The relationship between speed and time in URM is characterized by a zero-variation relationship, during which the speed remains constant throughout the entire duration of the movement.
To observe this relationship, the values of an object's speed as a function of time can be graphed.
Consider the motion of a car on a highway. The speed of the car was measured at specific points in time.
Speed of a Car on a Highway as a Function of Time
|
Time |\text {(s)}| |
Speed |\text {(m/s)}| |
| 0 | 25 |
| 10 | 25 |
| 20 | 25 |
| 30 | 25 |
| 40 | 25 |
The graph below represents the car's speed as a function of time.
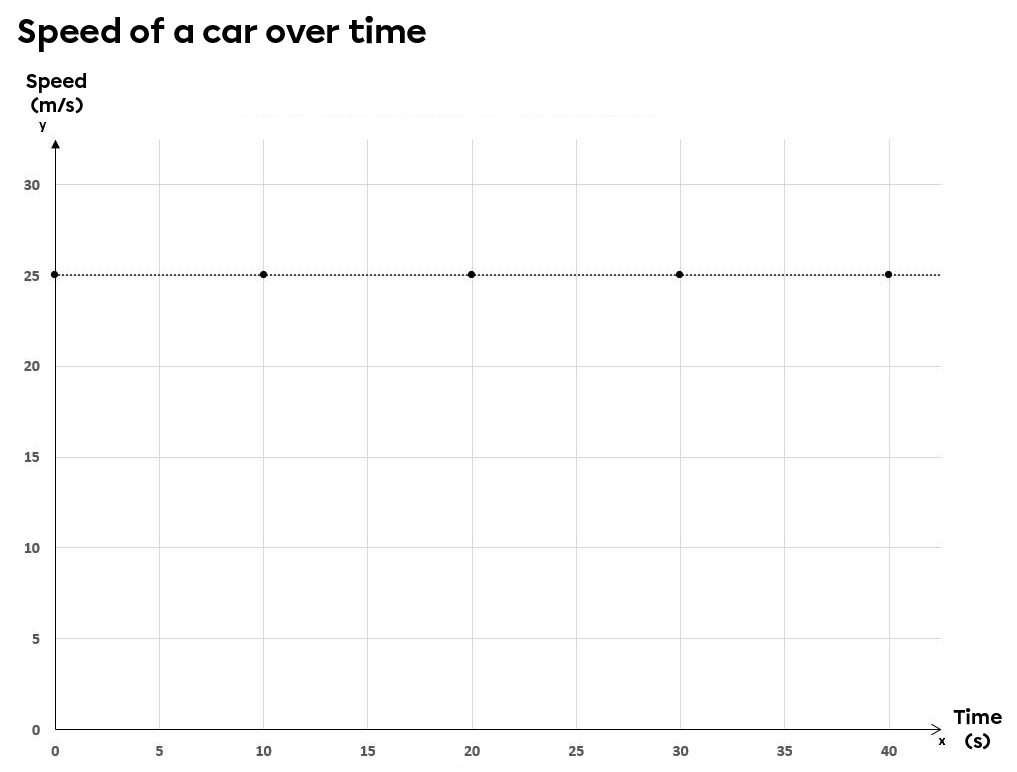
The resulting relationship is a zero-variation function, which means that the velocity never changes, regardless of when it's measured.
If the slope of this graph were calculated, the value obtained would be equal to the acceleration of the vehicle. However, since the graph is a constant function, the car's acceleration is equal to |\text {0 m/s}^2.|
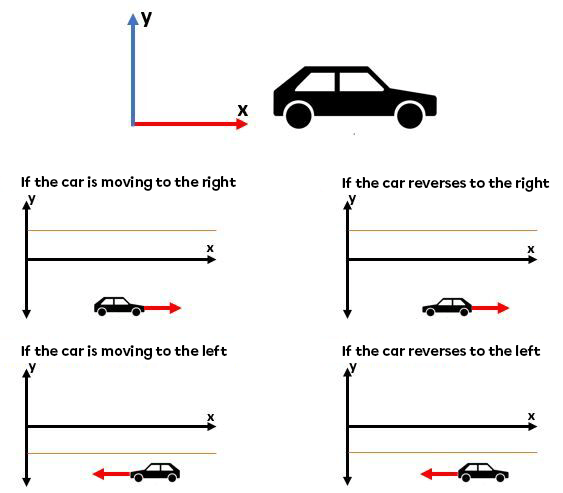
To determine if a speed is positive or negative, it's important to check the direction of movement, and not the type of movement. For example, a car that reverses direction as indicated by the frame of reference still has a positive speed.
To find the speed of an object in URM, the following formula applies:
|\overrightarrow{v}=\displaystyle \frac{\triangle \overrightarrow{x}}{\triangle t}|
where
|\overrightarrow{v}| represents the speed of the object |\text {(in m/s)}|
|\triangle \overrightarrow{x}| represents the object's displacement |\text {(in m)}|
|\triangle t| represents the change in time |\text {(in s)}|
As can be seen from the equation above, velocity and displacement are vectors. We can therefore deduce that the velocity's direction is always the same as that of the displacement, and vice versa.
However, it is possible to use the equation with just the magnitude of the velocity and displacement, as shown in the velocity formulas.
It is possible to have a negative velocity when working in a one or two-dimensional frame of reference.
A negative sign indicates that the object's displacement is in the opposite direction of the reference system.
If the displacements on the right-hand side are oriented towards the positive axis of the motion under study, a speed of |\text {-25 m/s}| represents an object moving to the left.
The relationship between speed and time in URM is different from the relationship between speed and time in UARM.