Ohm's law relates the potential difference, resistance and current intensity in an electrical circuit.
|V=RI|
where
|V:| potential difference in volts |\text{(V)}|
|R:| resistance in ohms |(\Omega)|
|I:| electric current intensity in amperes |\text{(A)}|
From the previous formula, we can establish the following three relationships.
-
If |R| is constant and |I| increases, then |V| increases.
-
If |I| is constant and |R| increases, then |V| increases.
-
If |V| is constant and |R| increases, then |I| decreases.
Here is a graph of the potential difference as a function of current intensity.
Move the sliders to change the current intensity or the resistance.
In the previous graph, we can see that:
-
when the current intensity increases, the potential difference increases proportionally;
-
the rate of change (slope) corresponds to the resistance;
-
the higher the resistance, the steeper the slope.
In the lab, we have an electrical circuit consisting of a power supply and a light bulb.
We add an ammeter connected in series and a voltmeter connected in parallel with the light bulb.
The ammeter measures a current intensity of |250\ \text{mA}.| The voltmeter measures a potential difference of |6.50\ \text{V}.|
What is the resistance of the light bulb?
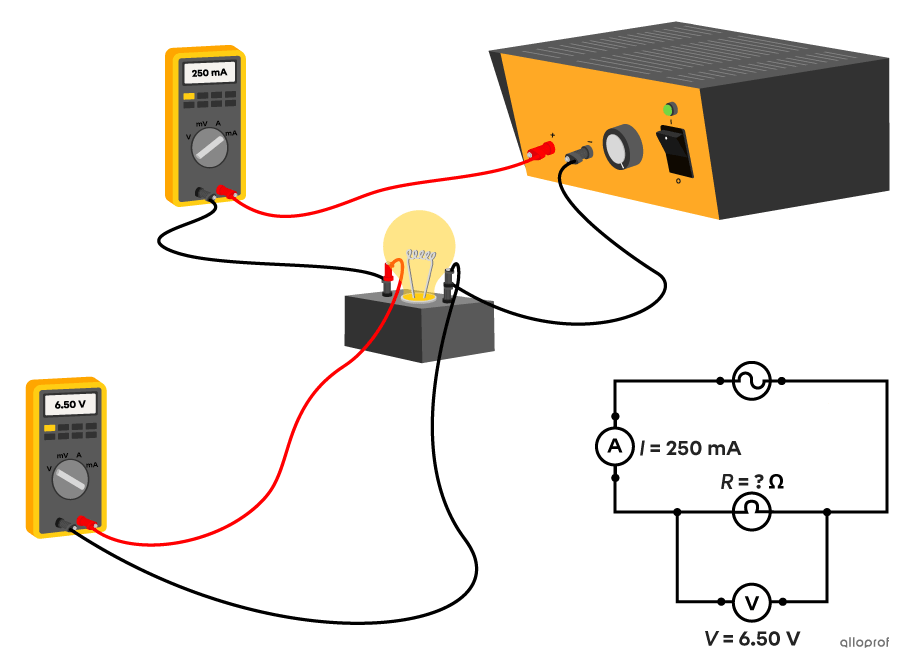
- Identify the given values.
||\begin{align} I&=250\ \cancel{\text{mA}}\times\ \dfrac{1\ \text{A}}{1\ 000\ \cancel{\text{mA}}}&=0.250\ \text{A}\\V&=6.50\ \text{V}\\R&=\text{?}\ \Omega\end{align}|| - Choose the formula and isolate |R.|
||\begin{align}V&=R\ \times \ I\\\\\dfrac{V}{I}&=\dfrac{R\ \times \ \cancel{I}}{\cancel{I}}\\\\\dfrac{V}{I}&=R\end {align}|| - Plug in the given values and calculate.
||\begin{align}R&=\dfrac{6.50\ \text{V}}{0.250\ \text{A}}\\\\R&=26.0\ \Omega \end{align}|| - Answer the question.
The resistance of the light bulb is |26.0\ \Omega.|
The electrical circuit of a remote control toy has a resistance of |120\ \Omega.| If it is designed for an electrical current intensity of |0.05\ \text{A},| what potential difference must the toy's battery provide?
-
Identify the given values.
||\begin{align} R&=120\ \Omega\\I&=0.05\ \text{A}\\
V&=\text{?}\ \text{V} \end{align}|| -
Choose the formula.
||V=R\times I|| -
Plug in the given values and calculate.
||\begin{align}V&=120\ \Omega\times0.05\ \text{A}\\
V&=6.00\ \text{V}\end{align}|| -
Answer the question.
The battery must provide a potential difference of |6.00\ \text{V}| to enable the toy to work.
A smartphone uses a |3.7\ \text{V}| battery. If the internal circuit resistance is |18.5\ \Omega,| what is the current intensity in milliampere |(\text{mA})| flowing through the circuit?
-
Identify the given values.
||\begin{align} V&=3.7\ \text{V}\\R&=18.5\ \Omega\\I&=\text{?}\ \text{mA} \end{align}|| -
Choose the formula and isolate |I.|
||\begin{align}V&=R\times I\\\dfrac{V}{R}&=\dfrac{\cancel{R}\times I}{\cancel{R}}\\\\\dfrac{V}{R}&=I\end{align}|| -
Plug in the given values and calculate.
||\begin{align}I&=\dfrac{3.7\ \text{V}}{18.5\ \Omega}\\\\I&=0.20\ \text{A}\end{align}|| -
Convert the |\text{A}| to |\text{mA}.|
||I=0.20\ \cancel{\text{A}}\times\dfrac{1000\ \text{mA}}{1\ \cancel{\text{A}}}=200\ \text{mA}|| -
Answer the question.
The current intensity flowing through the smartphone circuit is |200\ \text{mA}| or |2.0 \times \ 10^{2}\ \text{mA}.|
Pour valider ta compréhension à propos de l'électricité de façon interactive, consulte la MiniRécup suivante :

Pour valider ta compréhension à propos des calculs dans les circuits électriques de façon interactive, consulte la MiniRécup suivante :
