The commutative property allows for the order of the numbers to be changed in an addition without affecting the answer.
When adding 5 + 2, the sum is 7.
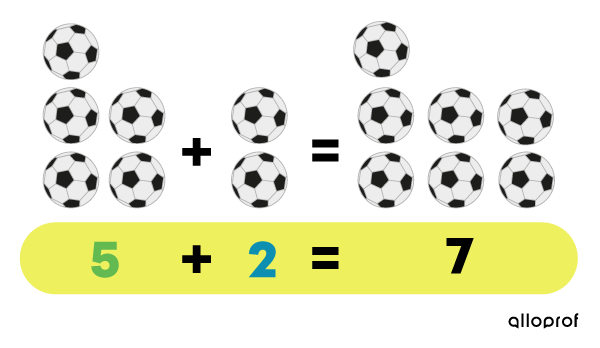
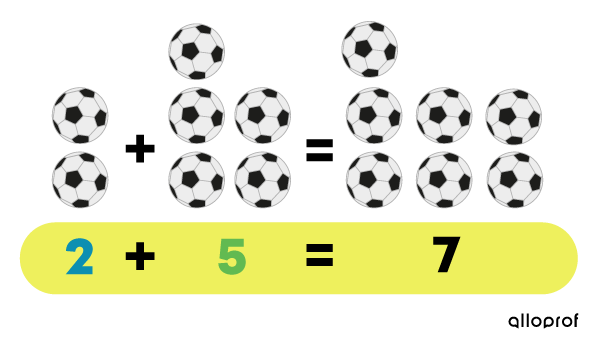
Even when the terms of this addition are reversed, the sum remains 7.
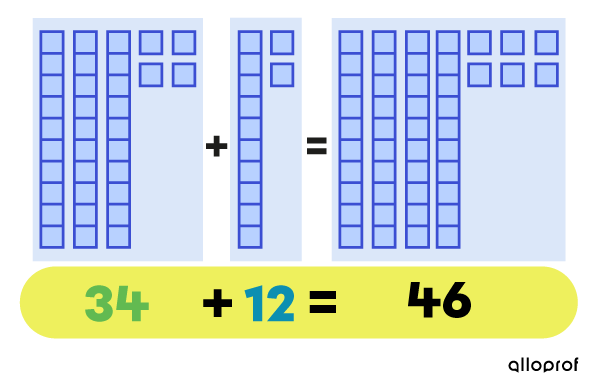
When adding 34 + 12, the sum is 46.
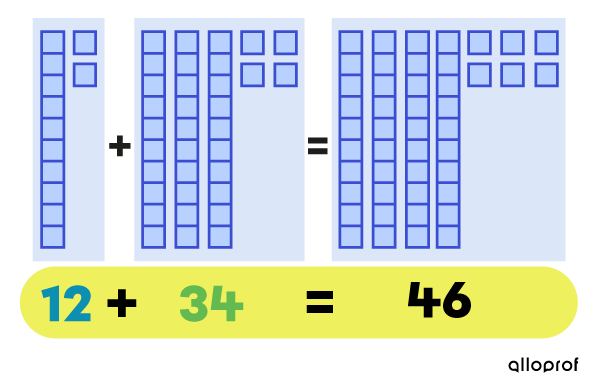
Even when the terms of this addition are reversed, the sum remains 46.
The commutative property allows for the order of the numbers to be changed in an operation without affecting the answer.
The commutative property applies to both addition and multiplication.
When adding 18 + 2, the sum is 20.
18 + 2 = 20
Even when the terms are reversed, the sum remains 20.
2 + 18 = 20
When multiplying 3 × 5, the product is 15.
3 × 5 = 15
Even when the factors are reversed, the product remains 15.
5 × 3 = 15
The commutative property also applies to the addition of decimals.
Example:
3.2 + 4.39 = 7.59
4.39 + 3.2 = 7.59
The associative property allows for the numbers in an operation to be grouped in different ways using brackets, without changing the final result.
The operation that is placed inside the brackets must be done first.
The associative property applies to both addition and multiplication.
When adding 4 + 2 + 3, the sum is 9.
4 + 2 + 3 = 9
When grouping the first 2 terms of this addition, the sum remains 9.
(4 + 2) + 3 = ?
6 + 3 = ?
