Pregnancy is carrying one or more children in the uterus.
Pregnancy follows fertilization. The baby-to-be passes through multiple stages of development, including the zygote, the embryo, and the fetus. Birth occurs at the end of pregnancy.
In this concept sheet, the term mother is used to describe the person who contributed the female gamete during fertilization and who carries the baby-to-be.
Once fertilization occurs, pregnancy lasts an average of 38 weeks, which is just under 9 months. This period is often separated into 3 trimesters which are characterized by the key moments in the baby’s development.
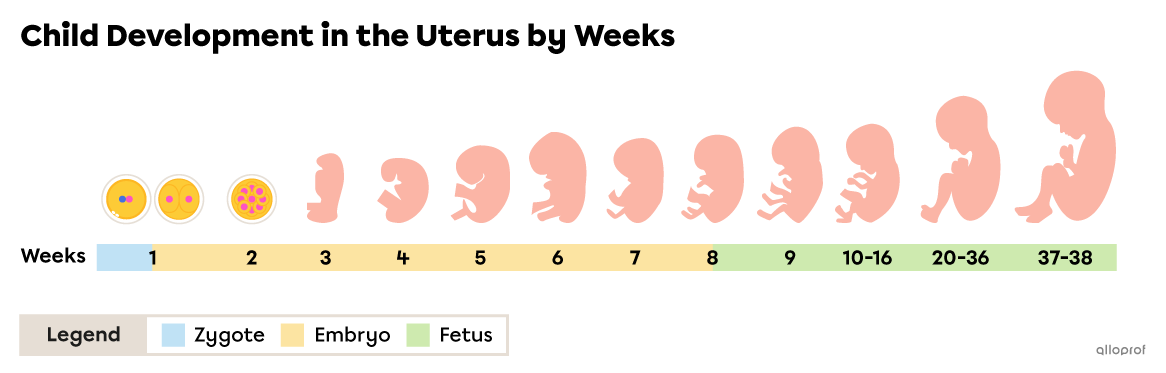
Weeks 1 to 12 of pregnancy correspond to the first trimester. During the first trimester:
-
the fertilized ovum (zygote) becomes a fetus approximately 9 cm long;
-
the amniotic sac and the placenta develop;
-
the organs start developing;
-
fingers and toes form;
-
the fetus starts moving.
Weeks 13 to 26 of pregnancy correspond to the second trimester. During the second trimester:
-
the fetus grows on average from 9 cm to 30 cm long;
-
the nervous system and the skeleton start developing;
-
hair and nails start growing;
-
the senses develop and sharpen.
Weeks 27 to 38 of pregnancy correspond to the third trimester. During the third trimester:
-
the fetus grows on average from 30 cm to 50 cm long;
-
all the organs are functional;
-
many bones harden;
-
the fetus settles in position for birth.
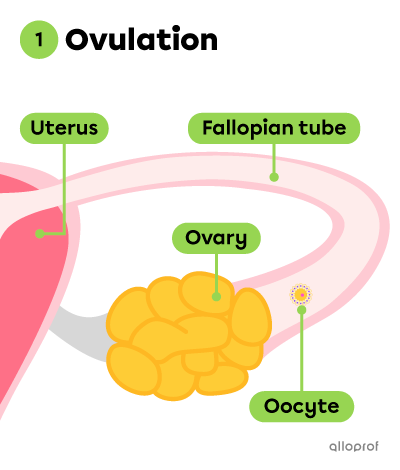
Fertilization occurs before pregnancy. This process takes place in one of the Fallopian tubes.
-
Fertilization is the union of two gametes: a male gamete, or a spermatozoon, and a female gamete, or an ovum.
-
The zygote is a single cell that forms as a result of fertilization.
The following images summarize the stages leading to the formation of a zygote.
