To access the other sheets in the Tools in Geography module, consult the See Also section.
Physical geography is the study of the various components of the Earth's surface. In the high school geography curriculum, three of these components are particularly important: relief, hydrography and climate.
Climate is the combination of a region's temperature and precipitation throughout a year. Climate has an enormous influence on plants, animals and human populations. There are different types of climate in the world.
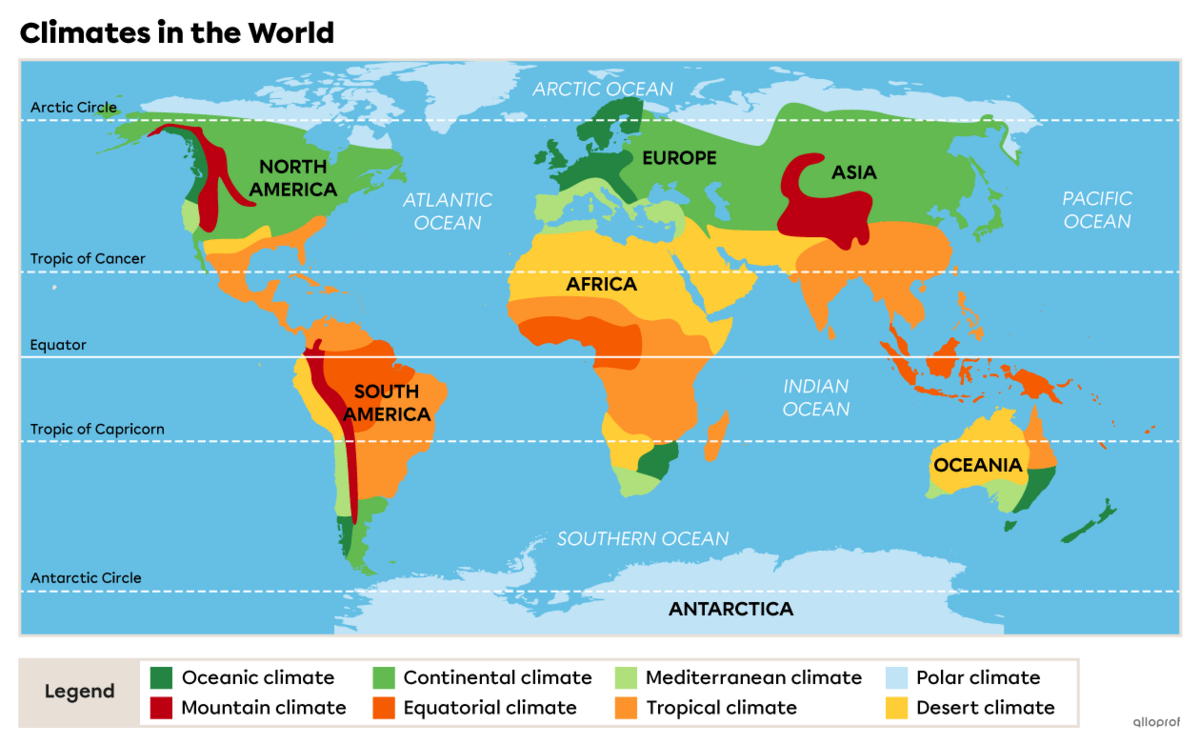
Cold climates can be divided into two sub-climates: polar and mountain.
Polar climate is the type of climate found at the poles. Whether to the south in the Antarctic or to the north in the Arctic, the climate is relatively similar- very cold. As both locations receive very little sunshine, winters are long and cold and summers, short and cool. Average temperatures in the Arctic range from -10°C to -20°C in winter and around 0°C in summer. In Antarctica, temperatures are much colder, ranging from -20°C to -65°C in winter and from -20°C to 0°C in summer[1].
The polar night and the midnight sun are two phenomena that occur in the polar circles every year. Polar night is the expression used to refer to the period when the Sun remains below the horizon, and never rises. Midnight sun is the expression used to refer to the period when the Sun remains above the horizon, and never sets. The polar night and midnight sun can last up to half a year, depending on latitude.
Both phenomena are caused by the Earth's axis of rotation, which is tilted in relation to its orbit. For example, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun during the summer. This creates a zone in the Arctic Circle that remains lit even as the Earth rotates. This is the midnight sun. The opposite phenomenon occurs in winter, when the Northern Hemisphere is no longer tilted towards the Sun. This creates a shadow zone in the Arctic Circle, corresponding to polar night.
The same phenomenon occurs in the Antarctic Circle, but at the opposite time. When it's polar night in the Arctic Circle (North), it's midnight sun in the Antarctic Circle (South), and vice versa.
Mountain climate is a type of climate found in high-altitude regions. The higher the altitude, the lower the temperature. Temperatures drop by around 0.6°C every 100 metres. Sometimes, mountain peaks are so high in altitude that there is snow all year round. In this type of climate, winters are cold and summers are cool[2]. This is the type of climate found in the Canadian Rockies.
Altitude is the elevation (height) of a place in relation to sea level.