6 + 3 = 9
Again, the sum remains the same when grouping the last 2 terms.
4 + (2 + 3) = ?
4 + 5 = ?
4 + 5 = 9
When multiplying 2 × 5 × 4, the product is 40.
2 × 5 × 4 = 40
When grouping the first 2 factors, the product remains 40.
(2 × 5) × 4 = ?
10 × 4 = ?
10 × 4 = 40
Again, the product remains the same when grouping the last 2 factors.
2 × (5 × 4) = ?
2 × 20 = ?
2 × 20 = 40
The associative property also applies to the addition of decimals.
Example:
3.45 + 2.7 + 9.12 = 15.27
(3.45 + 2.7) + 9.12 = 15.27
3.45 + (2.7 + 9.12) = 15.27
The commutative property allows for the order of the numbers to be changed in an operation without affecting the answer.
The commutative property applies to both addition and multiplication.
When adding 12 + 7, the sum is 19.
12 + 7 = 19
Even when the terms are reversed, the sum remains 19.
7 + 12 = 19
When multiplying 11 × 9, the product is 99.
11 × 9 = 99
Even when the factors are reversed, the product remains 99.
9 × 11 = 99
The commutative property also applies to the addition and multiplication of decimals.
Examples:
|
Addition |
Multiplication |
|---|---|
|
3.2 + 4.39 = 7.59 |
5.14 × 7.5 = 38.55 |
The associative property allows for the numbers in an operation to be grouped in different ways using brackets, without changing the final result.
The associative property applies to both addition and multiplication.
Don't forget to follow the order of operations. Always begin with the operations that are inside the brackets.
To learn more, read the concept sheet about the order of operations.
When adding 4 + 2 + 3, the sum is 9.
4 + 2 + 3 = 9
When grouping the first 2 terms, the sum remains 9.
(4 + 2) + 3 = ?
6 + 3 = ?
6 + 3 = 9
Again, the sum remains the same even when grouping the last 2 terms.
4 + (2 + 3) = ?
4 + 5 = ?
4 + 5 = 9
When multiplying 2 × 5 × 4, the product is 40.
2 × 5 × 4 = 40
When grouping the first 2 factors, the product remains 40.
(2 × 5) × 4 = ?
10 × 4 = ?
10 × 4 = 40
Again, the product remains the same when grouping the last 2 factors.
2 × (5 × 4) = ?
2 × 20 = ?
2 × 20 = 40
The associative property also applies to the addition and multiplication of decimals.
Examples:
|
Addition |
Multiplication |
|---|---|
|
3.45 + 2.7 + 9.12 = 15.27 |
4.15 × 1.6 × 4.5 = 29.88 |
The distributive property is a property of multiplication. It allows a multiplication to be distributed over an addition or a subtraction.
Don't forget to follow the order of operations.
To learn more, read the concept sheet about the order of operations.
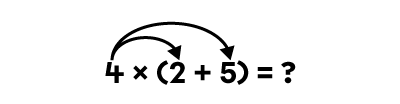
When completing the following chain of operations 4 x (2 + 5), the result is 28.
4 × (2 + 5) = ?
4 × 7 = ?
4 × 7 = 28
When distributing the multiplication over the addition, the result remains 28.
|
(4 × 2) + (4 × 5) = ? |
 |
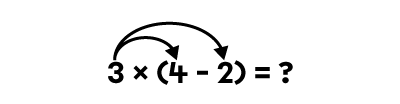
When completing the following chain of operation 3 x (4 - 2), the result is 6.
3 × (4 - 2) = ?
3 × 2 = ?
3 × 2 = 6
When distributing the multiplication over the subtraction, the result remains 6.
|
(3 × 4) - (3 × 2) = ? |
 |
The distributive property also applies to decimals.
Example:
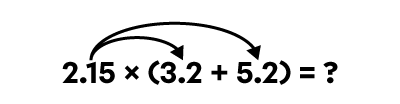
When completing the chain of operation 2.15 x (3.2 + 5.2), the result is 18.06.
2.15 × (3.2 + 5.2) = ?
2.15 × 8.4 = ?
2.15 × 8.4 = 18.06
When distributing the multiplication over the addition, the result remains 18.06.
|
(2.15 × 3.2) + (2.15 × 5.2) = ? |
 |