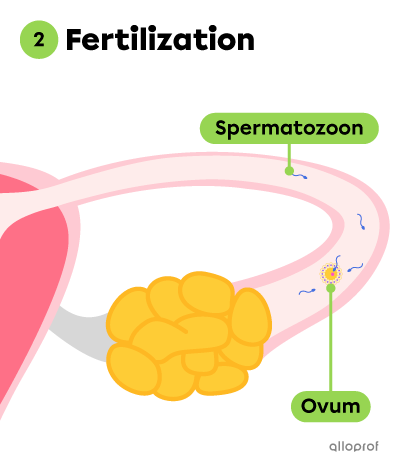
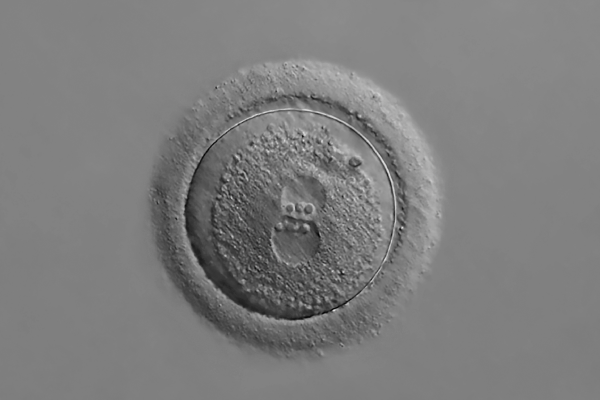
During fertilization, a spermatozoon enters an oocyte, which becomes an ovum.
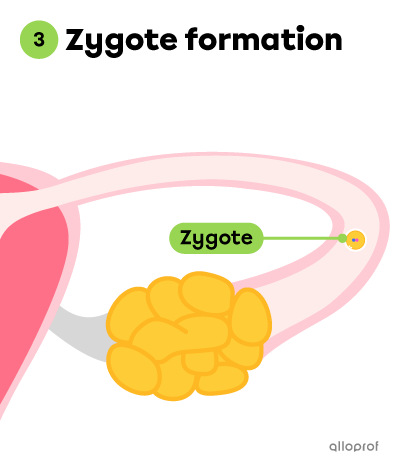
Once fertilized, the ovum becomes a zygote.
The ovum (a female gamete) and the spermatozoon (a male gamete) are reproductive cells produced during meiosis. Therefore, each gamete contains half of the genetic material. The union of a developing ovum and a spermatozoon during fertilization leads to the formation of a single cell (zygote) with a nucleus containing a complete set of genetic material. This set of genes predetermines many of the child’s characteristics, such as their eye and hair colour, as well as the presence or absence of genetic disorders.
Vladimir Staykov, Shutterstock.com
Not all unprotected sexual intercourse leads to pregnancy. In fact, intercourse has to take place during the fertile period of the menstrual cycle (around ovulation) for fertilization to happen and for the zygote to form.
In the previous section, natural conception is discussed: this means that fertilization occurs naturally as a result of sexual intercourse. If fertilization cannot happen naturally, medically assisted reproduction offers various procedures to make fertilization possible.
For instance, in vitro fertilization (IVF) is a procedure that is performed in a laboratory. Two to six days after IVF, an embryo is implanted in the uterus where it will continue developing. Often, multiple embryos are implanted at the same time to increase the chances of pregnancy.
The definition of the term embryo varies according to different sources. Some textbooks state that the cells can be categorized as an embryo 24 hours after fertilization, while others label the embryo 7 days after fertilization. Here, the embryo is defined from the moment the zygote undergoes the first round of cell division (i.e., 24 hours after fertilization).
In the previous section, the stages (Stages 1 to 3) required for the formation of the zygote are illustrated. The embryonic stage takes place after the three stages.
The following images show how an embryo forms and makes its way into the uterus (Stages 4 to 6).
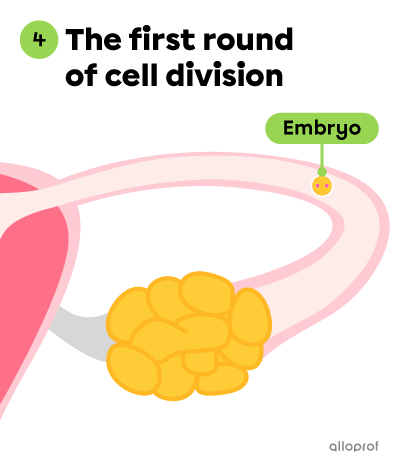
Approximately 24 hours after the zygote is formed, it divides into two identical cells. The cellular mass is called an embryo.