Continental climate is a type of climate found between the tropics and the polar circles. It is found inland in North America, Central and Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. This type of climate is characterized by long, cold winters and hot, rainy summers. Unlike other climates, continental climate is one of the only ones to experience extreme temperature variations over the course of a year. Temperatures can drop as low as -20°C in winter, and as high as 30°C in summer[3]. Continental climate is the type of climate found in Quebec.
Continental climate is sometimes considered a sub-climate of the temperate climate, since it also falls between the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle. Alternating hot and cold temperatures may also explain why the continental climate is also considered a temperate climate.
Temperate climates, like continental climates, are found between the tropics and the polar circles. However, it is more common on the coasts than inland. Temperate climates are characterized by wide seasonal variations in temperature. In general, temperate climates have mild temperatures in winter and warm temperatures in summer. They rarely exceed 25°C in summer and don't fall below -3°C in winter[1]. There are a variety of temperate climates, such as the oceanic climate and Mediterranean climate.
Oceanic climate is located, as its name suggests, on the edge of the oceans. It's a windy, rainy climate. Winters are mild and summers cool, with very little temperature variation between seasons. In fact, temperatures vary between 5°C and 15°C[4]. This type of climate is found among others in the coastal regions of France and Germany as well as along the west coast of North America.
Mediterranean climate is found around the Mediterranean Sea, but also in California (North America), Chile (South America) and even Australia (Oceania). It is characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, rainy winters. Summer temperatures can range from 25°C to 40°C, while winter temperatures average around 5°C[5].
Tropical climate is found between the tropics and the equator. This type of climate is characterized by very high temperatures and no prolonged cooling periods. Temperatures rarely drop below 18°C[1]. The tropical climate is an intermediate climate between the equatorial climate and the desert climate, since it has two seasons: the dry season and the wet season. This type of climate is found, among other places, in the African savannahs.
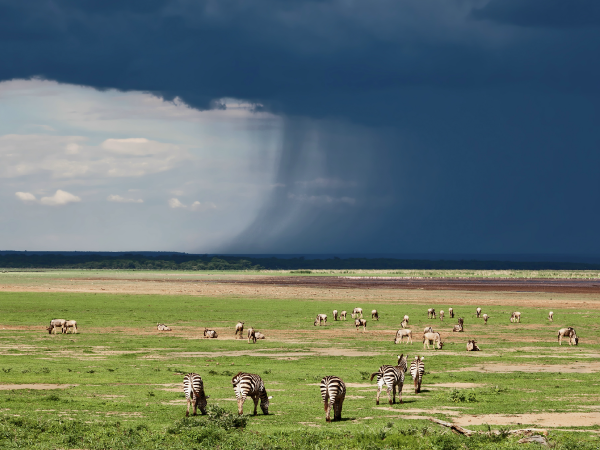

Source: Vadim Petrakov, Shutterstock.com
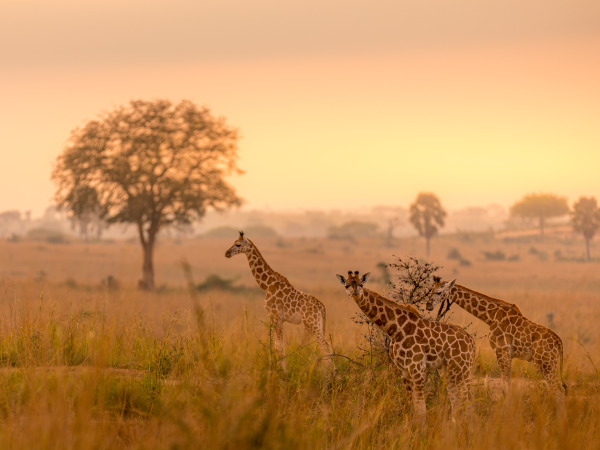

Source: Gunter Nuyts, Shutterstock.com
Equatorial climate is warm and humid all year round. It's one of the climates with the least variation in temperature. Temperatures range from 25°C to 28°C[2]. Equatorial climate is characterized by humidity levels of between 70% and 90%. Regions with this type of climate receive, on average, between 1 500 and 2 500 millimetres of rain per year, but some regions receive much higher amounts. This type of climate is found in the Amazon and around the Congo Basin, among other places.
Desert climate, also known as the arid climate, is characterized by low precipitation, so that drought reigns in these regions. There are two types of desert climate: hot desert and cold desert climate.
This type of climate is characterized by very low rainfall and very hot temperatures, regardless of the season. Indeed, during summer, temperatures can reach up to 60°C, while winters are very mild[6]. The Sahara Desert and the Namib Desert are two places where this type of climate is found.
