014[8]. |
|
Asia is the world's largest continent. It accounts for 30% of the world's land mass. Asia is also the most populous continent, with over 60% of the world's population[7].
When something emerges, it’s because it is exterior to the water.
When something is immersed, it is inside or below the water.
Asia's relief and climate are highly varied. It is the world's highest continent, with an average altitude of 950 m. It is home to the world's highest point, Mount Everest, which rises to over 8840 m above sea level. Conversely, the continent's deepest point, Lake Baikal, lies 1300 m below sea level[1].
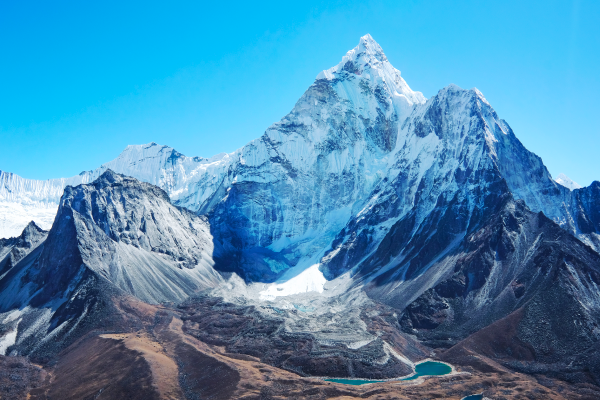

Mount Everest is the highest point in the world.
Source : Vixit, Shutterstock.com

Lake Baikal is the deepest point on the Asian continent.
Source : Zakirov Aleksey, Shutterstock.com
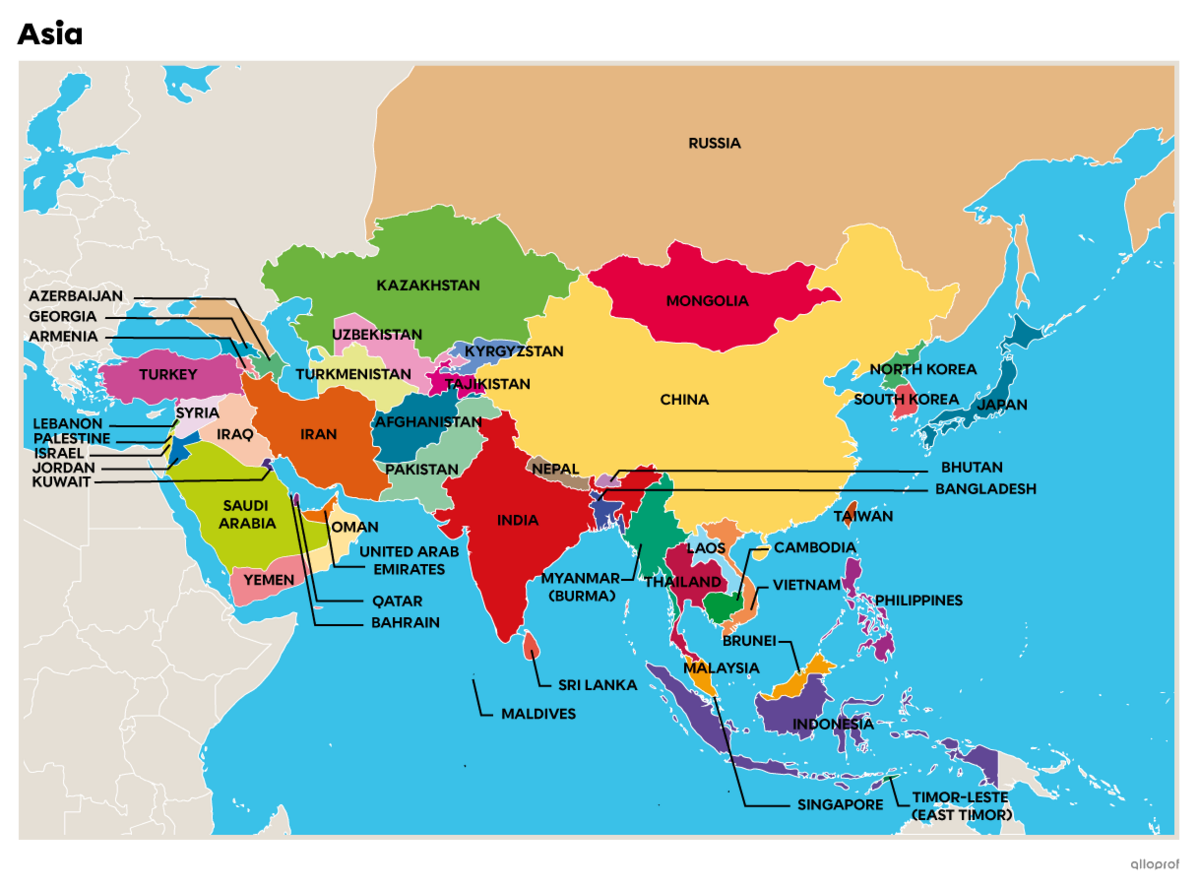
The Asian continent is divided into 5 regions.
