-
The characteristic of a variable is a common trait shared by the elements of a set.
-
A qualitative variable takes the form of a word, expression or code (colour, password, spoken language, etc.). It is not a quantitative trait.
-
A quantitative variable takes the form of a number or quantity. Depending on the nature of this number, this variable can be either discrete or continuous.
-
A discrete quantitative variable can only have certain values within a given range. In general, these are quantities that can be counted, meaning they are natural numbers.
-
A continuous quantitative variable can have any value in a given range. These are quantities that are real numbers.
-
Here are some examples of statistical variables that are related to survey questions:
-
What is your favourite colour?
Possible answers: red, blue, green, purple, etc.
The possible answers are colours.
-
What emotion are you feeling right now?
Possible answers: joy, sadness, anger, etc.
The possible answers are emotions.
-
How many siblings do you have?
Possible answers: 0, 1, 2, 3, etc.

The possible answers are numbers of people, which means a positive integer (whole number).
-
How many books do you own?
Possible answers: 0, 1, 5, 20, 50, etc.

The possible answers are numbers of books, so a positive integer (whole number).
-
What is your height?
Possible answers: |1.65\ \text{m},| |2.01\ \text{m},| etc.
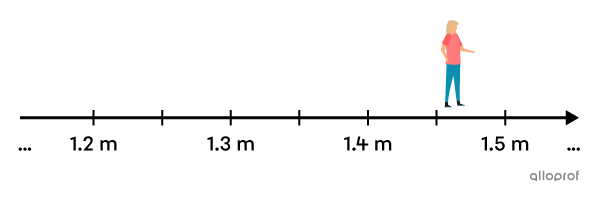
A person's height is a quantity that can be any positive real value (including decimal numbers).
-
How many litres of gas did you put in your car the last time you refueled?
Possible answers: |34.51\ \text{L},| |54.12\ \text{L},| etc.
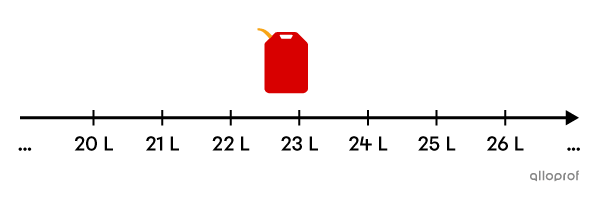
The number of litres of gas is a quantity that can take any positive real value.
-
The difference between discrete and continuous is not always easy to understand. For example, is a person's age a discrete or continuous variable? A person ages continuously, that is, at every moment. Age is therefore a continuous variable. However, when compiling data, it is possible to consider a person's age as a discrete quantitative variable. This is because, when people are asked their age, they answer with a natural number such as |12| years, |25| years or |87| years and not |12.36| years.
-
Just because the data collected is represented by numbers does not mean that the variable's characteristic is necessarily quantitative. For example, if we are looking at the area code of a telephone number, the answers could be |450,| |418,| |514,| and so on. These number combinations do not represent a quantity, but instead represent codes. It is therefore a qualitative variable, not quantitative.