A prime number is a number that has only two different divisors: 1 and itself.
When representing a prime number using objects or a drawing, there are only two ways to form equal groups.
The first way is to put all the objects in a single group. The divisor is therefore 1.
3 ÷ 1 = 3
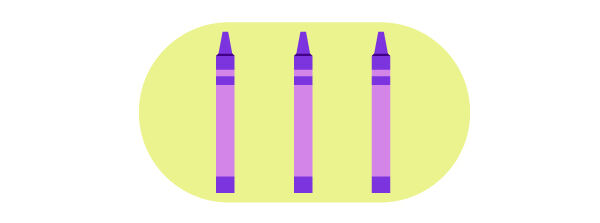
The second way is to put a single object in each group. The divisor is therefore the number itself.
3 ÷ 3 = 1
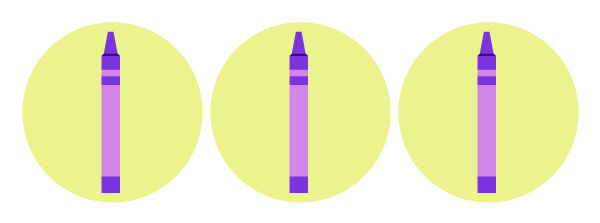
If it is possible to form one or more other equal groups, it means that the number is not a prime number. It is a composite number.
Note: To learn more about composite numbers, you can read the concept sheet Composite Numbers.
1 is not a prime number because it doesn't have two different divisors. A single item can only be placed in one group.
0 is also not a prime number because there are no (0) objects to put into groups.
All prime numbers are odd (5, 7, 11, 13...), except for the number 2!
You can verify whether a number is prime by using objects or a drawing and trying to form equal groups.
Is 7 a prime number?
To check if 7 is a prime number, I use objects or a drawing, then I try to form equal groups.

I can't form 2 equal groups since there is a remainder.
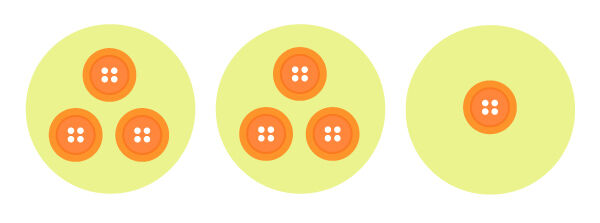
I can't form 3 equal groups since there is a remainder.
Even by trying to make 4, 5, and 6 equal groups in the same way, there is still a remainder.
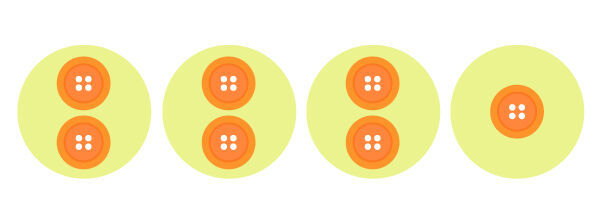
With the number 7, I can only form 1 group of 7 buttons or 7 equal groups of 1 button.

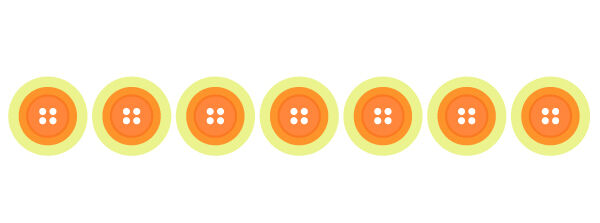
7 is a prime number because it can only be divided by 1 and itself.
Is 15 a prime number?
To check if 15 is a prime number, I use objects or a drawing and then I try to form equal groups.
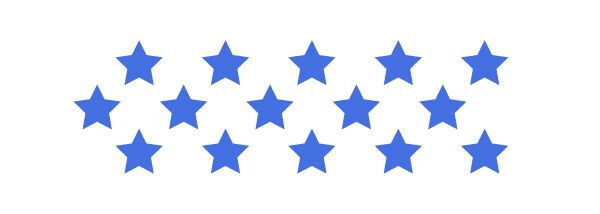
I can't form 2 equal groups since there is a remainder.
I can form 3 equal groups of 5 stars.
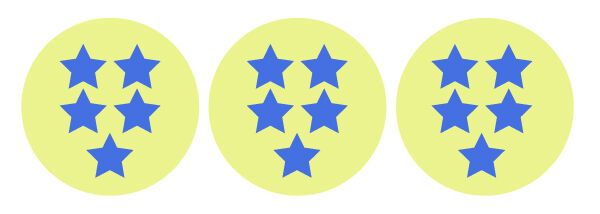
15 is not a prime number because it can be divided by a number other than 1 and itself.