| Anterior Asia (Western Asia or Middle East) |
Central Asia | South Asia (Southern Asia) |
Southeast Asia | Far East Asia (East Asia) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Afghanistan |
Armenia |
Bangladesh |
Brunei |
China |
Data source: Universalis, n.d.[9]; UN, n.d.[10]; Representative Office of Canada to the Palestinian Authority, March 22, 2022[11]. |
||||
The African continent is flanked by the Mediterranean Sea, the Indian Ocean, the Red Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The Strait of Gibraltar separates Africa from Europe while the Suez Canal divides the continent from Asia. Africa is the second largest continent in terms of surface area. In 2017, it was home to around 1.2 billion people[2].
The continent's climate varies greatly depending on the region you're in, with Mediterranean, desert, tropical and equatorial climates.
The Sahara Desert is the world's largest desert, with a surface area of almost 8 600 000 km2 [3]. It occupies virtually all of northern Africa, crossing 10 countries: Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, Sudan, Chad, Niger, Mali and Mauritania.
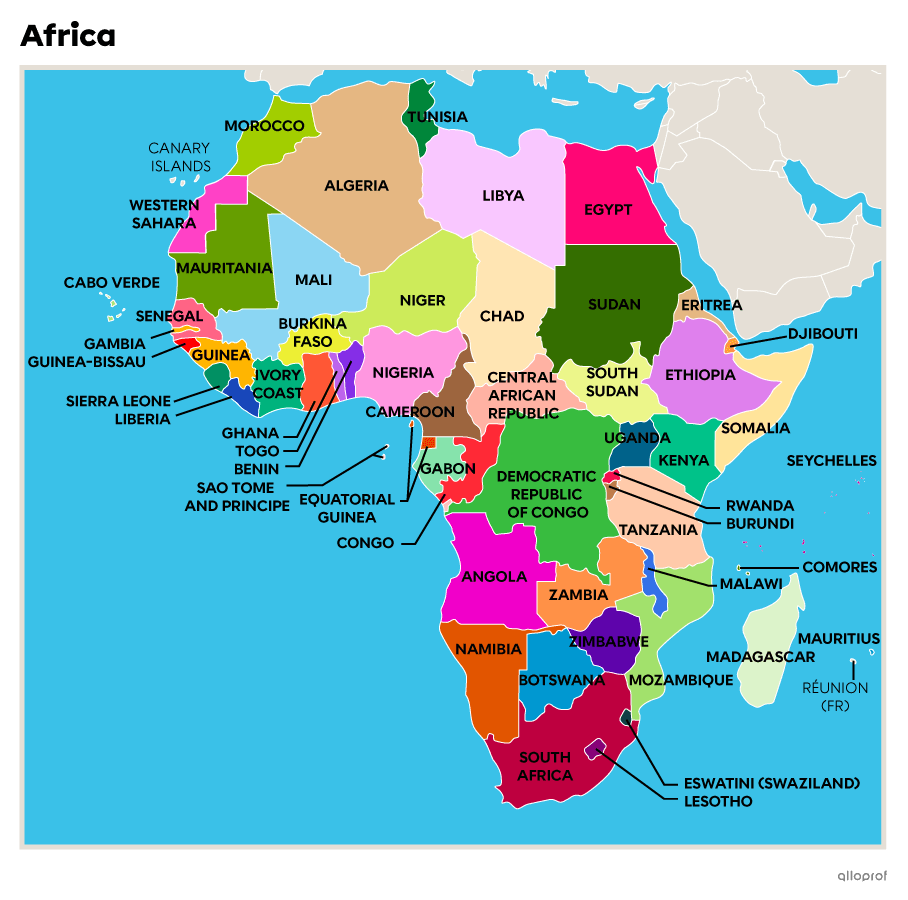
Africa is divided into 5 different regions.
| North Africa | West Africa |
East Africa | Central Africa | South Africa (Southern Africa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Algeria |
Benin |
Comoros |
Burundi |
South Africa |
|
*There is no clear consensus on the independence of this region, which is a former Spanish colony. The Polisario Front, Western Sahara's independence movement, is seeking recognition of its independence, while Morocco controls much of its territory. According to the UN, Western Sahara is a Non-Self-Governing Territory. |
||||
Data source: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, February 2017[12]. |
||||
Sub-Saharan Africa refers to the region of Africa south of the Sahara. Several countries are part of this region.
Southern Africa is a region in southern Africa comprised of 10 countries: Angola, Botswana, Eswatini (Swaziland), Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
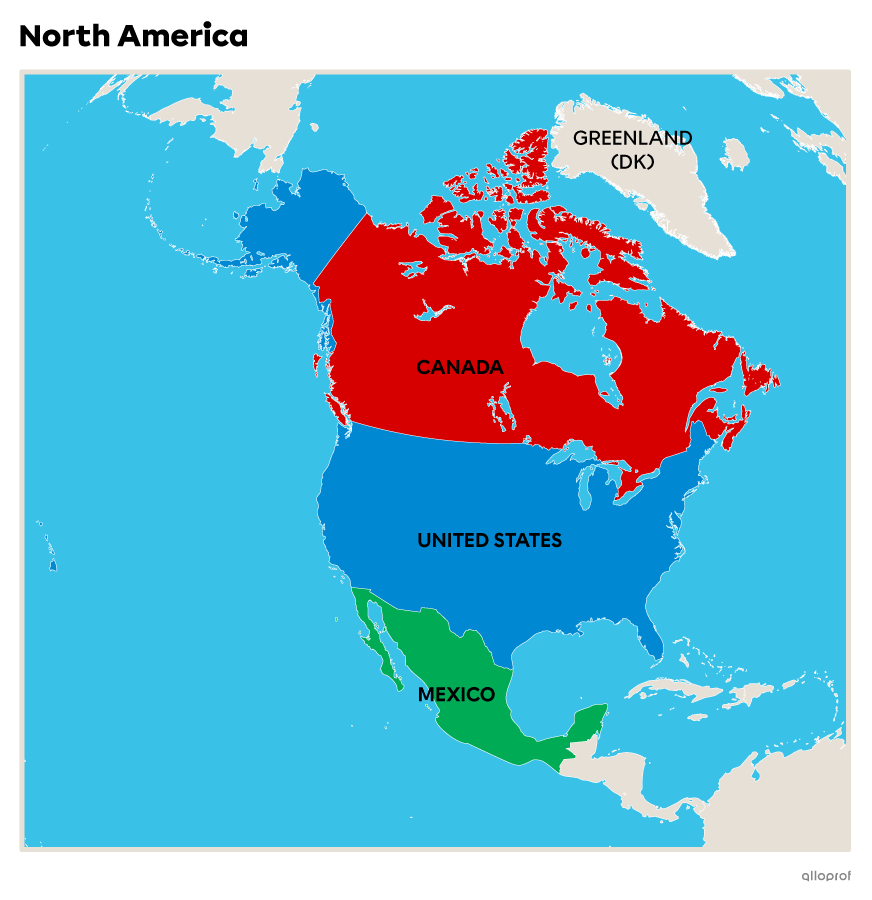
North America is surrounded by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Atlantic Ocean to the east. Climates on the continent vary from region to region, but include polar, mountain, continental, temperate and even desert climates.
To the west of the continent are high chains of mountains called The Rocky Mountains, or Rockies. To the east, there are smaller mountains, including the Appalachians. The centre of the continent is occupied by the Great Plains.
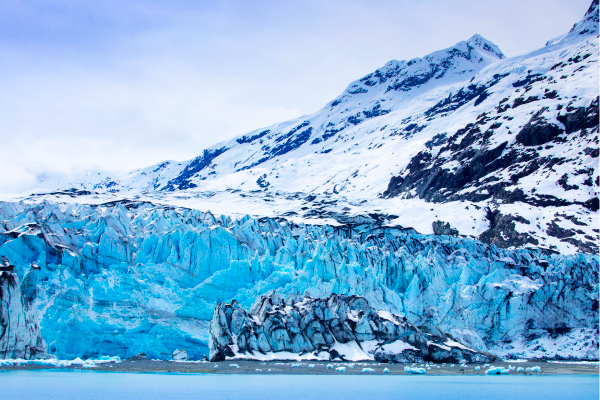

Alaska is the coldest state in the US. Its interior has a continental climate. The further north you go, the more polar the climate becomes.
