The imperative mood is used to tell somebody to do something.
Imperative sentences can be used to:
|
give warnings |
give advice |
give orders |
|
give instructions |
place an order |
make requests |
Give warnings

Give advice

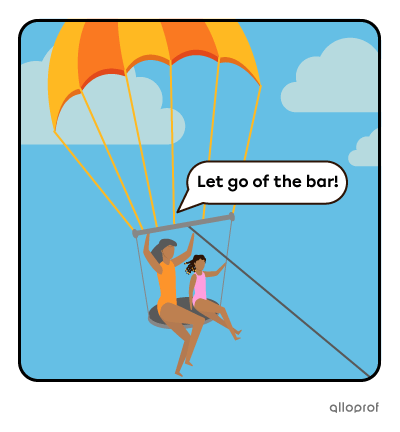
Give orders

Give instructions
Place an order*
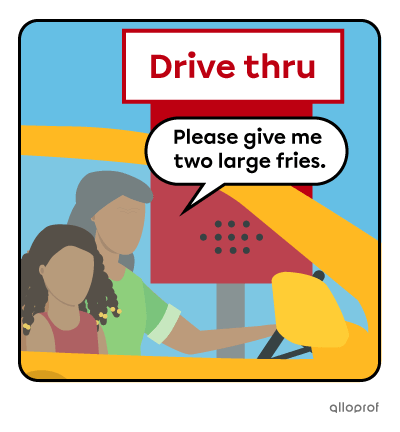
*The word please can be added at the beginning or at the end of an imperative sentence to add politeness.
Make requests*

*Imperative sentences can replace interrogative sentences (questions used to make requests).
To recognize imperative sentences, look for three specific elements:
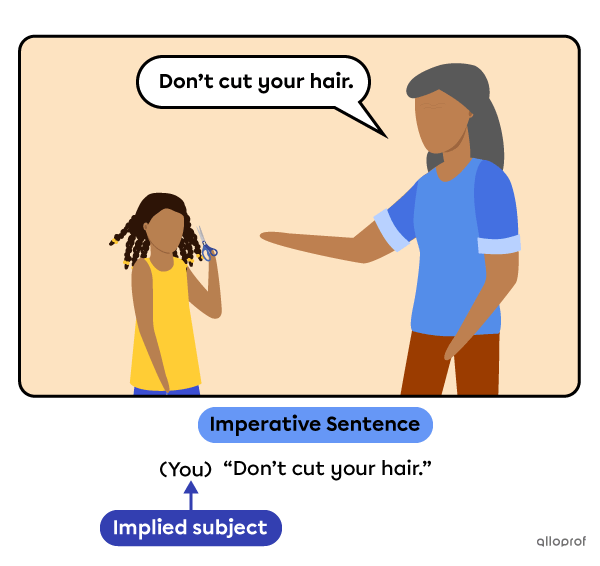
-
The subject is not mentioned, it is implied.
-
The implied subject is always you.
-
The verb is always in its base form (infinitive without the “to”).

