The phrases there is/was and there are/were are used to say that something exists or existed.
In basic sentences, the subject comes before the verb, but in a sentence that begins with There is or There are, the subject (a singular or plural noun) comes after.
For example:
If you want to say that a cow in the field exists, use there is:
There is a cow in the field.
To determine whether to use there is or there are, you must check the noun following it.
You must also consider the verb tense.
| Singular countable nouns/uncountable nouns |
Plural countable nouns |
|
| Simple Present | there is | there are |
| Simple Past | there was | there were |
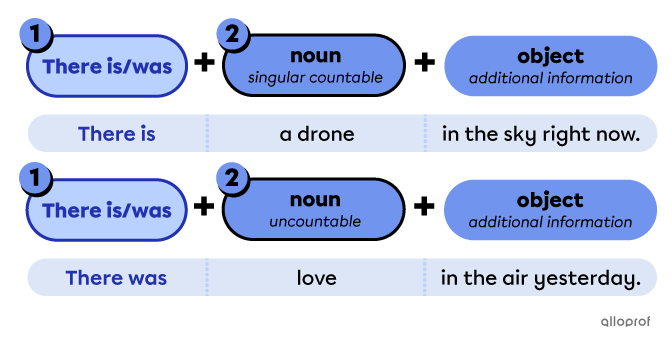
Points to remember when forming sentences using there is/was
-
Place there is/was in front of a singular countable noun or an uncountable noun.
-
Place the noun after there is/was.
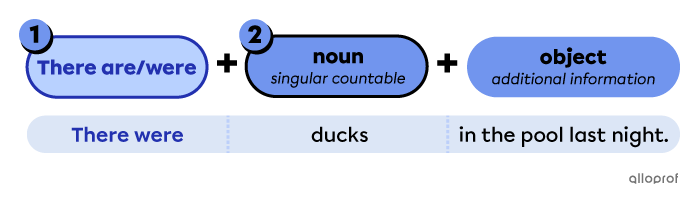
Points to remember when forming sentences using there are/were
-
Place there are/were in front of the plural countable nouns.
-
Place the noun after there are/were.
Simple Present
| Singular countable |
Singular uncountable |
Plural countable |
There is a mosquito in the tent. |
There is milk in the fridge.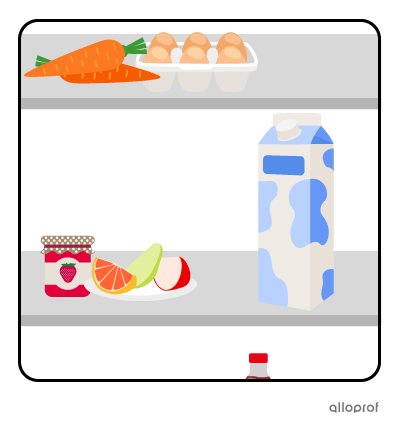 |
There are insects everywhere. |
There is a car in the driveway. |
There is sand on the beach. |
There are players on the ice. |
Simple Past
| Singular countable |
Singular uncountable |
Plural countable |
There was a job opening yesterday, but we hired someone this morning. |
There was water in the glass before I spilled it everywhere. |
There were dinosaurs on Earth before their mass extinction. |
There was a dog barking last night. |
There was soup for lunch yesterday. |
There were electric cars in 1895. |
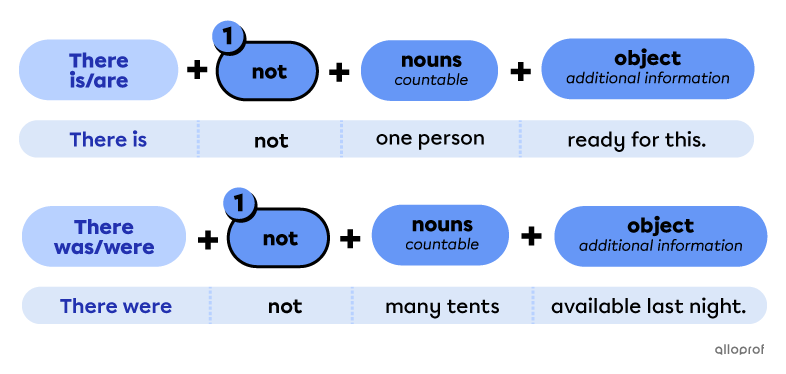
Point to remember when forming negative sentences with there is/are or there was/were
-
Place the function word not after there is/are or there was/were.
| Singular Countable | Plural Countable | |
| Simple Present | There is not a car in the driveway. | There are not many insects in the house. |
| There isn’t* a cow in the field. | There aren’t* any players on the ice. | |
| Simple Past | There was not a tree in the backyard. | There were not many movies to watch online in 2005. |
| There wasn’t* a bird in this forest. | There weren’t* many possibilities. |
*Contractions are often used in the negative.
