A gamete is a reproductive cell, which is a cell that allows reproduction.
In sexually reproducing species, each gamete contains half of the complete genetic makeup. During fertilization, a male gamete and a female gamete unite to form a new cell, called a zygote. The zygote contains the complete genetic makeup, which allows it to develop into a new individual.
In some species that reproduce asexually, reproduction may take place with gametes. The gametes produced this way already contain 100% of the genetic makeup necessary for the development of an individual. Fertilization is not necessary and the resulting individual is therefore a clone of its parent.
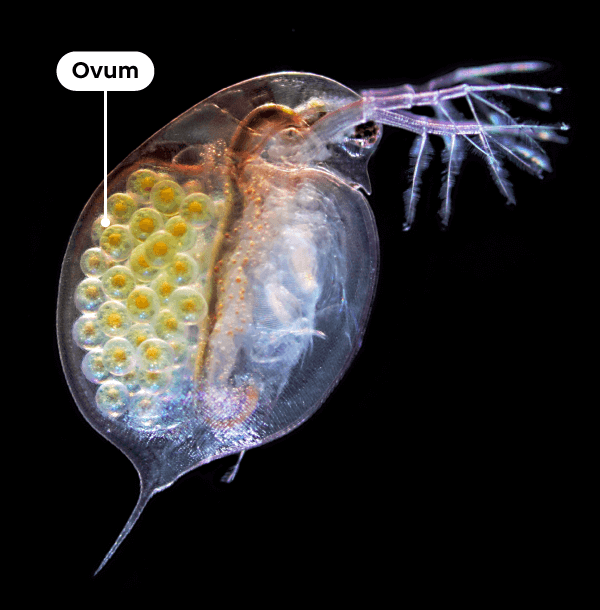
The red daphnia (Daphnia pulex) is a species of water fleas, which are small transparent crustaceans. They are capable of both sexual and asexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction occurs when the conditions are favourable and can support a large population. At that time, daphnia produce only female gametes, called ova, containing a complete genetic makeup. The resulting offspring is a clone of its single parent.
The name of gametes can vary from one species to another.
Flowering plants can reproduce sexually. The male gamete of a flower is called pollen, and its female gamete is called oosphere.

Adapted from Ribeiroantonio, Shutterstock.com
In humans, the male gametes are called spermatozoa, and the female gametes are called ova.
Spermatozoa seen under a microscope
Dimarion, Shutterstock.com
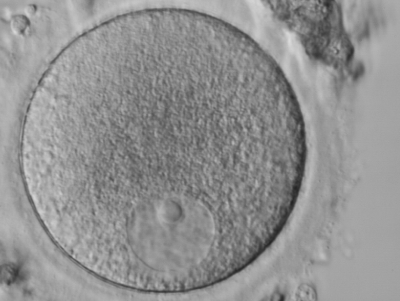
An immature ovum (oocyte) observed under a microscope [Photograph], Atlas of Human Embryology, 2009, (URL).
The characteristics of human gametes are presented below.
An ovum (pl. ova) is a female gamete, or a female reproductive cell.
In humans, ova are produced by the ovaries in a process called oogenesis. When it is released from the ovary, the ovum is not yet mature. This immature ovum is then called an oocyte. The oocyte becomes a full-fledged ovum after being fertilized by a spermatozoon.
The release of oocytes by the ovaries begins at puberty and ends at menopause (last menstruation). Over the course of their lifespan, the ovaries can release a total of about 300 to 400 oocytes.
In humans, on average, an oocyte measures 80 micrometres |(\mu \text{m}),| or |0.08\ \text{mm}| in diameter. It is one of the largest cells in the body!
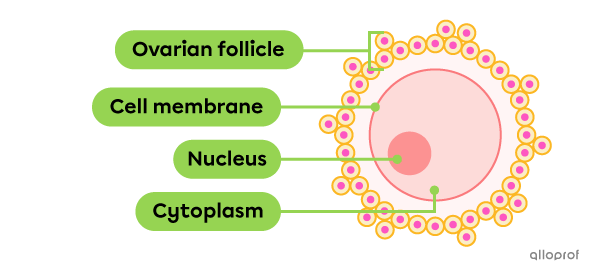
The oocyte is surrounded by an envelope which nourishes it. It is called an ovarian follicle.
The following image represents the ovarian follicle along with the cell membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus of the oocyte.
The nucleus of the oocyte contains half of a complete genetic makeup (23 chromosomes).
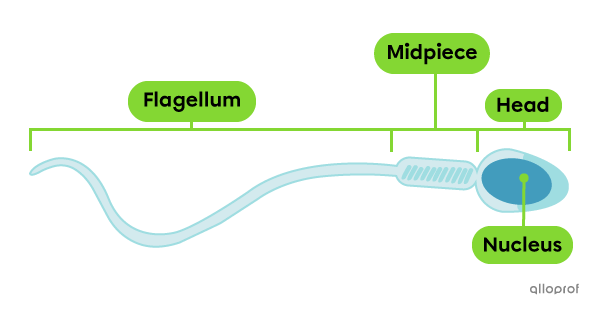
A spermatozoon (pl. spermatozoa) is a male gamete, or a male reproductive cell.
In humans, spermatozoa are produced by the testicles in a process called spermatogenesis.
The testicles start to release spermatozoa at puberty and can continue throughout a man’s life. Every day, the testicles produce a total of about 400 million spermatozoa.
In humans, on average, a spermatozoon is 50 micrometres |(\mu \text{m})| long, which is |0.05\ \text{mm}.|
The structure of spermatozoa is divided into 3 main parts: the head, the midpiece and the flagellum, which allows this cell to move. The nucleus of the cell is located in the head of the spermatozoon and contains half of a complete genetic makeup (23 chromosomes).