Endocytosis and exocytosis are both processes allowing exchanges between a cell and its extracellular environment. These mechanisms occur when certain substances (nutrients, toxins, etc.) cannot pass freely through the cell membrane.
During the two processes, the transport of substances inside the cell involves vesicles.
A vesicle is a small sac circulating in the cytoplasm. It is formed from the components of the cell membrane. Its role is to store and transport substances within the cell.
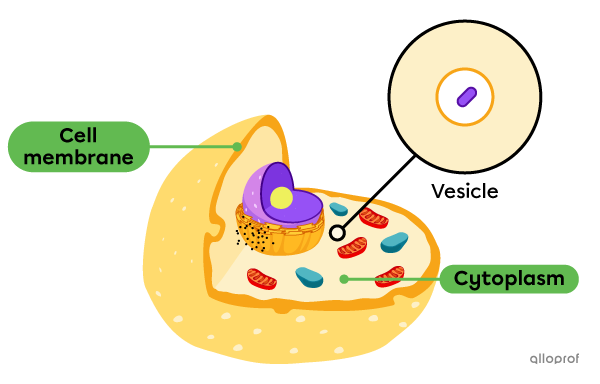
Endocytosis is a vesicular transport into a cell.
During endocytosis, the cell membrane is deformed to envelop the substances to be brought into the cell. Therefore, a vesicle is formed from the components of the cell membrane.
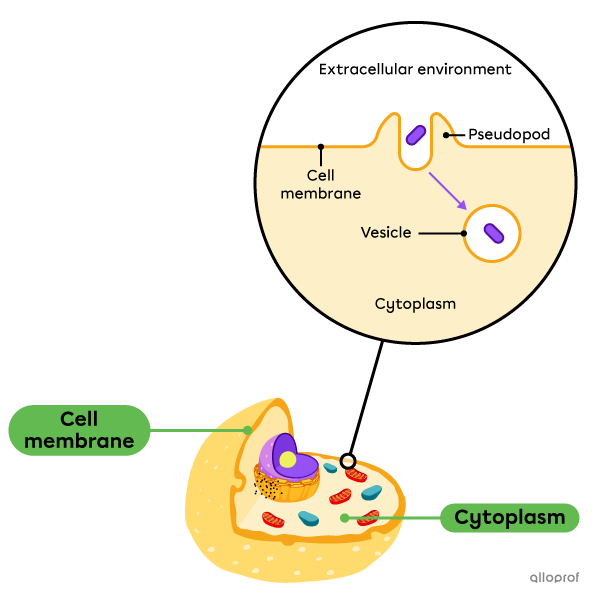
Phagocytosis and pinocytosis are two types of endocytosis.
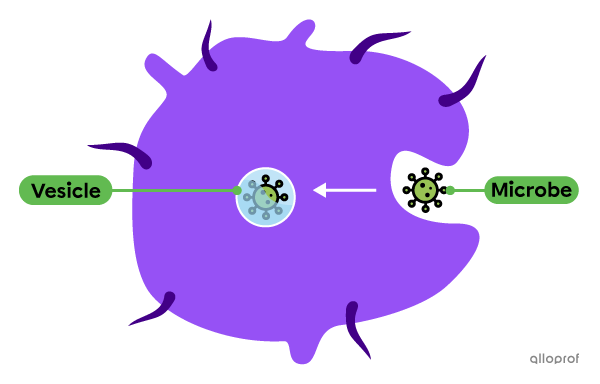
During phagocytosis, the cell membrane forms pseudopodia surrounding the contents to be brought into the cell. They enclose the contents, shaping the pseudopod membrane into a vesicle. It is transported into the cytoplasm towards the lysosomes where the digestion of its contents takes place.
Phagocytosis is often used to absorb very large molecules and even other entire cells.
