Adding the parameters |a,| |b,| |h,| and |k| to the basic function |f(x)=(c)^x| results in the standard form (or the transformed form) of the exponential function.
The standard form of an exponential function is: ||f(x)=a(c)^{b(x–h)}+k|| where |a,| |b,| |h,| and |k| are real numbers that act as parameters.
Note: The parameters |a,| |b,| and |c| must be non-zero. In addition, the base |c| must be greater than |0| and not |1|.
In the following interactive animation, experiment with the values of the parameters |a|, |b|, |h|, |k,| as well as the base |c| of the exponential function. Observe the changes which take place on the transformed curve (in black) compared to the base function with |c=2| (in blue). Use this opportunity to observe how changing the parameters affects the function’s properties. Afterwards, read the concept sheet to learn more about each of the parameters.
When |\mid a \mid >1|
The exponential function is stretched vertically relative to the base function. The larger the absolute value of the parameter |a|, the closer the curve of the exponential function is to the |y|-axis.
When |0< \mid a \mid <1|
The exponential function undergoes a vertical contraction relative to the base function. The smaller (closer to |0|) the absolute value of the parameter |a|, the farther the curve of the exponential function is from the |y|-axis.
When |a| is positive |(a>0)|
The curve of the exponential function turns upwards, therefore it is increasing.
When |a| is negative |(a<0)|
The curve of the exponential function turns downwards, therefore it is decreasing.
When |\mid b \mid >1|