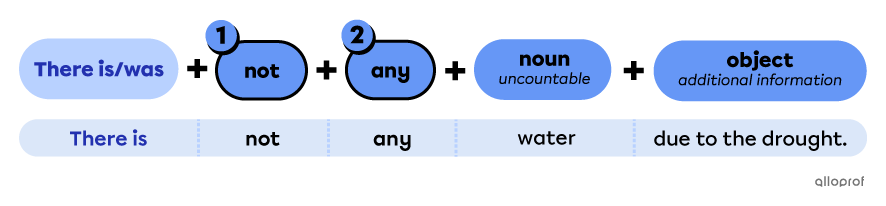
Points to remember when forming negative sentences with there is/was that are followed by an uncountable noun
-
Place the function word not after there is/was.
-
Place the determiner any before the uncountable noun.
| Uncountable | |
| Simple Present | There is not any juice left. |
| There isn’t* any snow falling. | |
| Simple Past | There was not any wind blowing. |
| There wasn’t* any water in the pool. |
*Contractions are often used in the negative.
Use there is when using the expression a lot of in front of an uncountable noun, for example:
-
There is a lot of snow outside.
-
There is a lot of current in this river.
Use there are when using the expression a lot of in front of countable plural nouns, for example:
-
There are a lot of students in that school.
-
There are a lot of possibilities.
Sometimes choosing between there is and there are is difficult with sentences like:
-
There is/There are a number of unknown animals in the sea.
The rule can be confusing since a number of is singular, but the noun that follows, animals, is plural.
If we focus on the group of nouns, we use there is:
-
There is a number of unknown animals in the sea.
But if we focus on the plural nouns we use there are:
-
There are a number of unknown animals in the sea.
The fact that both formulations can be correct makes it confusing. Your best bet is to reformulate your sentence, for example:
-
Many unknown animals are in the sea.
This way, you’re staying away from awkward formulations.
Another awkward formulation happens when using there are with a series of objects, for example:
-
There are a fork, a knife and a spoon in the kitchen drawer.
Using there are just before a singular noun is wrong. So, even if multiple objects are enumerated, using there is in front of the series of objects is correct because of the concept of ellipsis (leaving out words). When we say:
-
There is a fork, a knife and a spoon in the kitchen drawer.
What we really mean is:
-
There is a fork, there is a knife, and there is a spoon in the kitchen drawer.
But as you can see, repetition isn’t necessary.
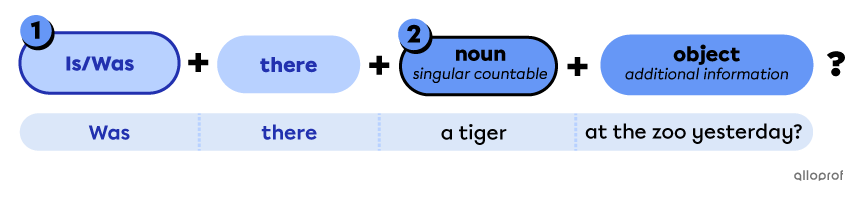
Points to remember when forming yes/no questions with singular countable nouns
-
Place the auxiliary verb to be (is/was*) before there for yes/no questions.
-
Place the singular countable noun after there.
*Use is in the simple present and was in the simple past.
| Singular Countable Nouns | |
| Simple Present | Is there a nurse available? |
| Is there a doctor in the room? | |
| Simple Past | Was there a dog in space? |
| Was there a scientist in the laboratory? |
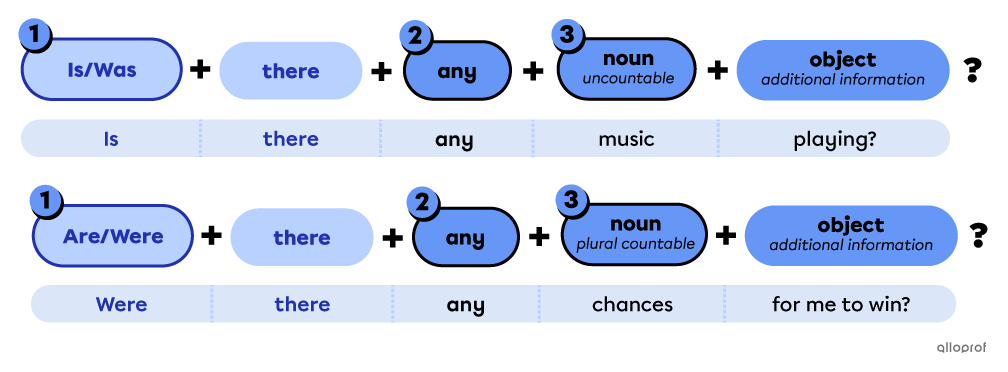
Points to remember when forming yes/no questions with plural countable nouns or uncountable nouns
-
Place the auxiliary verb to be (is/was/are/were*) before there for yes/no questions.