Source : Wu hsoung, Shutterstock.com
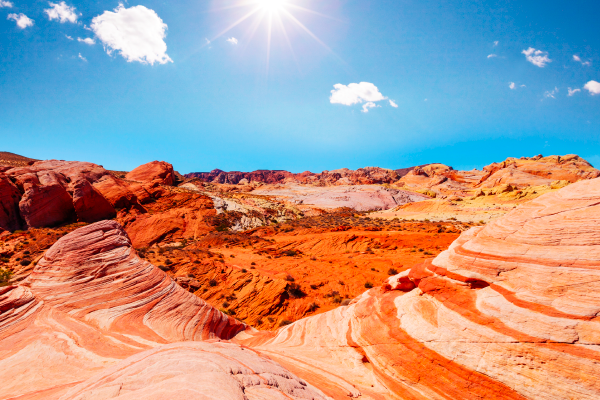

The Valley of Fire is located in Nevada’s Mojave Desert. The climate is desert-like.
Source : Galyna Andrushko, Shutterstock.com
There are only 3 countries on the North American continent: Canada, the USA and Mexico. This is because of the large size of these countries, with Canada being the second largest in the world, the USA the third and Mexico the fourteenth.
| Surface of North American countries (km2) | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Canada |
United States |
Mexico |
|
9 984 700 km2 |
9 831 500 km2 |
1 964 400 km2 |
Data source: Global data, n.d.[13] |
||
Central America is the narrowest part of the American continent, between North and South America. Central America can sometimes be considered the third American continent.
There are 7 countries in Central America: Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama.
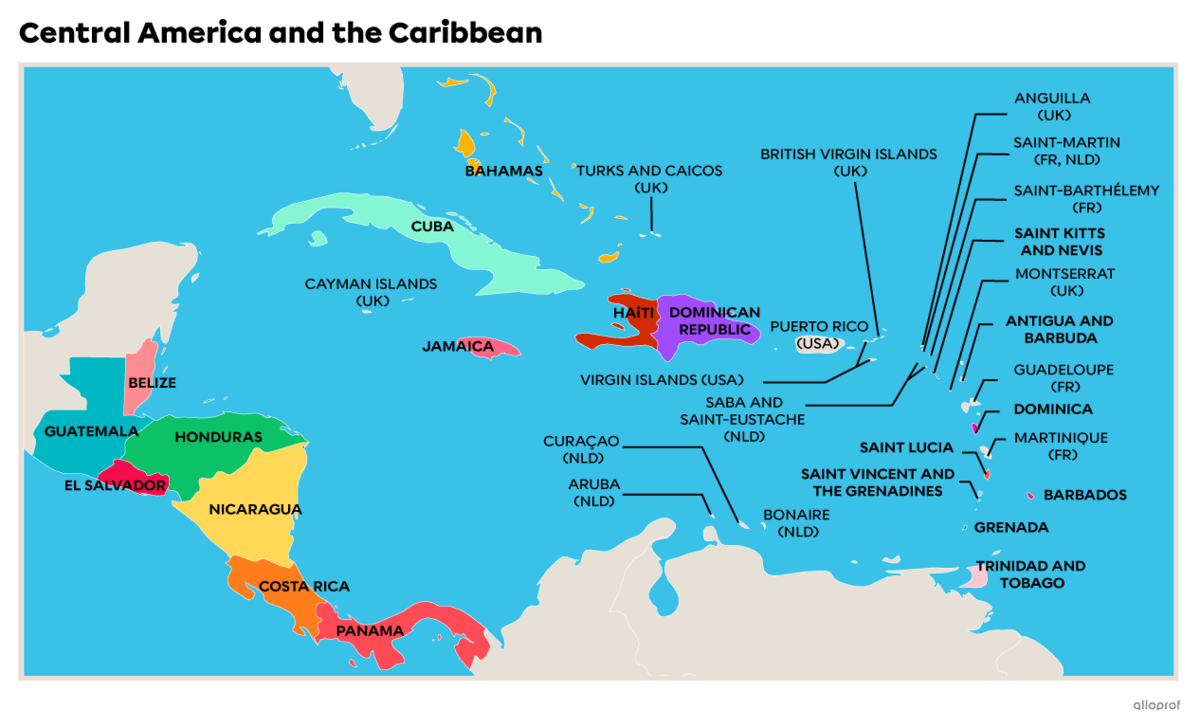
The Countries and Territories of the Caribbean
The Caribbean region comprises the states surrounding the Caribbean Sea. The region is sometimes also referred to as the West Indies.