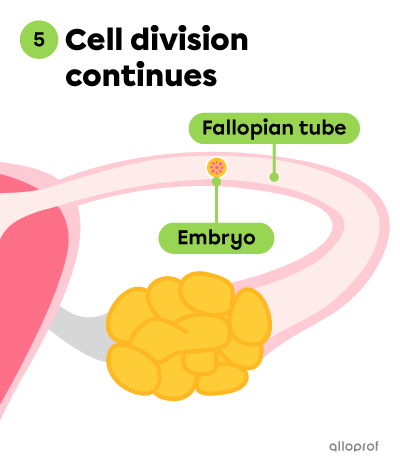
The cell division continues and the embryo is moving through the Fallopian tube. It reaches the uterus around 3 days after fertilization. At this point, the embryo is made up of approximately 100 cells.
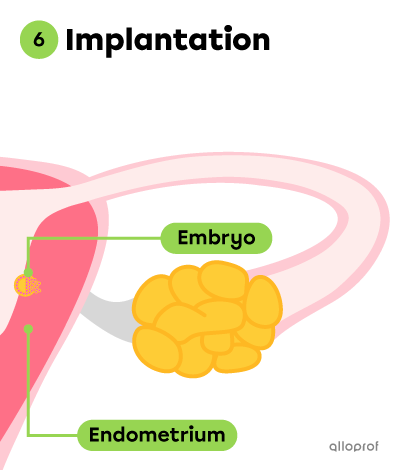
Around Day 7, the embryo attaches to the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus. This is called implantation.
The endometrium contains many blood vessels, which are responsible for delivering nutrients, water, and oxygen to the embryo. This allows the embryo to grow and develop.
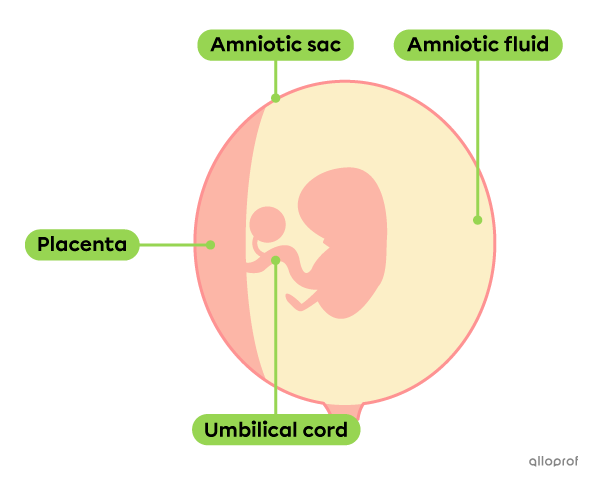
From the moment of implantation, the amniotic sac and the placenta start forming. However, they become completely functional only after 3 months.
The amniotic sac is a pouch filled with amniotic fluid, a liquid protecting the embryo by cushioning sudden movements.
The placenta is an organ containing many blood vessels that is connected to the baby by the umbilical cord. The placenta allows exchanges between the mother’s blood and the embryo’s (later fetus’) blood. It ensures gas exchanges and the supply of nutrients, while allowing the removal of waste from the embryo.
