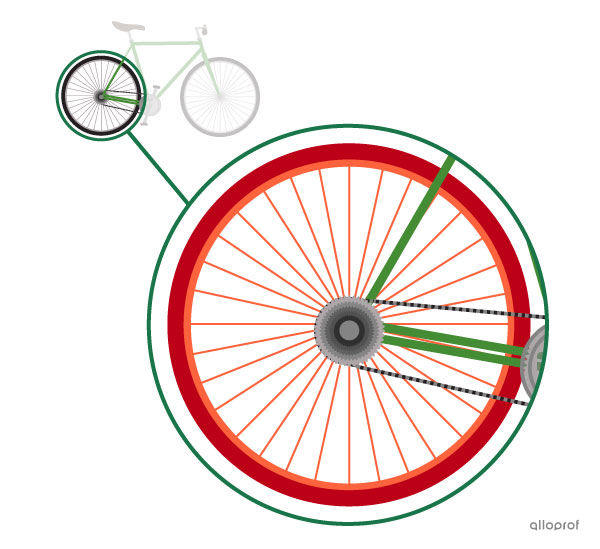
Each component of a technological system has a specific mechanical function to ensure that it functions properly.
-
A component is a part of a technological system.
-
A technological system is an organized set of interconnected components that influence one another to accomplish an overall function.
-
The mechanical function is the role fulfilled by a component or a mechanism in a technological system.
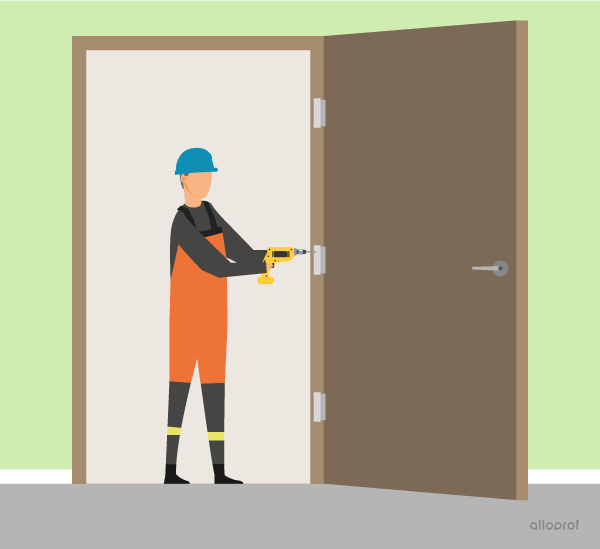
Here are two examples referring to a door with hinges and screws.

-
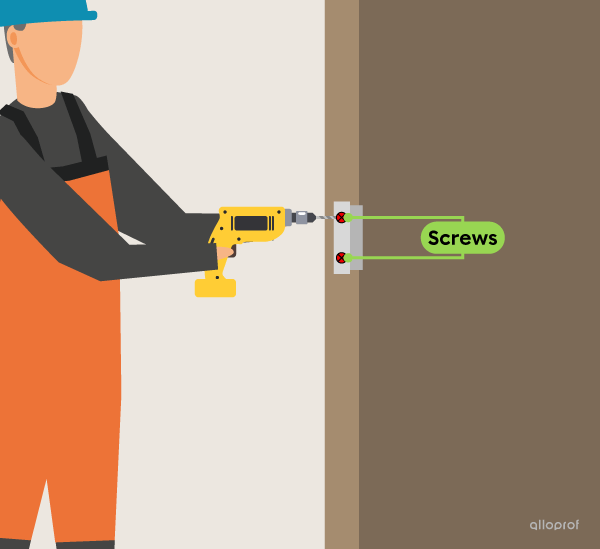
The screws on a door hinge hold the door within its frame. The screws are the components that serve the mechanical function of linking in the door’s technological system. They are called linking components.
-
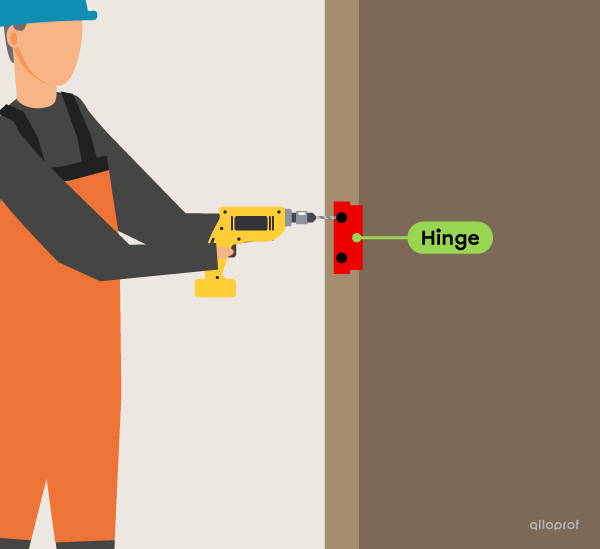
The hinge guides the rotational motion of the door. The mechanical function of the hinge is guiding control, so it is called a guiding component.
A basic mechanical function is the role fulfilled by a component in a technological system.
There are four basic mechanical functions.
A component can perform more than one basic mechanical function.
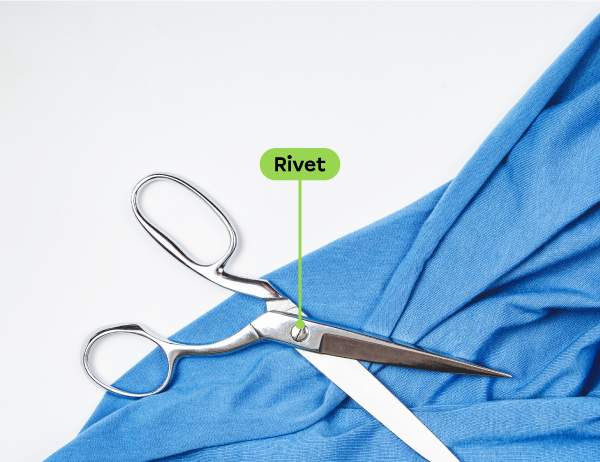
For example, the rivet in a pair of scissors performs a linking function and a guiding function.
Adapted from MARIIA_MALYSHEVA, Shutterstock.com
Linking is the function provided by a component that holds different parts of a technical object or technological system together.
A component that provides the linking function is called a linking component. When the link between parts is direct, there is no linking component.
A screw connects a bicycle’s brake pads to the brake caliper. The screw is the linking component.
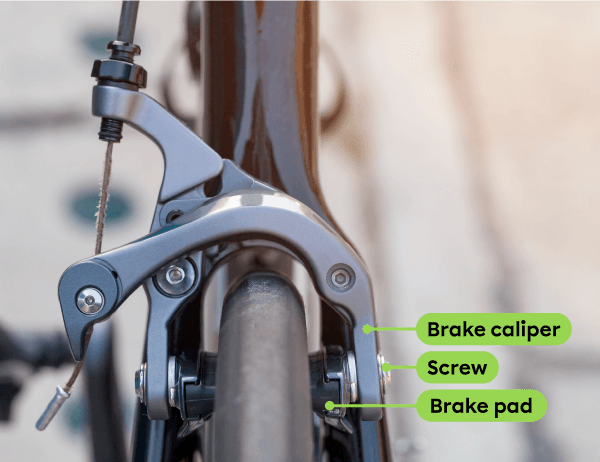
Adapted from SIN1980, Shutterstock.com
Guiding control is the function provided by a component that directs and controls the motion of one or more other components.
The component that fulfills the guiding control function is called the guiding component.
The hub guides the wheel in a rotational motion. The hub is the wheel’s guiding component.
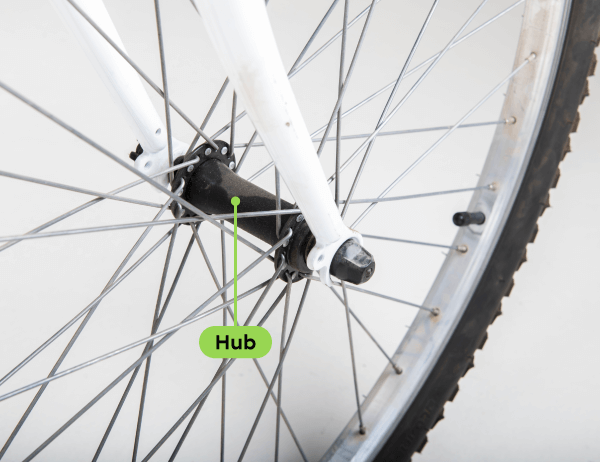

Adapted from vali.lung, Shutterstock.com
The component that ensures the sealing function is called the sealing component.
A valve prevents air from escaping from a bicycle tire. The valve is the sealing component.

Adapted from Pedal to the stock, Shutterstock.com
Lubrication reduces friction between two components.
The component ensuring the lubrication function is called the lubricating component.
Applying oil to a bicycle chain reduces the friction between the components of the chain and sprocket system. Oil is the lubricating component.
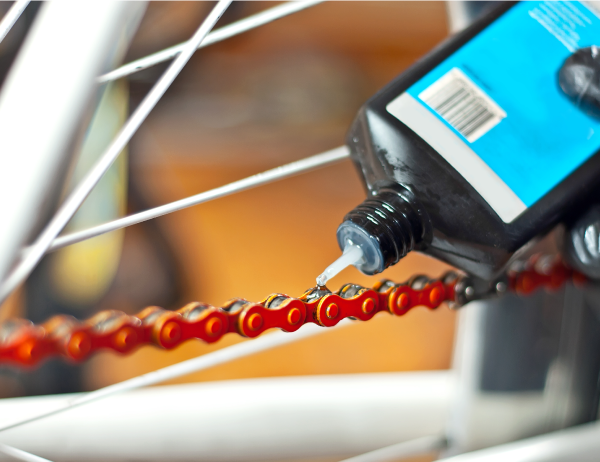

Adapted from Ivan Kovbasniuk, Shutterstock.com
-
A complex mechanical function is the role fulfilled by a single component or a mechanism inside a technological system.
-
A mechanism, often called a system, is a set of components that transmits or transforms motion in a technological system.
In a technological system, there are two groups of complex mechanical functions: motion transmission, with or without a speed change, and motion transformation.
When there is motion transmission, the type of motion between the driver and driven components of a system is the same.
Usually during motion transmission, a rotating driver component causes the driven component to rotate as well. The rectilinear translational motion of the driver component may also cause the rectilinear translational motion of the driven component.
In a bicycle, when the crankset rotates, it drives the rear sprocket to rotate too. It is a chain and sprocket motion transmission system.
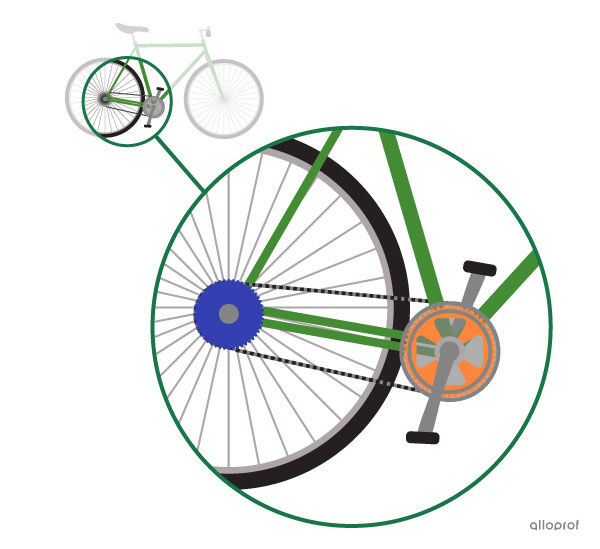
Speed Change During Motion Transmission
A speed change is a variation between the rotational speed of the driver component and the rotational speed of the driven component in a system.
In a bicycle, the chain and sprocket system can transmit a rotational motion with a speed change.
The speed change allows the rider to rotate the bicycle’s rear wheel with varying degrees of difficulty. The number of teeth in the wheel gears determines the gear ratio.
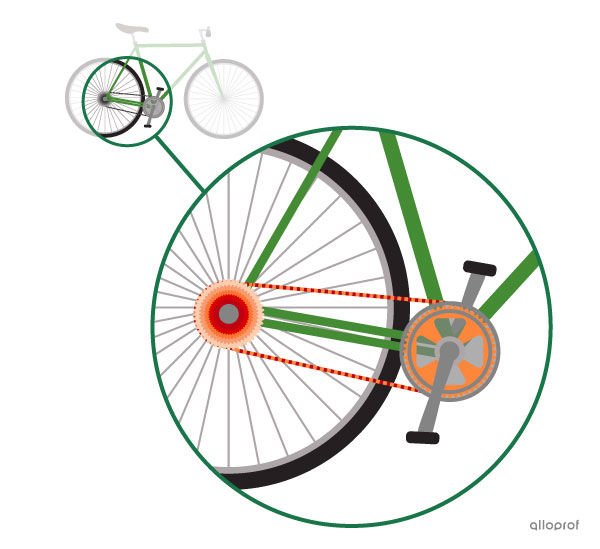
When there is motion transformation, the type of motion between the driver component and driven component of a system changes.