Bahamas
Cuba
Haiti
Jamaica
Antigua and Barbuda
Barbados
Dominican Republic
Dominica
Grenada
Saint Lucia
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint-Kitts-et-Nevis
Saint-Vincent-et-les-Grenadines
Trinité-et-Tobago
As well as including numerous states, this region also has territories belonging to different countries.
Anguilla (UK)
Aruba (P.B.)
Bonaire (B.P.)
Curaçao (P.-B.)
Guadeloupe (Fr.)
Cayman Islands (UK)
Virgin Islands (U.S.)
British Virgin Islands (UK)
Martinique (Fr.)
Montserrat (UK)
Puerto Rico (USA)
Saba (P.B.)
Saint-Barthélemy (Fr.)
Saint-Eustache (P.-B.)
Saint-Martin (Fr., P.B.)
Turks and Caicos Islands (U.K.)
South America is surrounded by the Southern Ocean to the south, the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Atlantic Ocean to the east. As in North America, to the west of the continent is the chain of mountains known as the Cordillera of the Andes. The Brazilian plateau is on the east coast and the Amazon rainforest is located in the centre, on flatter terrain.
The climate is mainly tropical and equatorial, but also continental and mountainous in places.

The Amazon rainforest lies in the middle of the South American continent and extends over 9 countries. It has an equatorial climate.
Source : Streetflash, Shutterstock.com
South America includes Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay and Venezuela.
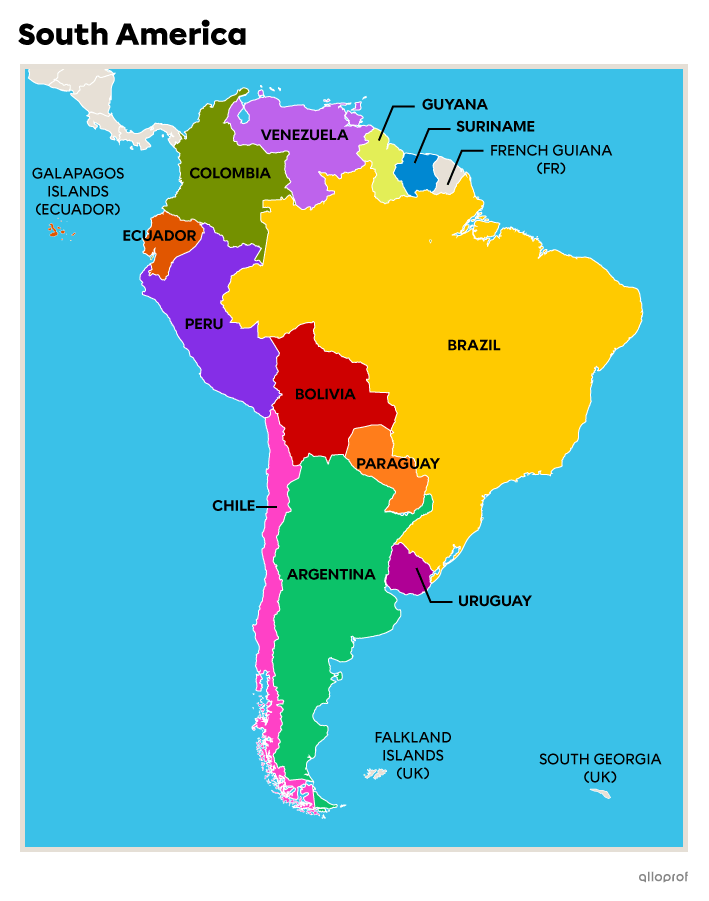
Latin America is a term frequently used to describe the Latin American countries of Central and South America. Although located in North America, Mexico is included in this group.