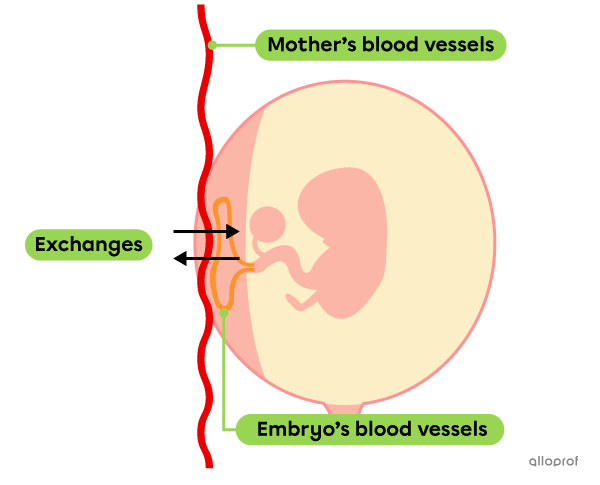
During pregnancy, the mother has to take care of her health, because everything she ingests is shared with the baby. Both the nutrients and toxins consumed by the mother are directly transmitted to the baby’s blood.
Towards the end of the 8th week of pregnancy, the organs of the baby-to-be are not yet fully developed. However, most organs are already in place. The embryo has reached a more advanced stage of development: it is now a fetus. As the weeks pass, the heart, brain, and other organs become more complex. The fingers, nose and mouth mature and become better defined.
Around the 24th week, the fetus measures about thirty centimeters and most of the organs are functional.
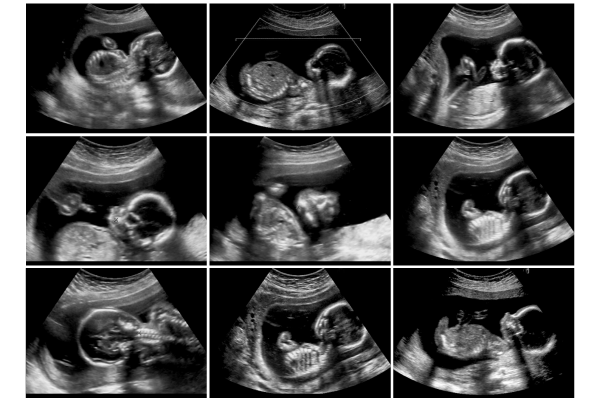
Many tests can be performed to assess how the fetus is developing. For example, ultrasound scans are scheduled throughout the entire pregnancy.
This technique uses ultrasound to create an image, or a sonogram. The size of the fetus, their sex and the overall anatomic development are determined with this procedure. It is also used to examine the heartbeat of the fetus, its position in the uterus, etc. The information helps determine if the fetus is developing normally and if it is healthy.
GagliardiPhotography, Shutterstock.com
Childbirth occurs at the end of pregnancy. It usually happens between the 38th and the 40th week. If it happens earlier, the baby is called premature.
Towards the end of pregnancy, contractions caused by the increase in the size of the uterus and release of certain hormones trigger the onset of labour. Labour is the series of events that take place during the different stages of childbirth. The stages include dilation, birth, and delivery. The duration of childbirth varies case-by-case.
Before childbirth, the uterine cervix is closed, which keeps the baby safely inside the uterus.
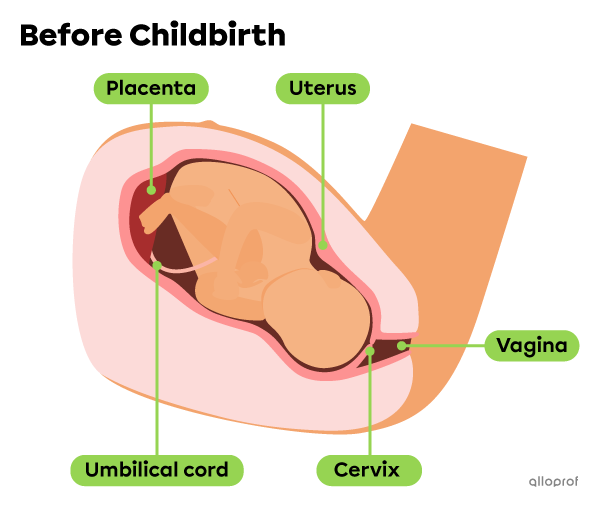
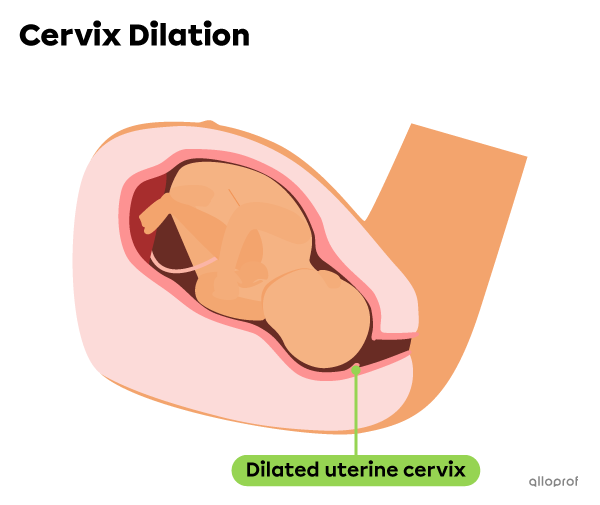
The first stage of childbirth is dilation. During this stage, the contractions of the uterus push the baby against the cervix, which gradually dilates, or opens. Usually, the pressure exerted on the amniotic sac causes it to tear, and the amniotic fluid leaks out. This is commonly referred to as the water breaking.