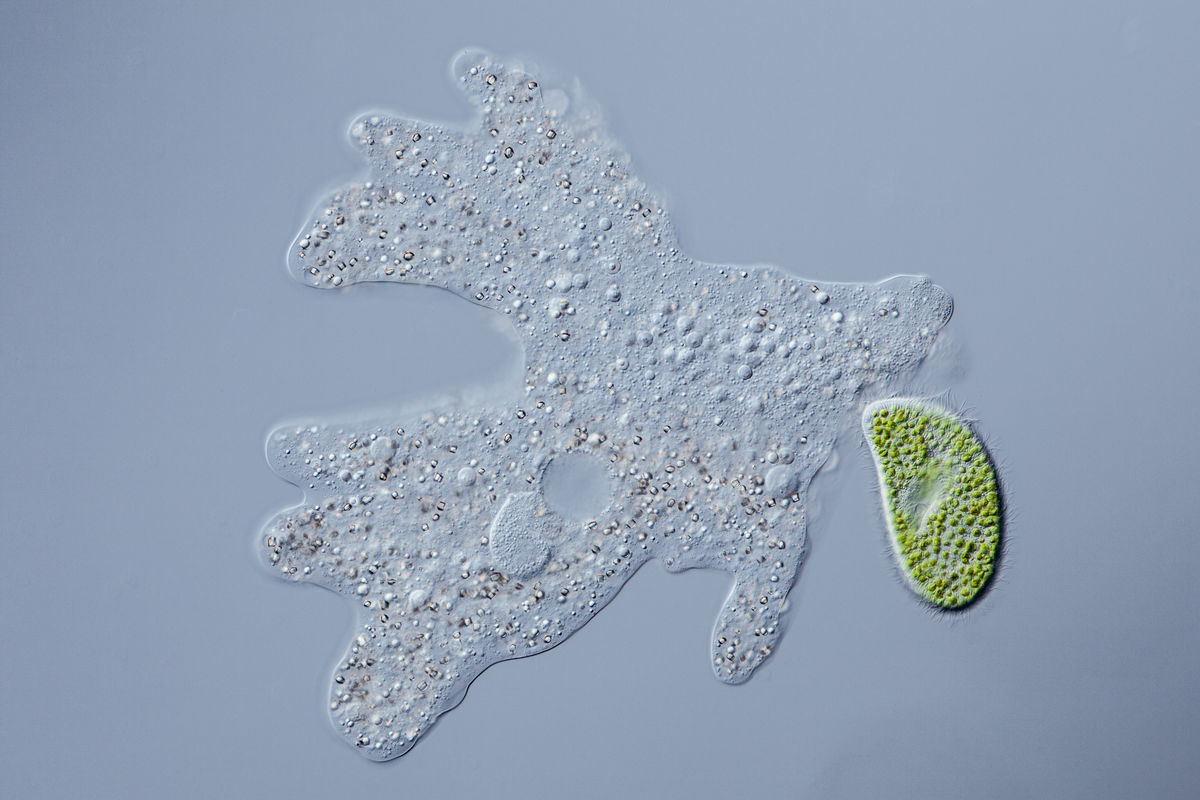
Amoeba proteus is a protist that feeds by phagocytosis.
In the image, it is preparing to form its pseudopodia in order to engulf a paramecium (in green).

Lebendkulturen.de, Shutterstock.com
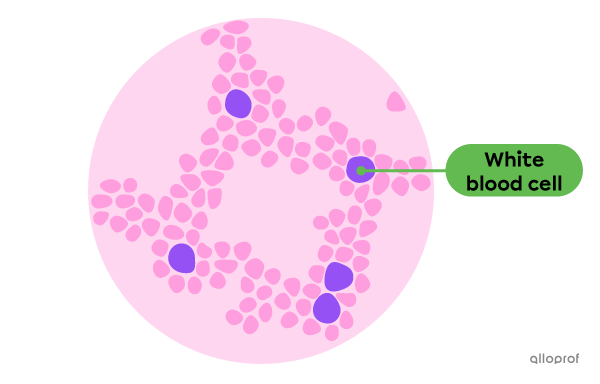
White blood cells are blood cells that destroy foreign bodies. Some types of white blood cells act by phagocytosis.
During pinocytosis, an invagination (or infolding) develops in the cell membrane and encompasses the contents to be transported into the cell, creating a vesicle. It carries out the transport in the cytoplasm towards the lysosomes where the digestion of the contents takes place.