The exponential function undergoes a horizontal contraction relative to the base function. The larger the absolute value of the parameter |b|, the farther away the graph of the exponential function is from the |x|-axis.
When |0< \mid b \mid <1|
The exponential function is stretched horizontally relative to the base function. The smaller (closer to |0|) the absolute value of the parameter |b|, the closer the graph of the exponential function is to the |x|-axis.
When |b| is positive |(b>0)|
The curve of the exponential function increases from left to right.
When |b| is negative |(b<0)|
The curve of the exponential function decreases from left to right.
The parameter |c| determines the variation of the exponential function.
When |c>1|
The exponential function increases from left to right.
When |0 < c < 1 |
The exponential function decreases from left to right.
When |h| is positive |(h>0)|
The curve of the exponential function shifts horizontally to the right.
When |h| is negative |(h<0)|
The curve of the exponential function shifts horizontally to the left.
To properly identify the value of the parameter |h|, it is important to remember the definition of the standard form of an equation. For example, |h(x)=2^{x+2}| contains the parameter |h,| whose value is |h=-2.|
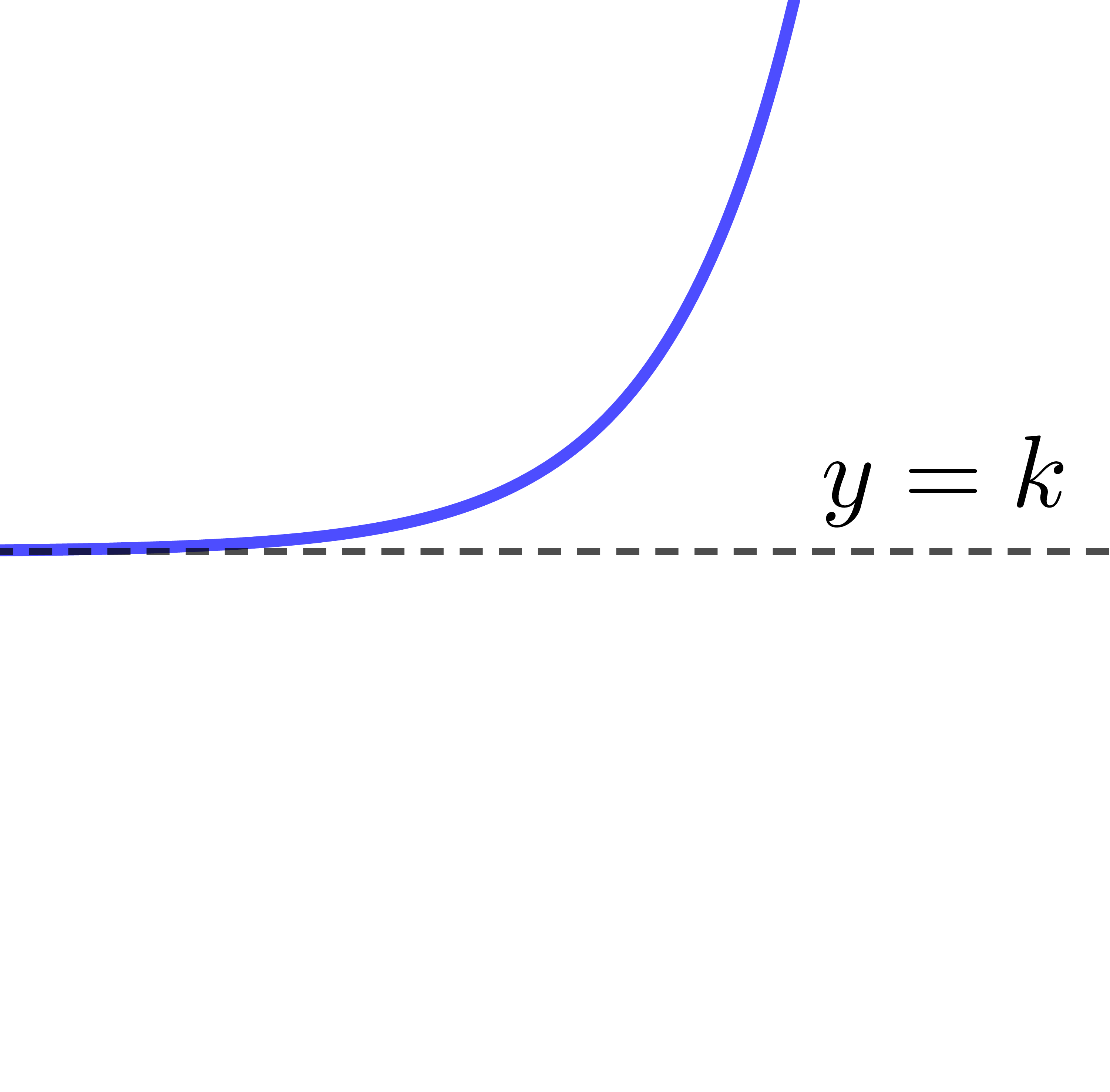
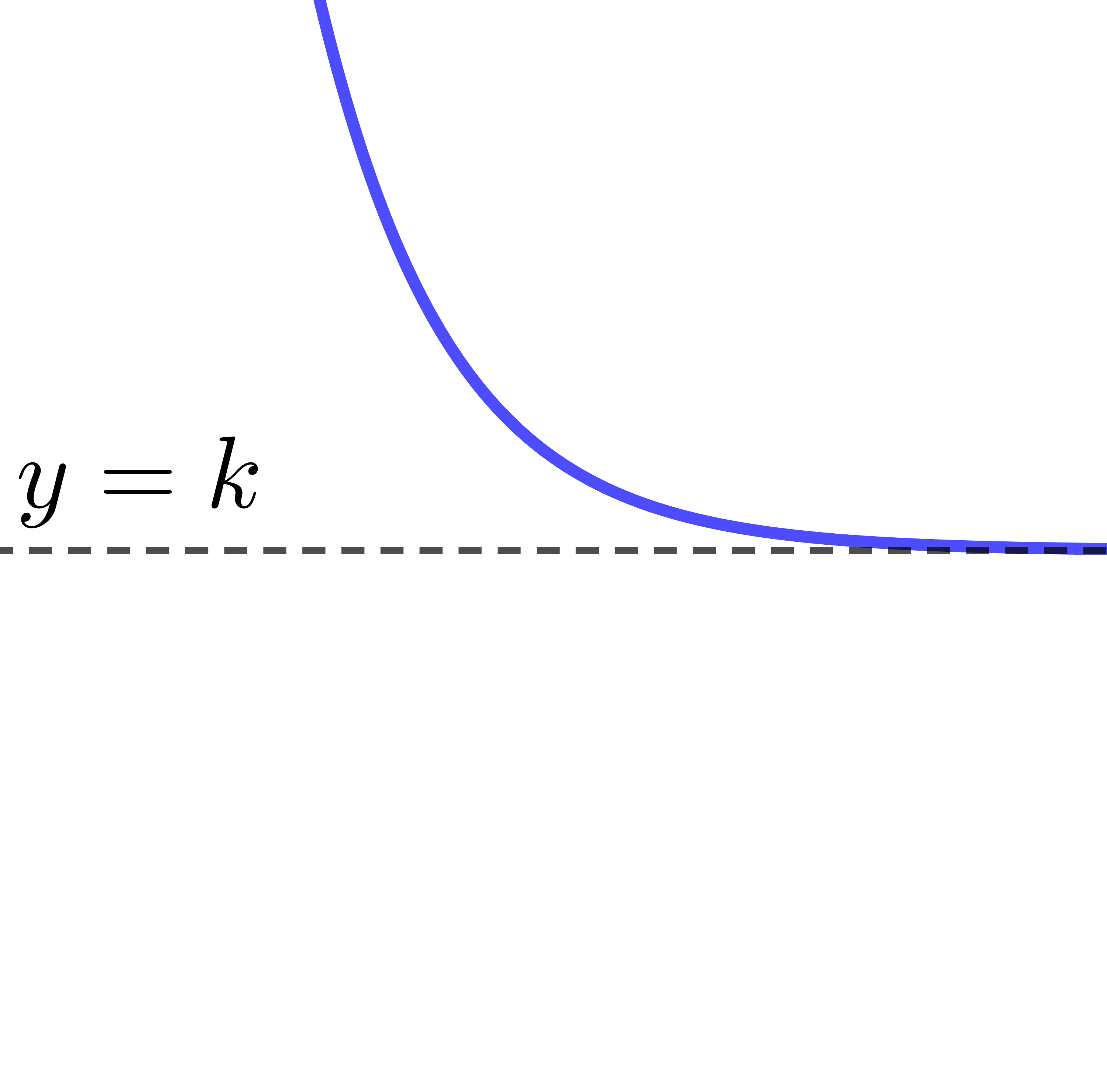
When |k| is positive |(k>0)|
The curve of the exponential function shifts vertically upwards.
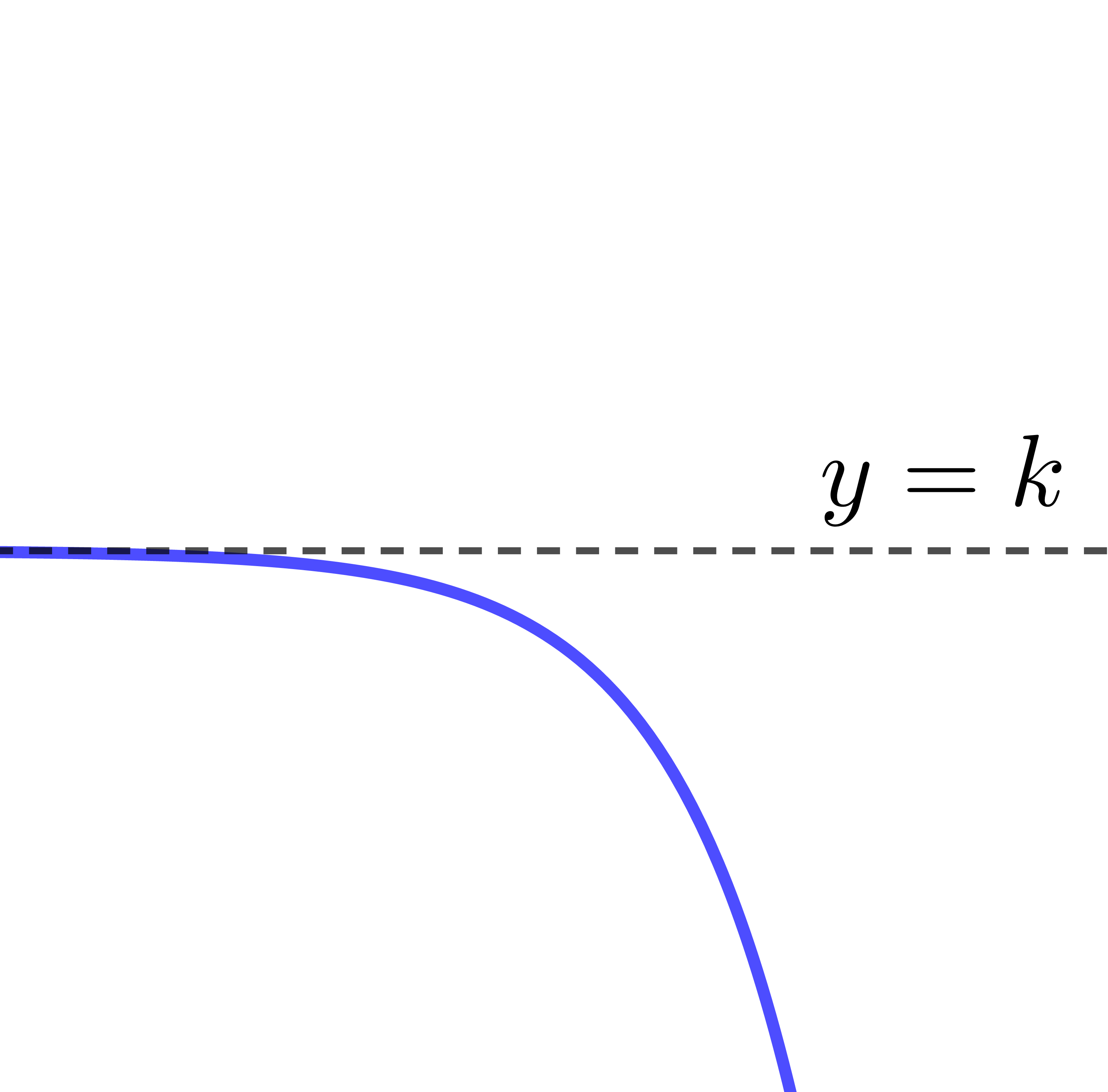
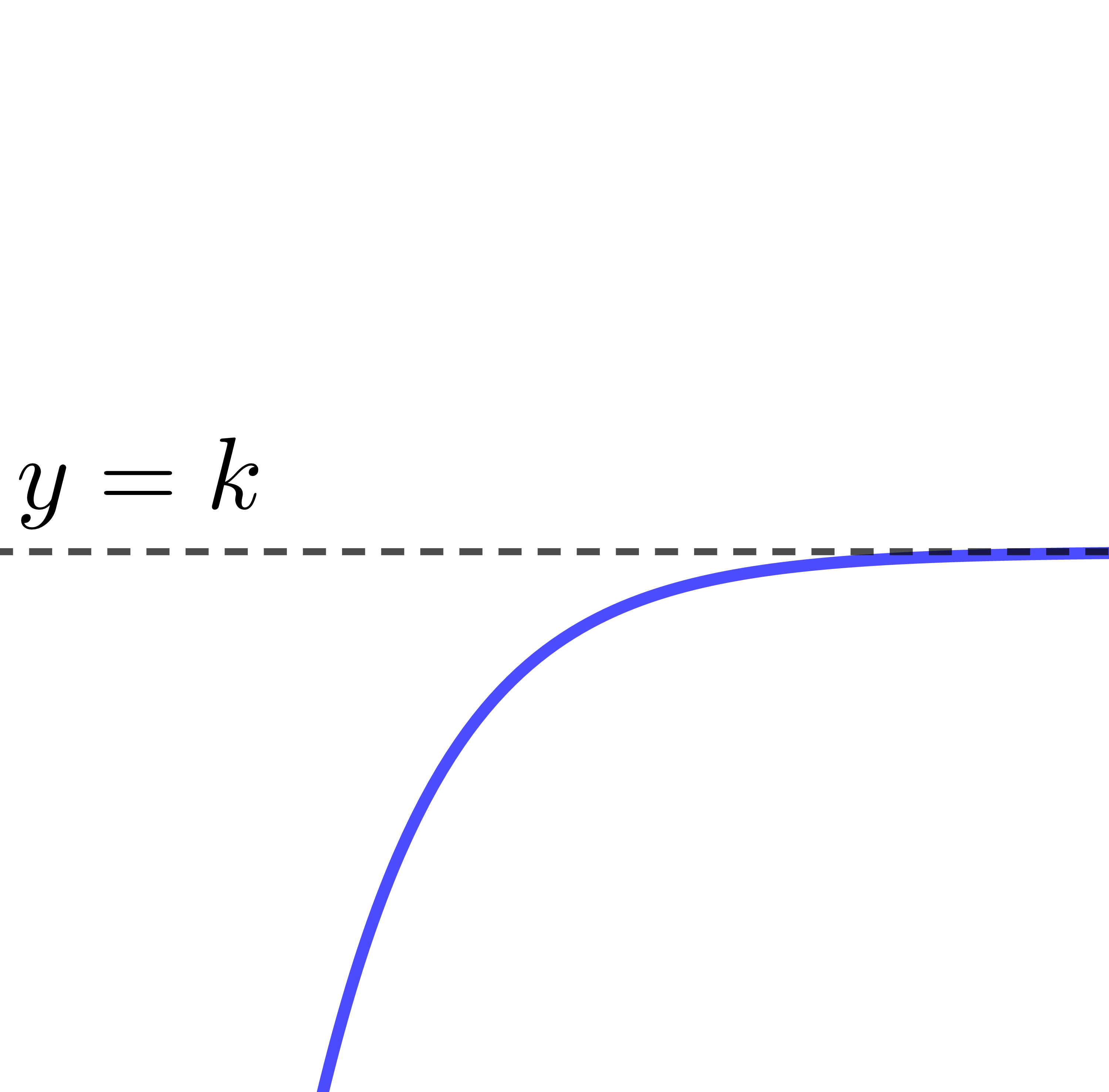
When |k| is negative |(k<0)|
The curve of the exponential function shifts vertically downward.
The parameter |k| provides the location of the asymptote of the exponential function.
The equation of the asymptote is |y=k|.
If |c>1|
|
|a>0| |
|a<0| |
|
|---|---|---|
|
|b>0| |
|
|
|
|b<0| |
|
|
If |0<c<1|
|
|
|a>0| |
|a<0| |
|---|---|---|
|
|b>0| |
|
|
|
|b<0| |
|
|
As the summary table above shows, certain combinations of values of the parameters give the same result. For example, |c>1|, |a>0|, and |b>0| is equivalent to |0<c<1|, |a>0|, and |b<0|. For this reason, the equation of an exponential function in standard form is often simplified by omitting the parameters |b| and |h|. ||\large{f(x)=a(c)^{b(x-h)}+k \ \ \ \Rightarrow \ \ \ f(x)=a(c)^x+k}||
For the simpler way to write the equation of an exponential function, the summary table would be the following.
|
|
|a>0| |
|a<0| |
|---|---|---|
|
|c>1| |
|
|
|
|0<c<1| |
|
|