During dilation, the intensity and frequency of contractions gradually increase. The dilation ends when the opening of the cervix is about 10 cm wide. This stage can last an average of 6 to 12 hours.
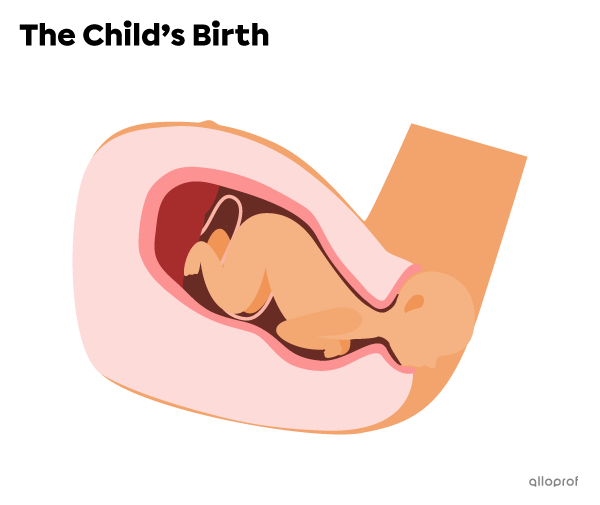
The next stage is birth. Once the dilation is complete, the frequency and intensity of the contractions increase and pushing is necessary to birth the child. This stage is over once the child is completely out of the uterus and vagina. This stage can last anywhere from 20 minutes to 2 hours.
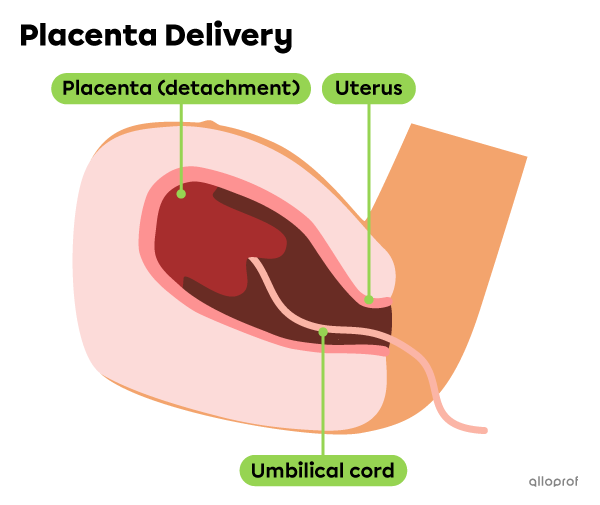
The third and final stage of childbirth is the delivery. Once the child is born, the contractions of the uterus continue until the placenta and the rest of the umbilical cord is delivered. This phase generally lasts about 30 minutes.
Generally, it is preferable for a birth to take place vaginally, as presented above. However, if the health of the mother or the baby is at risk, a Cesarean section (often called a c-section) can be performed. During a c-section, an incision is made in the mother's abdomen and uterus to remove the baby.