Pinocytosis is used for certain solutes and liquids that cannot be absorbed by diffusion.
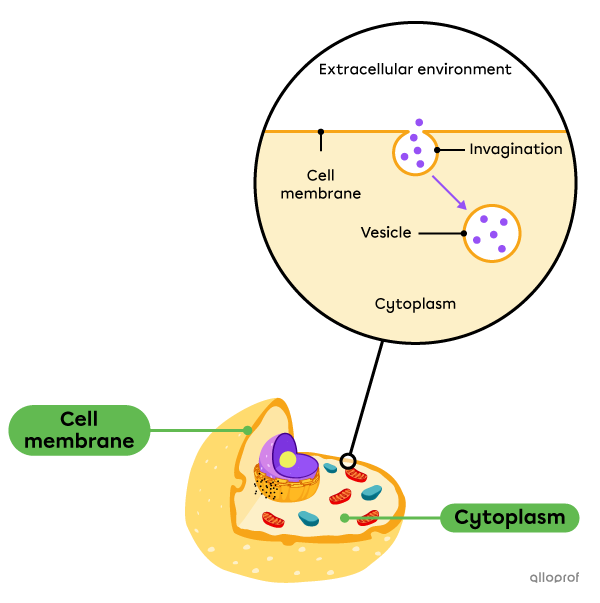
Fat (adipose) cells absorb lipids, fatty acids, and cholesterol by pinocytosis.
Jose Luis Calvo, Shutterstock.com
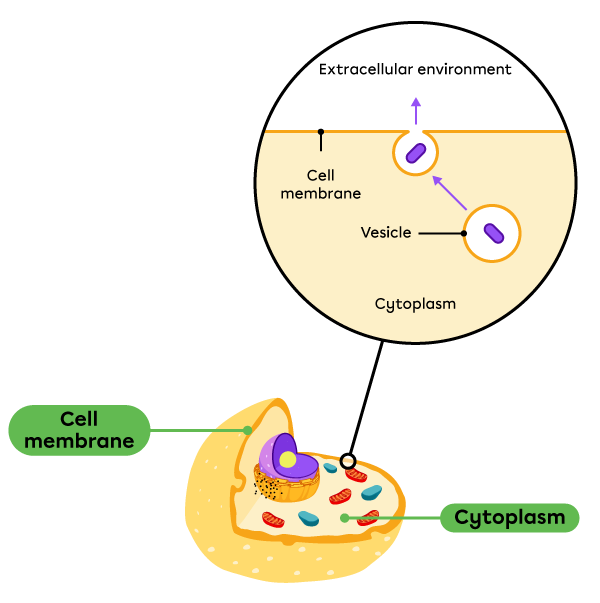
Exocytosis is a vesicular transport out of a cell.
During exocytosis, a vesicle inside the cell fuses with the cell membrane. The vesicle opens and releases its contents outside the cell.
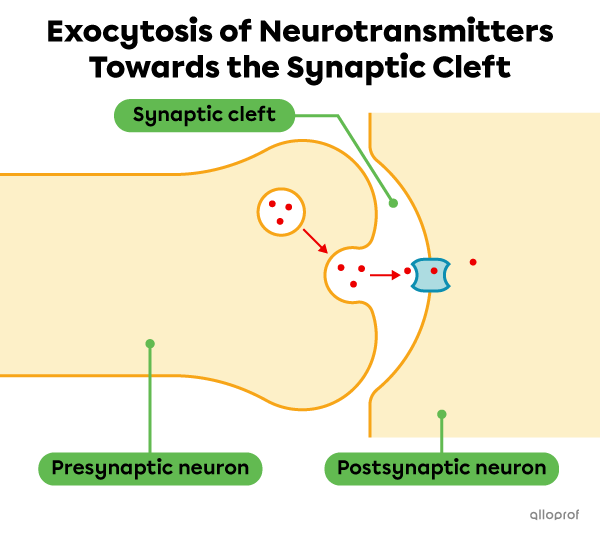
Exocytosis occurs abundantly between neurons. In fact, the neurotransmitters are transported in vesicles. They are then released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis.
To validate your understanding about the cell in an interactive way, consult the following MiniRécup:
