Just like the regular convex polyhedrons, a cube has very particular characteristics.
A cube is a polyhedron (also called a prism or regular hexahedron). It has six isometric (congruent) square faces.
When examining its construction, other characteristics become apparent.
To ensure that its definition and construction are respected, it is important to keep the following characteristics in mind.
The characteristics of a cube are the following:
-
two edges that meet at a common vertex are perpendicular;
-
opposite faces are parallel;
-
adjacent faces are perpendicular;
-
diagonals of the opposite vertices intersect in their middle.
If these properties are respected, the end result will always be a cube.
Other properties emerge when analyzing the composition of a cube in greater detail.
Barycentre
An intersection point called the “barycenter” is obtained when a diagonal is drawn between each pair of opposite vertices.
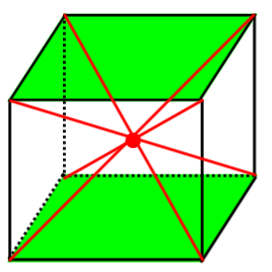
In other words, the barycentre is the centre of a cube’s gravity. When a cube’s weight is distributed equally, the barycentre is then called isobarycentre.
