Atmospheric pressure is the air pressure at any point on Earth. Atmospheric pressure is measured using a barometer.
The normal atmospheric pressure at sea level is 101.3 kPa.
Atmospheric pressure varies from one place on Earth to another. The higher you go, the lower the pressure. Because air is rarer at higher altitudes than at lower ones, there are fewer gas molecules per unit volume.
Cold air has a higher density than warm air. This means that for the same number of particles, cold air will occupy a smaller volume than warm air.
For this reason, cold air will tend to be heavier and will be directed towards the ground, while warm air will tend to be lighter and will rise into the air.
When making their forecasts, meteorologists must always take atmospheric pressure into account. Here are some weather forecasts associated with atmospheric pressure.
|
Observations on the Barometer |
Weather Forecast |
| The pressure fluctuates rapidly. |
Strong winds are forecast. |
| Atmospheric pressure remains above normal (high pressure). |
We are in the presence of an anticyclone (high pressure). Generally speaking, an anticyclone is associated with cold, dry weather. |
| Atmospheric pressure remains below normal (low pressure). |
This is a cyclone (low-pressure system). Generally speaking, a low-pressure system brings cloudy, rainy weather. |
Pressure measurement instruments
The atmosphere exerts pressure on the Earth's surface and a barometer measures how much pressure the atmosphere exerts at that point. The scale on a barometer is usually measured in kilopascals (kPa) according to the international system of units.
The two most common types of barometer are the liquid barometer and the aneroid barometer.
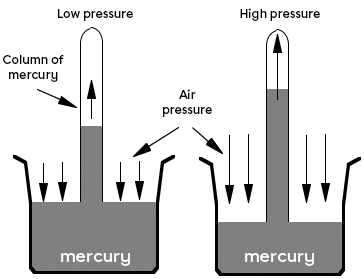
- The liquid barometer (or mercury barometer) is an instrument invented by the physicist and mathematician Torricelli in 1643. The mercury barometer consists of a graduated glass tube that is inverted in a vessel filled with mercury. Atmospheric pressure exerts a force on the free surface of the mercury. As atmospheric pressure increases, the thrust on the free surface of the mercury becomes greater and the mercury rises inside the graduated tube. Conversely, when atmospheric pressure decreases, the thrust exerted on the free surface of the mercury also decreases and the mercury descends inside the graduated tube.
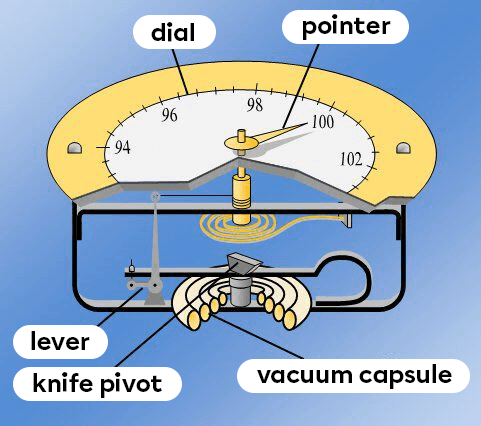
- The aneroid barometer is an instrument for measuring atmospheric pressure. Essentially, the aneroid barometer consists of a metal capsule inside which a vacuum has been created. When atmospheric pressure rises, the capsule is compressed. When atmospheric pressure falls, the capsule relaxes and increasingly returns to its original shape. A pointer is connected to a small mechanical system that amplifies the capsule's motions. This pointer is used to read the value of the atmospheric pressure on a graduated dial.
Relative humidity is the percentage of water vapour in the air. Relative humidity is measured using a psychrometer or hygrometer.
If the air contains no water particles, then the relative humidity is said to be 0%. However, if the air is saturated with water, i.e. cannot contain any more water vapour, then the relative humidity is said to be 100%.
Evaporation is influenced by relative humidity. When the air is full of moisture, evaporation is low. Conversely, when the air is dry, evaporation is high and rapid.
When warm, moist air cools, it reaches a temperature at which it can no longer retain the amount of water it contains. The water vapour condenses to form fog. Dew can also be observed on the ground.