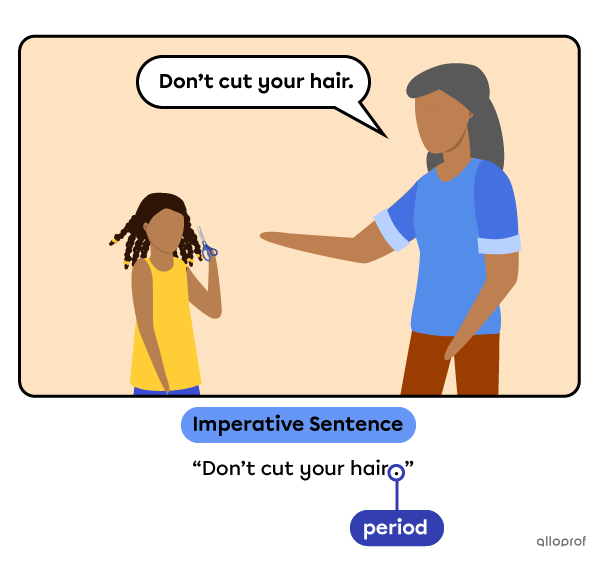
Imperative sentences:
-
usually end with a period.
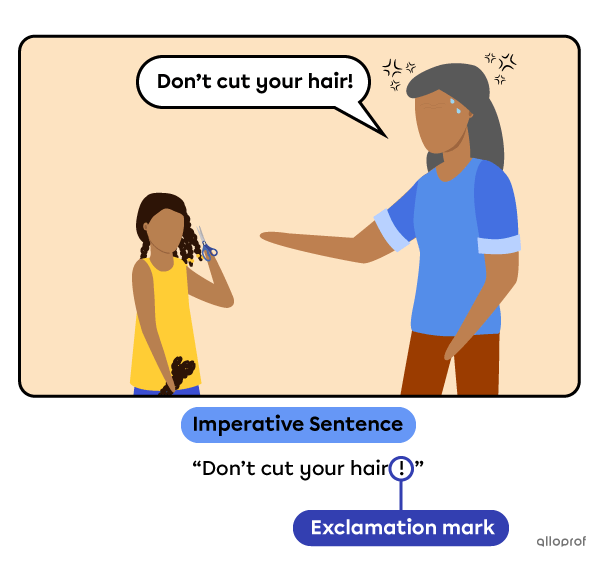
-
can end with an exclamation mark to express urgency or emotion.
|
Sentence Type |
Example |
|
Declarative |
Everyday, you wash your hands before dinner. |
|
Interrogative |
Could you wash your hands before dinner? |
|
Exclamative |
You must wash your hands before dinner! |
|
Imperative |
Wash your hands before dinner. |
Points to remember when forming affirmative imperative sentences:
-
Use the base form of the verb.
-
Place the object*.
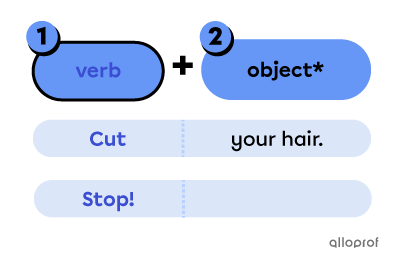
*The object is not always necessary.
Points to remember when forming negative imperative sentences:
-
Use the negative form do not or don’t.
-
Use the base form of the verb.
-
Place the object*.

To indicate the way an action should be done: add an adverb.
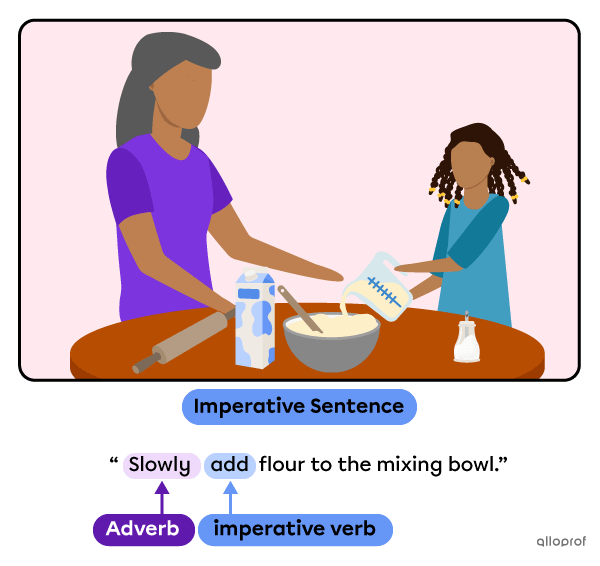
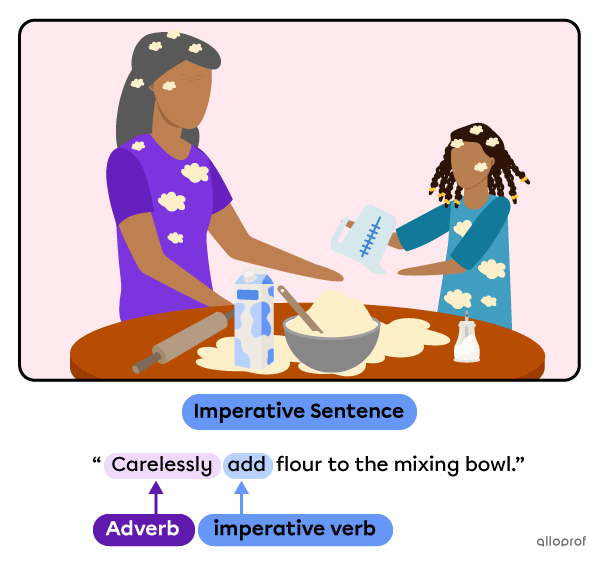


