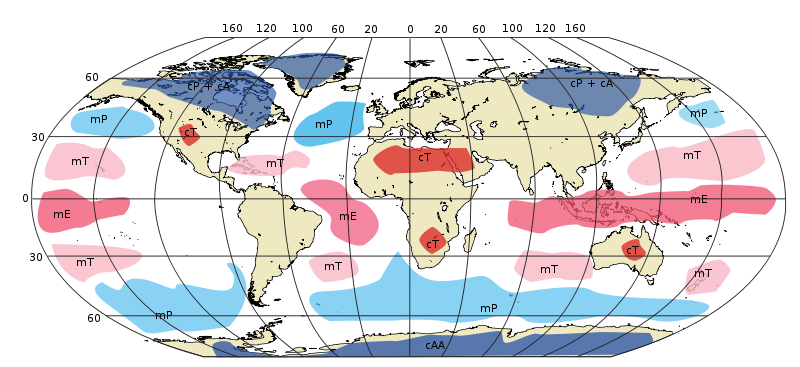
An air mass is an area of the atmosphere where temperature and humidity are relatively homogeneous.
Although air is almost constantly in motion in the atmosphere, very large volumes of air remain in one place long enough to acquire the temperature and humidity conditions of the place they are above. These immense air volumes are called air masses.
Two terms are generally used to designate the humidity of air masses: dry and humid. Dry air is a continental air mass while humid air is a maritime air mass.
To qualify the temperature of the air mass, we can say that the air is warm (tropical air), cold (polar air), and very cold (arctic air). Based on these qualifiers, air masses are generally classified into six types.
|
AIR MASS TYPE |
HUMIDITY |
TEMPERATURE |
|
Continental polar (cP) |
Dry |
Cold |
|
Continental arctic (cA) |
Dry |
Very cold |
|
Continental tropical (cT) |
Dry |
Warm |
|
Maritime polar (mP) |
Humid |
Cold |
|
Maritime arctic (mA) |
Humid |
Very cold |
|
Maritime tropical (mT) |
Humid |
Warm |

When two air masses meet, they do not mix. Rather, an area is created, known as the front, where pressure, temperature, and humidity change rapidly. This area is also where clouds form. The movement of air masses causes two types of phenomena, depending on whether the movement is horizontal or vertical: