The equivalent resistance, or total resistance, is the value of the resistance that would replace all the resistances in a circuit with a single resistance.
To determine the equivalent resistance of an electrical circuit, Kirchhoff's laws and Ohm's law must be used.
In a series circuit, the voltage values add up to give the total voltage:
||V_{tot} = V_{1} + V_{2} + V_{3} + ...|| Using Ohm's law, it is possible to substitute the voltage |(V)| with |RI| .
||R_{tot}I_{tot}= R_{1}I_{1} + R_{2}I_{2} + R_{3}I_{3} + ...|| In a series circuit, the current intensity is always the same. By eliminating the current intensity in each of the terms, we obtain the formula that can be used to calculate the equivalent resistance in a series circuit.
The formula to use to calculate the equivalent resistance in an electrical circuit is:
|R_{eq} = R_{1} + R_{2} + R_{3} + ...|
The equivalent resistance in a series circuit is therefore equivalent to the sum of the resistances in the circuit.
What is the equivalent resistance in the following circuit?
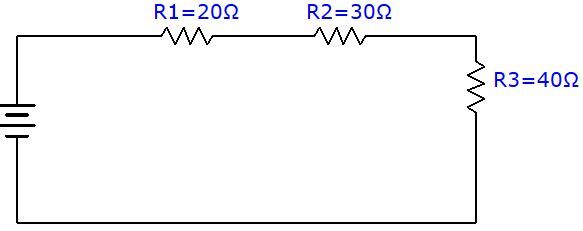
To determine the equivalent resistance, simply use the formula and replace the variables with the known values.
||\begin{align} R_{eq}= R_{1} + R_{2} + R_{3} \quad \Rightarrow \quad R_{eq}&= 20 \:\Omega+30\:\Omega+40\:\Omega \\&= 90 \:\Omega \end{align}||
What is the value, in ohms, of the third resistance in the following circuit?
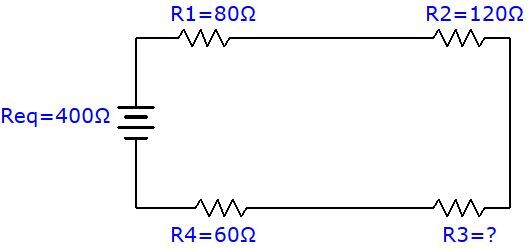
To determine the missing resistance, use the equivalent resistance formula and isolate the missing variable to find the answer.
||\begin{align} R_{eq}= R_{1} + R_{2} + R_{3} + R_{4} \quad \Rightarrow \quad R_{3} &= R_{eq} - R_{1} - R_{2} - R_{4} \\ &= 400 \: \Omega - 80 \: \Omega - 120 \: \Omega - 60 \:\Omega \\ &= 140 \:\Omega \end{align}||
In a parallel circuit, the current values add up to give the total current in the electrical circuit:
||I_{tot} = I_{1} + I_{2} + I_{3} + ...|| Using Ohm's law, it is possible to substitute the intensity |(I)| with |\dfrac {V}{R}| .
||\displaystyle \frac {V_{tot}}{R_{tot}}= \frac {V_{1}}{R_{1}} + \frac {V_{2}}{R_{2}} + \frac {V_{3}}{R_{3}} + ...|| In a parallel circuit, the voltage is always the same. By eliminating the voltage in each of the terms, we obtain the formula which allows us to calculate the equivalent resistance in a parallel circuit.
The formula to use to calculate the equivalent resistance in an electrical circuit is:
|\displaystyle \frac {1}{R_{eq}} = \frac {1}{R_{1}} + \frac {1}{R_{2}} + \frac {1}{R_{3}} + ...|
It can be deduced from this formula that the equivalent resistance of a circuit will decrease each time a resistor is added in a parallel circuit.
The value of the equivalent resistance in a parallel circuit will always be smaller than the value of the lowest resistance of the electrical circuit.
What is the value of the equivalent resistance in the following parallel circuit?
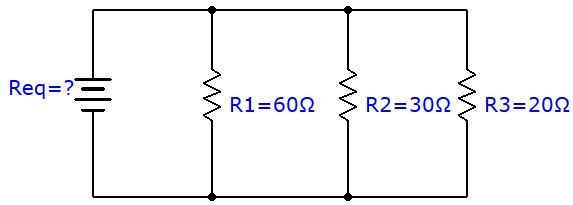
To determine the equivalent resistance, simply use the formula and replace the variables with the known values.
||\begin {align} \dfrac {1} {R_ {eq}} = \dfrac {1} {R_ {1}} + \dfrac {1} {R_ {2}} + \dfrac {1} {R_ {3 }} \quad \rightarrow \quad \dfrac {1} {R_ {eq}} & = \dfrac {1} {60 \: \Omega} + \dfrac {1} {30 \: \Omega} + \dfrac { 1} {20 \: \Omega} \\\dfrac {1} {R_ {eq}} & = \dfrac {6} {60 \: \Omega} \\r_ {eq} & = 10 \: \Omega \end {align} ||
As it was mentioned before, the equivalent resistance is smaller than the smallest resistance in this circuit |(10 \space \Omega < 20 \space \Omega)|.
What should be the value of the resistance |R_{1}| so that the equivalent resistance of this parallel circuit is equal to |\small 150 \space \Omega| ?
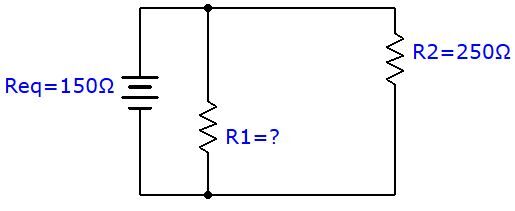
To determine the missing resistance, the equivalent resistance formula must be used and the missing variable isolated to find the answer.
||\begin{align} \frac{1}{R_{eq}}= \frac{1}{R_{1}}+\frac{1}{R_{2}} \quad \Rightarrow \quad \frac{1}{R_{1}} &= \frac{1}{R_{eq}}-\frac{1}{R_{2}} \\\frac{1}{R_{1}} &= \frac{1}{150 \: \Omega}-\frac{1}{250 \: \Omega} \\ \frac{1}{R_{1}}&= \frac{4}{1\:500 \: \Omega} \\ R_{1} &= 375 \:\Omega \end{align} ||
Pour valider ta compréhension à propos des calculs dans les circuits électriques de façon interactive, consulte la MiniRécup suivante :