-
Place the pronoun any after there.
-
Place the plural countable noun or uncountable noun after any.
*Use is/are in the simple present and was/were in the simple past.
| Plural Countable Nouns | Uncountable Nouns | |
| Simple Present | Are there any penguins in Arctica? | Is there any milk left at the grocery store? |
| Are there any sandwiches in the fridge? | Is there any sand on that beach? | |
| Simple Past | Were there any mosquitos on the cruise? | Was there any trouble on the flight? |
| Were there any protesters downtown yesterday? | Was there any ice cream in the freezer? |
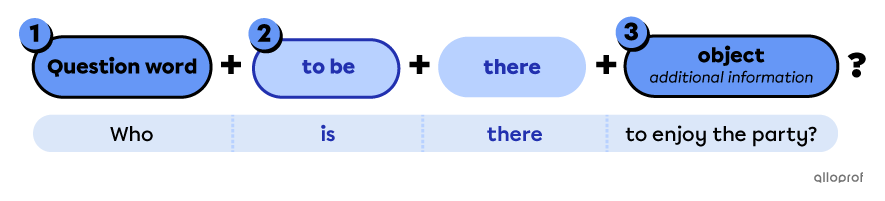
Points to remember when forming information questions
-
Place the question word first.
-
Place the auxiliary verb to be (is/are/was/were*) before there.
-
Place the object after there.
*Use is/are in the simple present and was/were in the simple past.
| Question word | to be | there | object |
| Who | is | there | today? |
| What | was | there | to do in Toronto last weekend? |
| Where | are | there | wild horses? |
| Why | were | there | demonstrations in Ottawa? |
Specific Questions with how many
-
Place the question word first.
-
Place the plural noun after how many.
-
Place the auxiliary verb to be (is/are/was/were) before there.
-
Place the object after there.
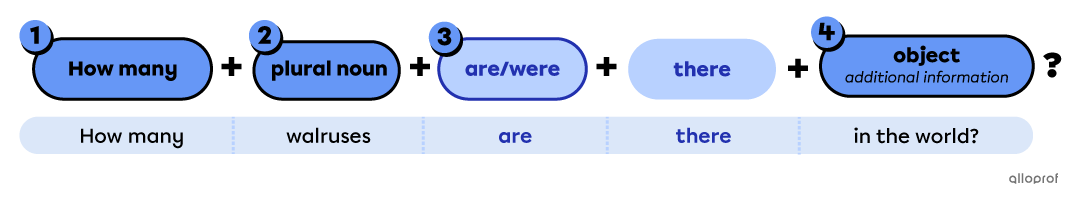
| How many | How many pigs are there on the farm? |
| How many casualties were there in WWII? |
It is possible to form complete sentences combining there with auxiliary verbs.
Points to remember when forming affirmative sentences with auxiliary verbs
-
Place the auxiliary verb after there.
-
Place be/been* after the auxiliary verb.
-
Place the singular/plural countable noun or uncountable noun after be/been.
*Use been with perfect tenses.
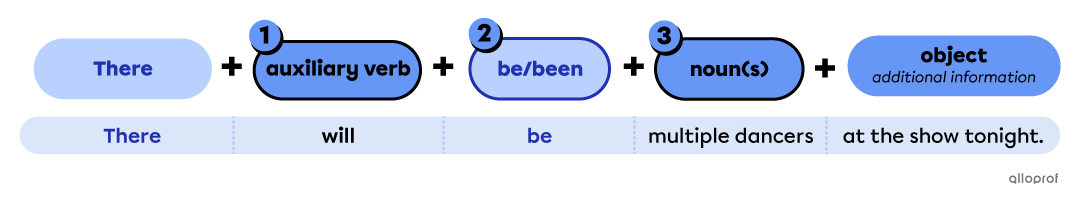
| Singular Countable | Uncountable | Plural Countable | |
| Simple Future | There will be a new electric car. | There is going to be internet access everywhere soon. | There will be new viruses in the future. |
| Present Perfect | There has been a scientific breakthrough this morning. | There has been trouble all day long. | There have been many casualties today. |
| Singular Countable | Uncountable | Plural Countable | |
| Modals | There could be new laws. | There might be trouble ahead. | There would be kiwis in Australia if they could fly from New Zealand. |
| The architect says there can be 2 or 3 bathrooms in the new house. | There could be oil in the engine. | There should be 7 players on the field. |
Points to remember when forming negative sentences with auxiliary verbs
-
Place the auxiliary verb after there.