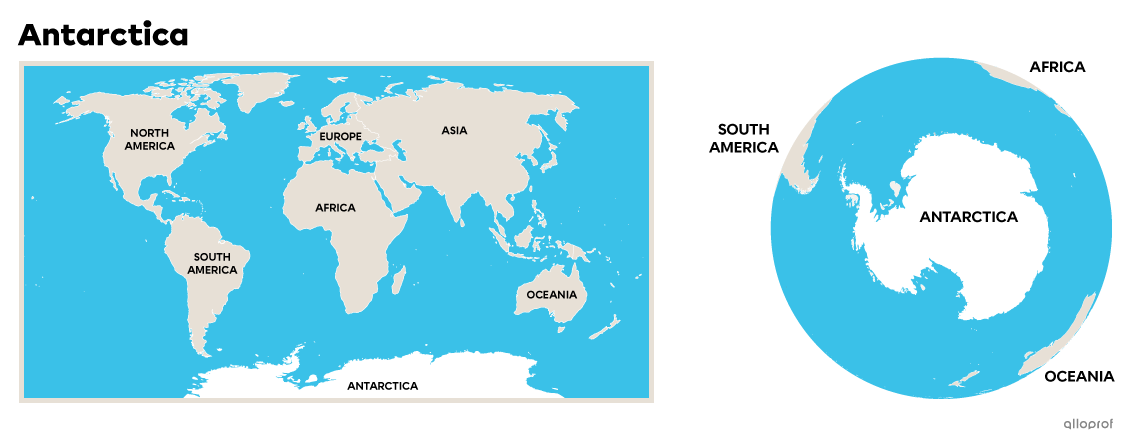
Antarctica, located at the Earth's South Pole, is the world's only uninhabited continent. This is due to its extreme climate. Over 99% of its territory is covered by a thick layer of ice. The climate on this continent is the harshest in the world, with average temperatures ranging from -10°C to -60°C as well as violent winds[4].
The continent was first explored in the 1800s. Although no one lives there, many people continue to travel there to explore and research the continent.
Antarctica does not belong to any country. Countries may, however, settle there to carry out scientific research, but the main aim is always to preserve the territory, not to exploit it.
Europe is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the Arctic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. The European continent is one of the most fragmented, with many inland seas, peninsulas and small mountain ranges, such as the Pyrenees, the Alps and the Ural Mountains.
There are 3 types of climate on the European continent: oceanic, continental and Mediterranean.

The Alps are shared by France, Italy, Switzerland, Germany, Liechtenstein, Austria and Slovenia.
Source : Canadastock, Shutterstock.com
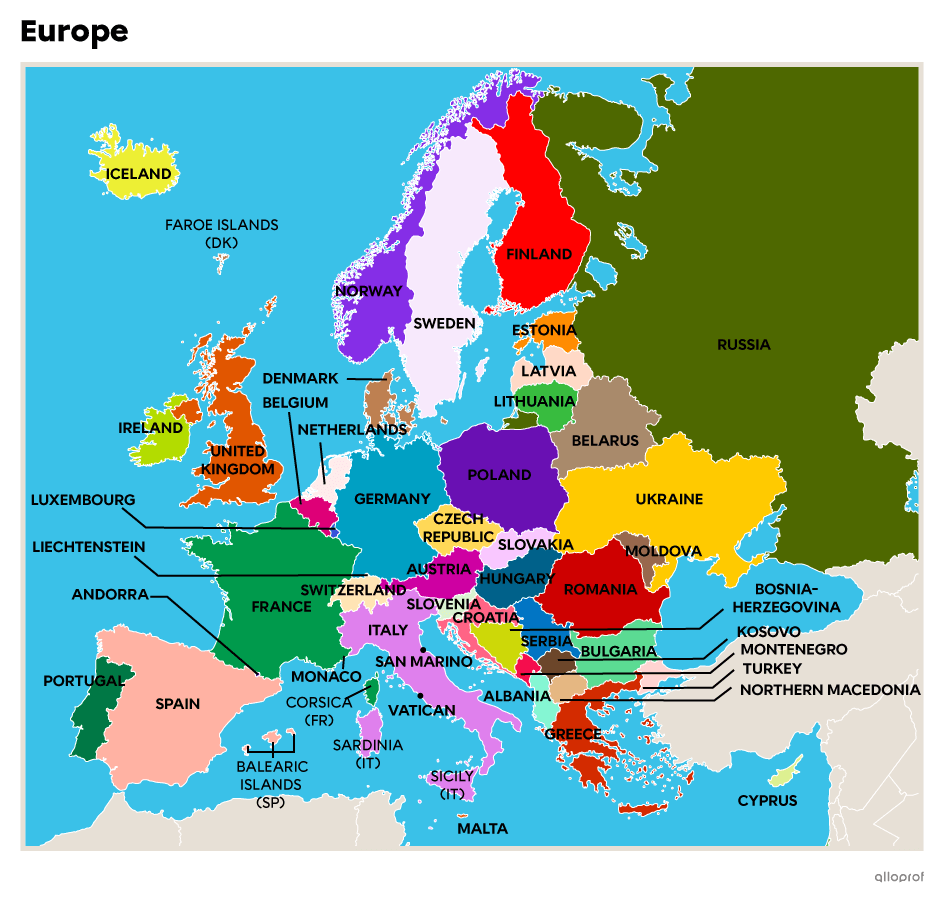
Generally speaking, Europe is divided into 2 regions: eastern and western.