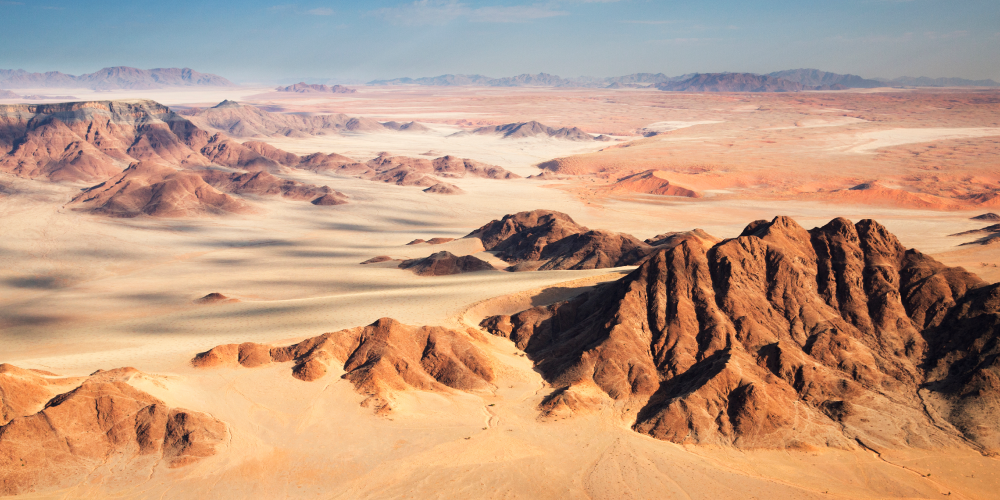

The Namib Desert is considered to be the oldest desert in the world, since it has the same climatic conditions as 80 million years ago[7].
Source: Zaruba Ondrej, Shutterstock.com
Summer temperatures in the cold desert climate are very similar to those in the hot desert climate. The difference between the two mainly concerns winter temperatures. Indeed, during winter, a cold desert can see its temperatures drop below 0°C[1]. This type of climate is often found in higher altitude regions, such as the Gobi Desert in Mongolia and China.
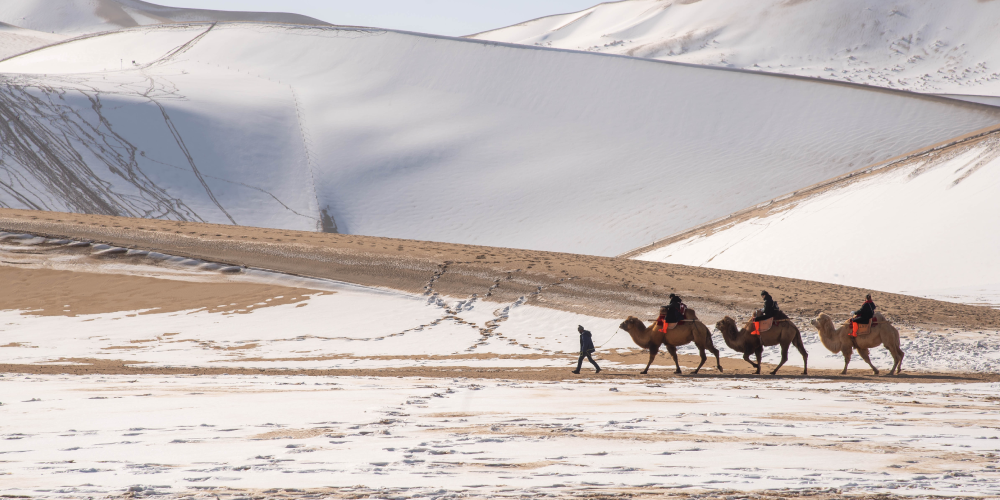

The Gobi Desert covers an area of 1 300 000 km2 and stretches south from Mongolia to China. Temperatures can reach 45°C in summer and drop to -25°C in winter. It's the coldest desert on the planet after Antarctica[8].
Source: Sutthi Chuvichit, Shutterstock.com
To access the rest of the unit, consult the Tools in Geography concept sheet.
- Climats (notions de base). (n.d.). Dans Encyclopédie Universalis. https://www.universalis.fr/encyclopedie/climats-notions-de-base/#c_12
- Climat : les climats du monde. (n.d.). Dans Dictionnaire Larousse en ligne. https://www.larousse.fr/encyclopedie/divers/climat__les_climats_du_monde/185927
- Mayer, N. (n.d.). Climat continental : qu’est-ce que c’est? Futura Planète. https://www.futura-sciences.com/planete/definitions/climatologie-climat-continental-16836/
- Climats.com. (n.d.). Climat tempéré. https://www.climats.com/climat/tempere.html
- Mayer, N. (n.d.). Climat méditerranéen : qu’est-ce que c’est? Futura Planète. https://www.futura-sciences.com/planete/definitions/climatologie-climat-mediterraneen-16806/
- Climats.com. (n.d.). Climat aride/désertique. https://www.climats.com/climat/aride-desertique.html
- Namibie en liberté. (n.d.). Désert du Namib. https://www.namibie-en-liberte.com/conseils-voyage/ou-aller/desert-du-namib
- Haberthur, F. (2022, January 1). Quel est le meilleur moment pour visiter le désert de Gobi? Geo. https://www.geo.fr/voyage/quel-est-le-meilleur-moment-pour-visiter-le-desert-de-gobi-207637