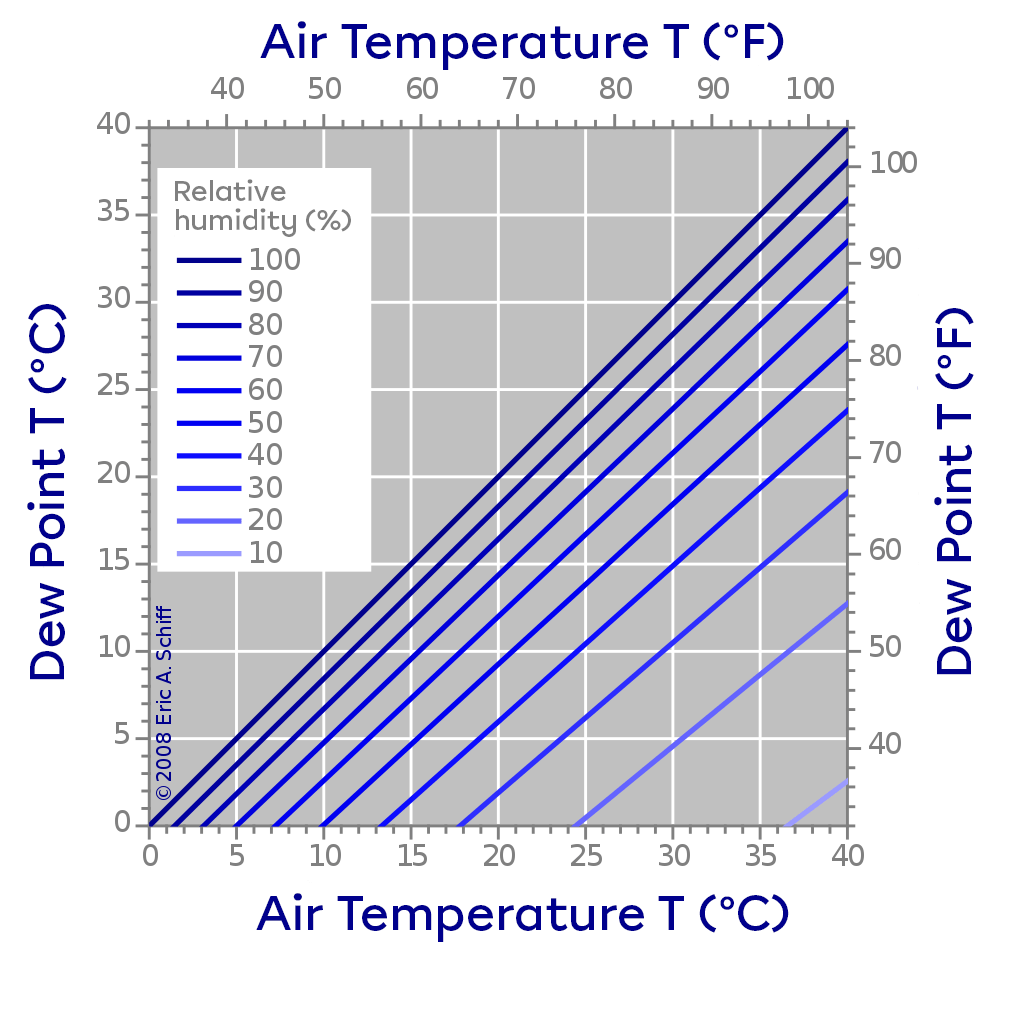
The dew point is the temperature at which the water vapour in the air condenses to form water droplets. The image on the left shows this phenomenon. The graph on the right shows the relationship between the air temperature, the percentage of relative humidity and the dew point. It should be noted that when the air temperature is low, the amount of water vapour in the air is very limited and the dew point is more easily reached. However, if the air temperature is higher, a greater amount of water vapour is needed to reach the dew point.
At home, we recommend keeping relative humidity between 30 and 50% for maximum comfort. Too much humidity in the home can lead to problems such as mould and respiratory problems.
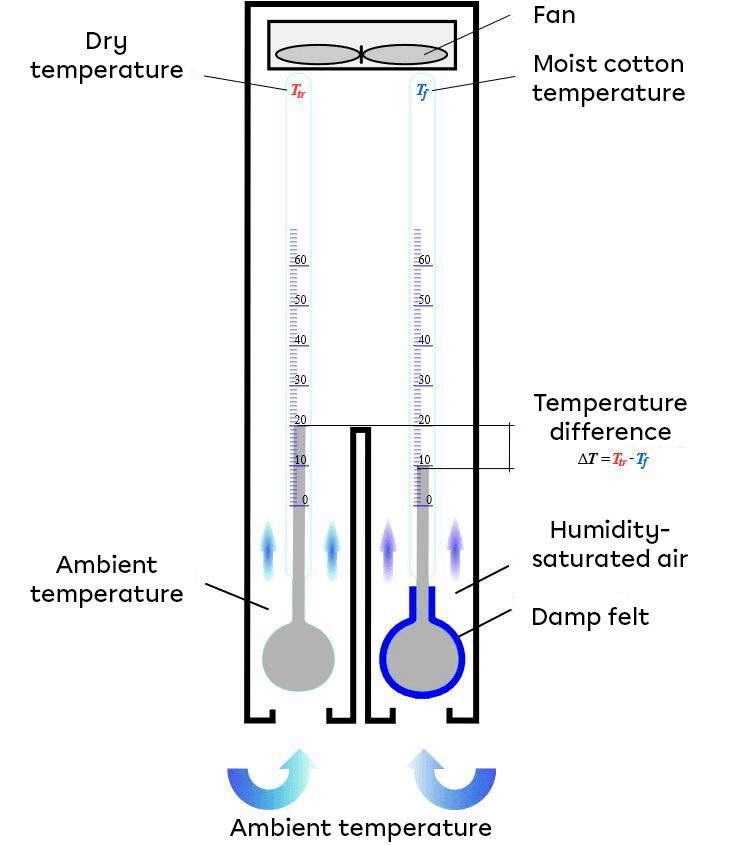
The psychrometer measures the percentage of relative humidity in the air.
This instrument is composed of two thermometers. The first measures the ambient temperature in degrees Celsius (°C), while the second measures the temperature of the damp cotton in which it is immersed. To find the relative humidity measurement, take the difference between the two temperatures and plot it on a psychrometric table.
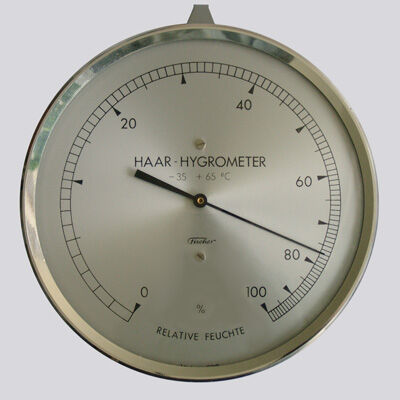
The hair hygrometer is an instrument that measures the relative humidity of the air.
This instrument uses the property of hair or horsehair to lengthen when relative humidity increases. Women's blond hair is the most sensitive to this property.
A weight is attached to one end of the hair, which is placed vertically, and the whole is connected to a system of levers so that a pointer can travelled and display the percentage of humidity on a graduated dial.