An electric charge is a property of matter responsible for electrical and electromagnetic phenomena. An electric charge is either negative or positive.
Most objects are electrically neutral, meaning that the atoms that make up the object contain as many negative electric charges as positive electric charges. When an object loses this neutrality, it becomes electrically charged. The object can be negatively charged or positively charged.
-
A negatively charged object has an excess of negative charges.
-
A positively charged object has a deficit of negative charges.
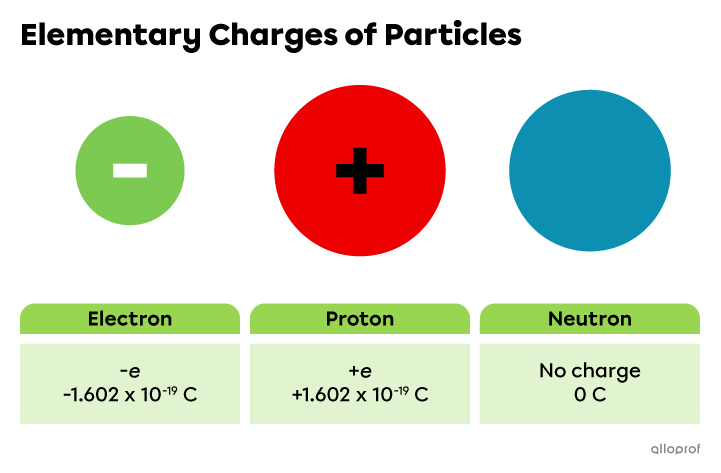
The electron, the proton and the neutron are the subatomic particles.
The electron and the proton have a charge of the same value, but of opposite sign. This charge is called the elementary charge and its symbol is |e.|
|q\ _{\text{electron}}=-e=-1.602\times10^{-19}\ \text{C}|
|q\ _{\text{proton}}=+e=1.602\times10^{-19}\ \text{C}|
The neutron does not carry an electric charge. It is electrically neutral.
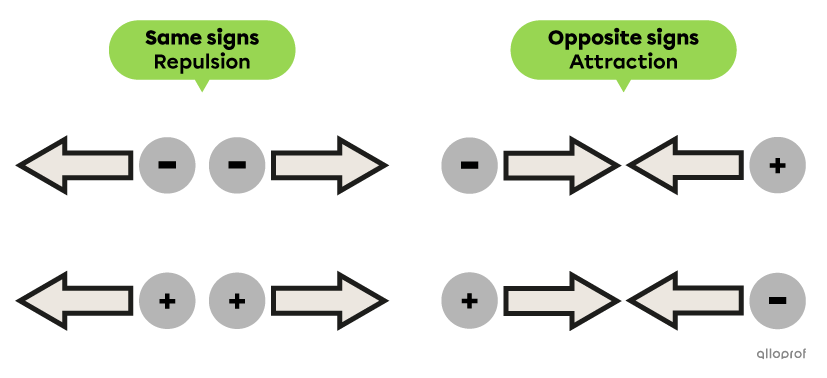
The law of electric charges describes the behaviour of charges when they are placed close to each other.
-
Charges of the same sign undergo repulsion.
-
Charges of opposite signs undergo attraction.
When a person touches the Van der Graaf generator, their hair becomes negatively charged.
Since the hairs have charges of the same sign, they repel each other and stand up in the air.
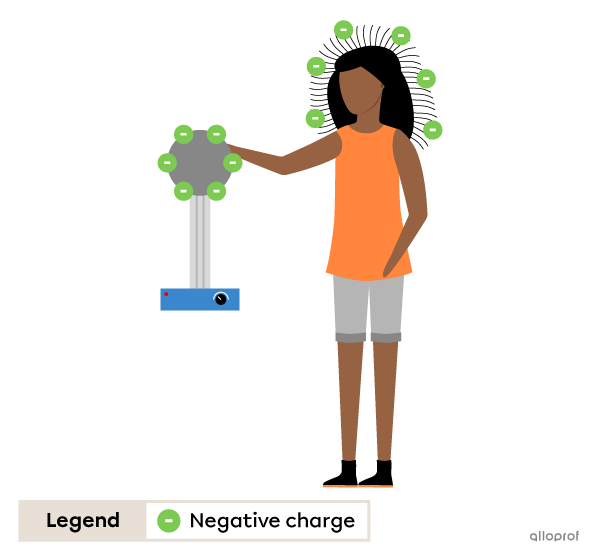
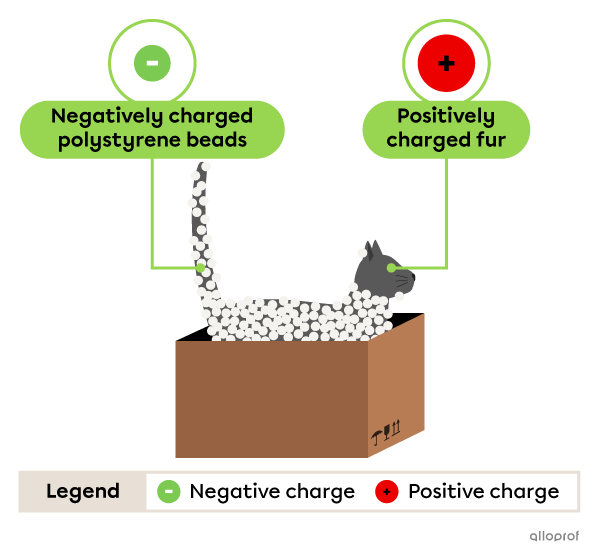
A cat who played in a box filled with polystyrene beads ended up with them stuck all over its fur. As a result of friction, the cat's fur became positively charged and the polystyrene beads became negatively charged.
Since the charges are of opposite signs, the cat's fur and the polystyrene beads attract each other.
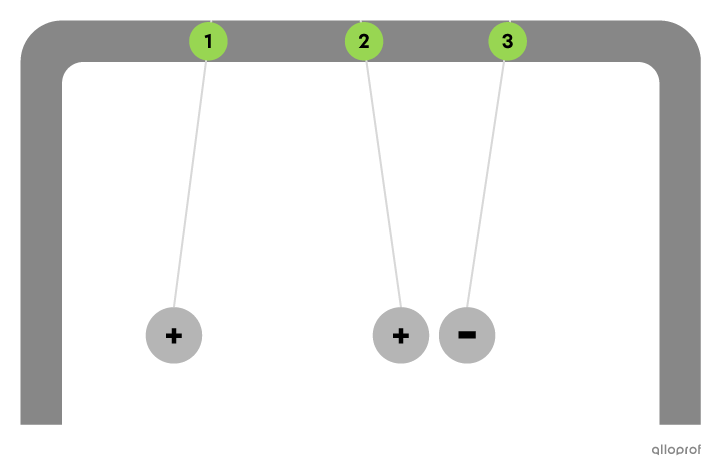
Charged spheres hang next to each other. Determine if Sphere 2 and Sphere 3 are negatively or positively charged.

Spheres 1 and 2 repel each other. This means that they carry charges of the same sign. Since Sphere 1 is positively charged, Sphere 2 must be positively charged as well.
Spheres 2 and 3 attract each other. This means that they carry charges of the opposite sign. Since Sphere 2 was determined to be positively charged, Sphere 3 must be negatively charged.