-
Place the function word not after the auxiliary verb.
-
Place be/been after the auxiliary verb.
-
Place the singular/plural countable noun or uncountable noun after be.
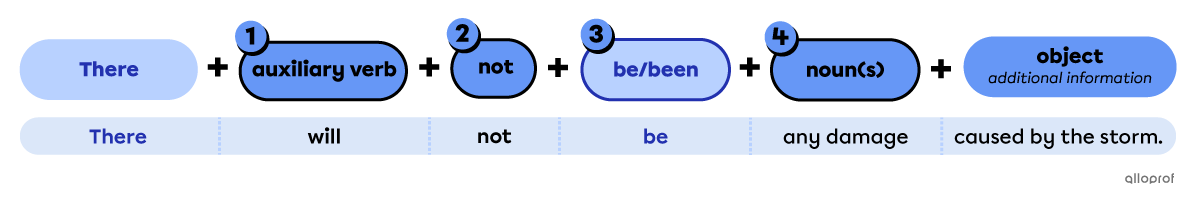
| Singular Countable | Uncountable | Plural Countable | |
| Simple Future | There will not be a new version of Windows in the years to come. | There won't* be any meat for supper. | There will not be any flying cars soon. |
| Present Perfect | There has not been one injured person since the attack. | There hasn’t* been any reported damage to the building. | There have not been any reports after 22:00. |
| Singular Countable | Uncountable | Plural Countable | |
| Modals | There could not be anyone in the area. | There might not be any trouble ahead. | There wouldn’t* be any problem if everyone respected the rules. |
| There can’t* be more than 3 bedrooms in this new house. | There would not be water in the basement if it weren’t for the storm outside. | There shouldn’t* be more than 5 players on the ice. |
*Contractions are often used in the negative.
Points to remember when forming yes/no questions with auxiliary verbs
-
Place the auxiliary verb before there for yes/no questions.
-
Place be/been after the auxiliary verb.
-
Place the singular/plural countable noun or uncountable noun after be/been.
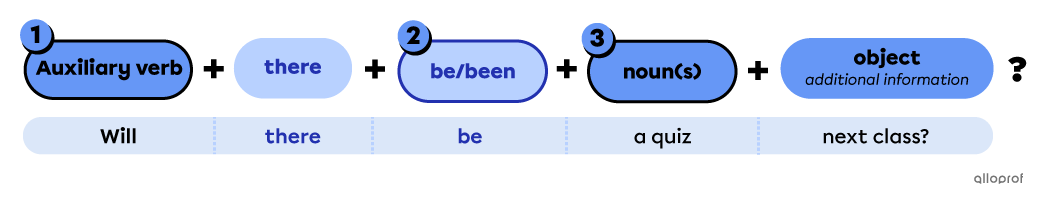
| Singular Countable | Uncountable | Plural Countable | |
| Simple Future | Will there be a new version of Windows soon? | Will there be any meat for supper? | Will there be any flying cars soon? |
| Present Perfect | Has there been a casualty in the attack? | Has there been any reported damage to the building? | Have there been any reports after 22:00? |
| Singular Countable | Uncountable | Plural Countable | |
| Modals | Should there be anyone in the area? | Could there be any trouble ahead? | Would there be problems if people respected the rules? |
| Can there be more than 3 bedrooms in this new house? | Would there be water in the basement if it hadn’t been for the storm? | Should there be more than 5 players on the ice? |
Points to remember when forming information questions with auxiliary verbs
-
Place the question word first.
-
Place the auxiliary verb before there.
-
Place be/been after there.
-
Place the object after be/been.
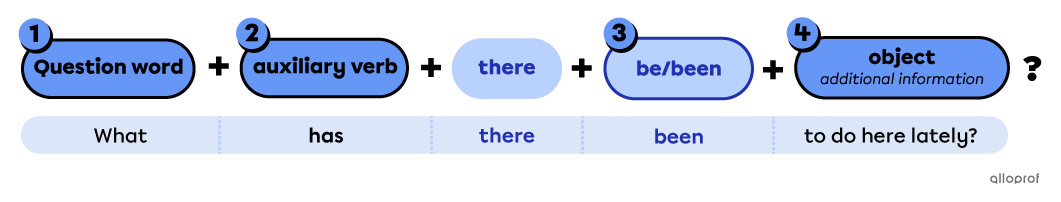
| Question word | auxiliary verb | there | be/been | object |
| When | should | there | be | a new government? |
| What | would | there | be | if there was no universe? |
| Where | might | there | be | microclimates? |
| Why | have | there | been | protesters? |