During motion transformation in a system, the rotational motion of the driver component can cause the rectilinear translational motion of the driven component. The opposite is also possible. The rectilinear translational motion of the driver component can cause the rotational motion of the driven component.
In an adjustable wrench, when the worm rotates, it drives the rectilinear translation of the mobile jaw. It is a worm and rack motion transformation system.
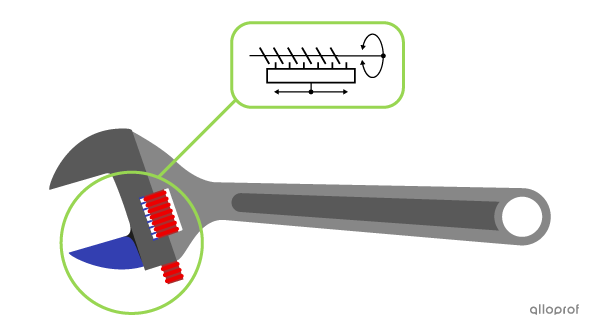
There are three different complex mechanical functions fulfilled by components in a technological system.
A technological system always has a driver and a driven component. There may also be zero, one or multiple intermediate components.
The driver component, also called the driving unit, transmits the motion generated by an external force to another component in order to enable the operation of the technological system.
The pedals act as the driver component. They transmit the motion generated by the driving torque from the cyclist’s legs to the rear wheel.
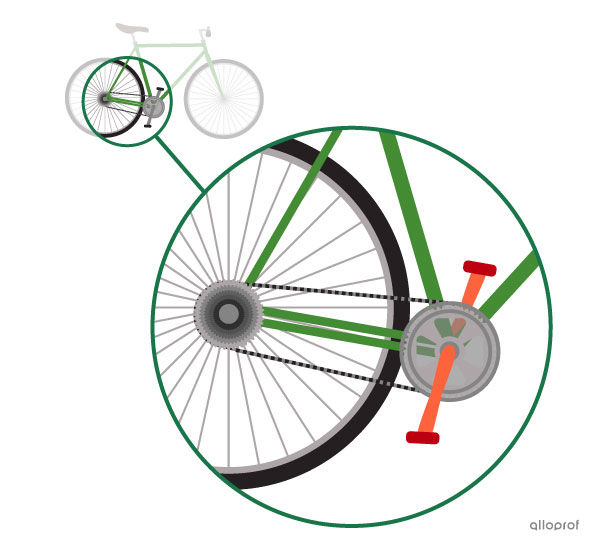
The intermediate component is located between the driver and driven components and sets the driven component in motion.
A chain and sprocket system acts as an intermediate component. It transmits the motion from the pedals (driver component) to the rear wheel (driven component).
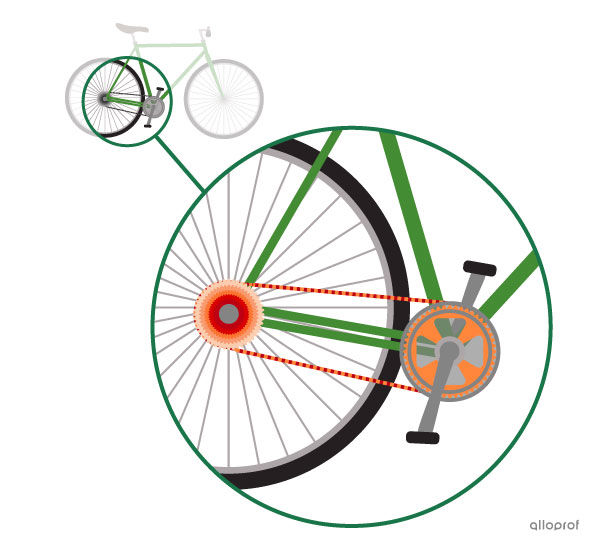
After a series of transmissions or transformations of the motion from the driver and/or intermediate component(s), the driven component, also called the receiving unit, receives the final motion.
Generally, the motion of the driven component is closely related to the overall function of its technological system.
The driving torque exerted by feet pushing on the pedals (driver component) causes the crankset to rotate. This rotation is transmitted to the rear wheel (driven component) by a chain and sprocket system (intermediate component).