| Western Europe | Eastern Europe |
|---|---|
|
Germany |
Albania |
Data source: Government of Canada, January 2014[13]. |
|
Scandinavia refers to the northern region of Europe, encompassing Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Finland and Iceland.
The Balkans are located on the Balkan Peninsula and include Greece, Bulgaria, Northern Macedonia, Albania, Serbia, Montenegro, Kosovo, Slovenia and Bosnia-Herzegovina.
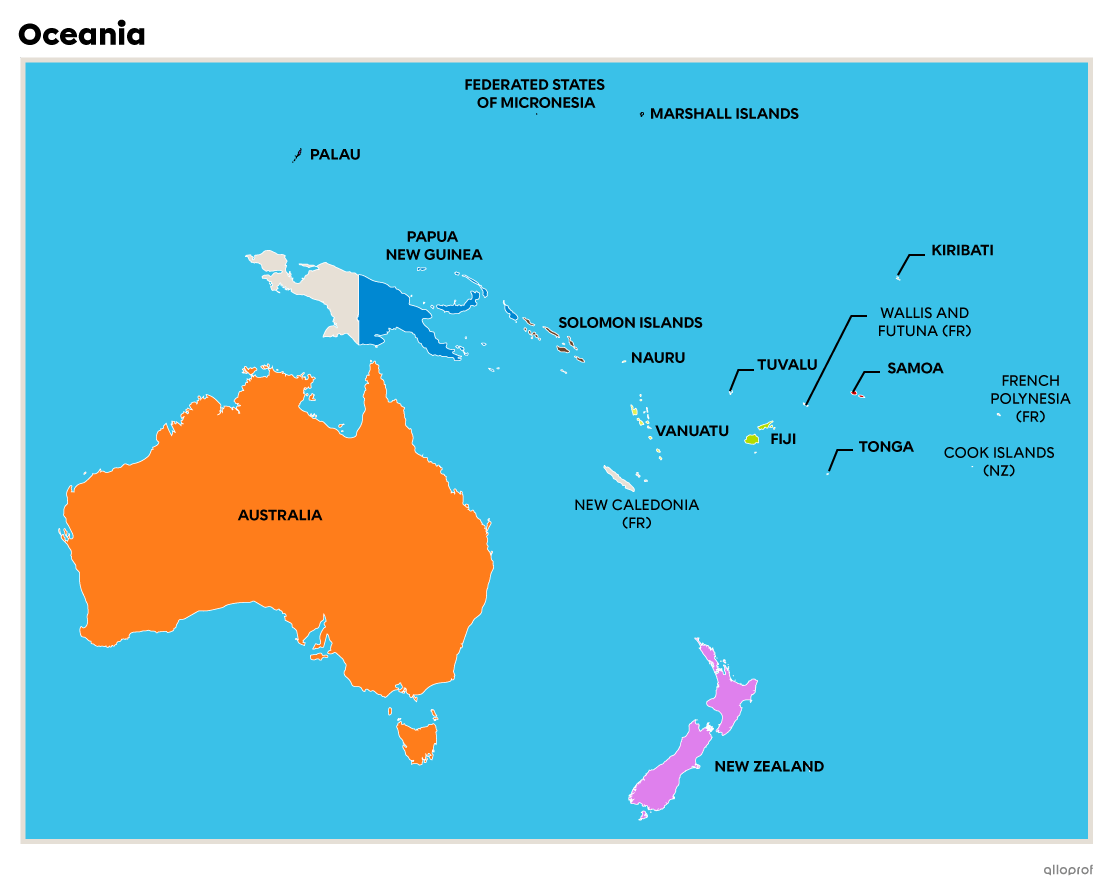
Oceania is the smallest of the world's 7 continents. Australia accounts for 85% of the continent's total surface area. New Zealand is Oceania's second largest island. Around 70% of the continent's population is found in Australia and New Zealand[5]. The other countries on this continent are scattered over more than 10 000 islands[6].