Although the subject of imperative sentences is an implied second person, subjects can be specified as a way to clarify who is addressed or to get that person’s attention.
|
Addressed to: |
Imperative sentence: |
|
Mom, |
look at me when I am talking to you. |
|
Somebody |
get the door! |
|
Okay Google, |
start a timer. |
The imperative form is often used to make unreal commands: Sentences that are structured like commands, but that mean to suggest something or express what we wish for someone.
|
Function |
Example |
Explanation |
|
Suggestion |
If you don’t eat meat, choose the vegan macaroni. |
Offering a suggestion, not an obligation. |
|
Wish |
Don’t panic! Everything will be fine. |
Wishing the person would not panic. |
|
Wish |
Feel better! |
Wishing the person would feel better. |
Imperative sentences are usually written in the active voice. However, in rare cases, to add formality, it is possible to make passive imperatives.
Passive imperatives with the form: Let + object + be + past participle
|
Active |
Passive |
|
Bring your suitcase to your room. |
Let your suitcase be brought to your room. |
|
Celebrate Christmas at my home. |
Let the Christmas be celebrated at my home. |
The words let’s can be added to the beginning of an bsentence to form affirmative or negative suggestions which include ourselves:
Let’s is the contraction of let us, which implies that the subject is the 1st person plural we (you and me).
|
Let’s go to the planetarium. |
|
Let’s not go our own ways. Let’s stick together. |
|
Let’s spend a week in Florida. |
Adding the word do before an imperative sentence adds emphasis, politeness and formality to the command.
|
Request |
Do wait for your turn to speak. |
|
Complaint |
Do turn down the volume of your tablet. I can’t sleep. |
|
Apology |
Do forgive me for my tone. I know I was wrong. |
Tag questions can be added to imperative sentences to add politeness or insistence to the request.
Tag questions are either formed with an affirmative statement and a negative tag question or a negative statement and an affirmative tag question.
However, to express a different intention, it is possible to use an affirmative imperative sentence followed by an affirmative tag question.
|
Example |
Structure |
Intention |
|
Sit in the waiting room, will you? |
affirmative-affirmative |
To politely invite the person to sit in the waiting room. |
|
Sit in the waiting room, won’t you? |
affirmative-negative |
To strongly insist that the person sits in the waiting room. |
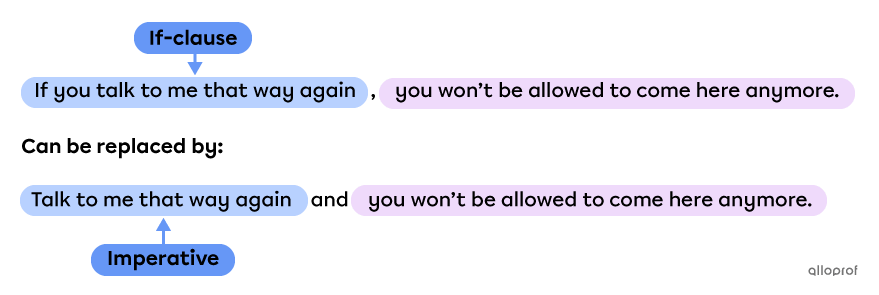
A conditional if-clause can replace an imperative clause.
The if-clause uses a comma ( , ).
The imperative uses the word and.