Trees are connected graphs without a simple cycle, i.e., a chain cannot be established in graphs which start and end at the same point without passing through the same edge twice.
Trees are also used in probability for counting problems.
Example of a tree in a probability situation
Trees can also be used to determine the lowest common multiple (LCM) of a group of numbers.
Here are some examples that are NOT trees
It’s not connected!
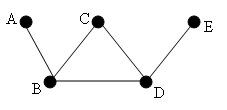
BCDB is a simple chain!
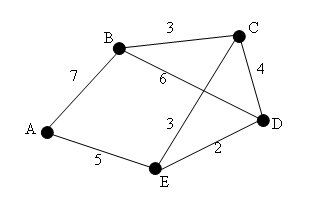
A weighted graph is a graph where each of the edges has a value. The valued graph can either be directed or not.
We calculate the value of a chain (or a cycle) by adding the values of the edges in it.
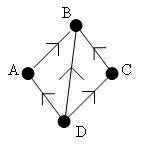
A directed graph is a graph where the edges have a direction (→). Chains and cycles must respect the direction of the arrows.
The name of an edge takes into account its direction. AB ≠ BA
Occasionally, a coloured graph may be encountered. This concept is used when solving chromatic number problems.