These islands are divided into 3 major regions: Melanesia, Polynesia and Micronesia.

Palau is a country in Oceania. Its islands are a good example of the large number of islands that make up the continent.
Source : BlueOrange Studio, Shutterstock.com
Some of these islands are independent countries, such as Nauru, Tonga, Palau, Fiji, Vanuatu, Tuvalu, Samoa, Kiribati, the Marshall Islands, the Solomon Islands and the Federated States of Micronesia, which includes the Mariana Islands and the Caroline Islands.
The Cook Islands belong to New Zealand, while French Polynesia, New Caledonia as well as Wallis and Futuna belong to France. Papua New Guinea represents a unique situation in that the eastern part of the island is an independent country, while the western part belongs to Indonesia.
In general, the archipelagos of Oceania have a tropical climate. In New Zealand, the climate is more oceanic. Australia is divided between temperate and desert climates.
For more information, please consult the following concept sheets:
To access the rest of the unit, consult the Tools in Geography concept sheet.
1. Carrière, P., Delvert, J. Planhol, X. (s.d.). Asie (Structure et milieu) - Géographie physique. Dans Encyclopédie Universalis. https://www.universalis.fr/encyclopedie/asie-structure-et-milieu-geographie-physique/
2. Pourtier, R. (s.d.). Afrique (Structure et milieu) - Géographie physique. Dans Encyclopédie Universalis.
https://www.universalis.fr/encyclopedie/afrique-structure-et-milieu-geographie-generale/
3. Bensaâd, A. (s.d.). Sahara. Dans Encyclopédie Universalis. https://www.universalis.fr/encyclopedie/sahara/
4. Gouvernement du Canada. (2021, 3 juin). Le Canada et l’Antarctique. https://www.canada.ca/fr/savoir-polaire/faireavancersavoirpolaire/le-canada-et-lantarctique.html
5. Océanie (s.d.) Dans Dictionnaire Larousse en ligne. https://www.larousse.fr/encyclopedie/autre-region/Oc%C3%A9anie/126906
6. Huetz de Lemps, A., Huetz de Lemps, C. (s.d.). Océanie - Géographie physique. Dans Encyclopédie Universalis. https://www.universalis.fr/encyclopedie/oceanie-geographie-physique/
7. Franck, M., Hourcade, B., Mutin, G. (s.d.). Asie (Géographie humaine et régionale) Dynamiques régionales. Dans Encyclopédie Universalis. https://www.universalis.fr/encyclopedie/asie-geographie-humaine-et-regionale-dynamiques-regionales/#c_2
8. Bergevin, R., Charette, J. et Méthé, M. (2014). GÉO à la carte - Cartes et croquis - 1er cycle du secondaire [Cahier d’activités]. CEC.
9. Universalis. (s.d.). Asie. https://www.universalis.fr/atlas/asie/
10. Nations Unies. (s.d.). États membres. https://www.un.org/fr/about-us/member-states
11. Bureau de représentation du Canada auprès de l’Autorité palestinienne. (2022, 22 mars). Les relations entre le Canada et la Cisjordanie et Gaza. Gouvernement du Canada. https://www.canadainternational.gc.ca/west_bank_gaza-cisjordanie_bande_de_gaza/bilateral_relations_bilaterales/index.aspx?lang=fra#:~:text=Le%20Canada%20reconna%C3%AEt%20le%20droit,paix%20global%2C%20juste%20et%20durable
12. Organisation de coopérative et de développement économique. (février, 2017). Les six régions de l’Union africaine. Club du Sahel et de l’Afrique de l’Ouest. https://www.oecd.org/swac/maps/48-six-regions-African-Union.pdf
13. Gouvernement du Canada. (16 janvier 2014). Liste des pays. https://www.ic.gc.ca/eic/site/tdo-dcd.nsf/fra/00028.html

