Once measuring and laying out are completed, the machining of materials can begin.
Machining, also called shaping, refers to modifying a material to the desired configuration using tools and machine tools.
During machining, different tools and techniques are used to shape parts according to the manufacturing drawings presented in the manufacturing process sheet.
Machining generally takes place as follows.
-
Roughing
-
Choosing tools and techniques
-
Shaping the material
First, roughing, as the name suggests, involves cutting the material to a rough approximation of the finished part, removing excess material, and keeping only the portion necessary for manufacturing.
Next, the techniques, instruments, and tools are chosen according to the type of material. For example, since metals are generally harder than wood, specific types of drill bits and saw blades are used to work with them.
Finally, shaping the part involves turning the materials into the desired shape.
Many techniques are used to shape material. Here are the ones used most frequently.
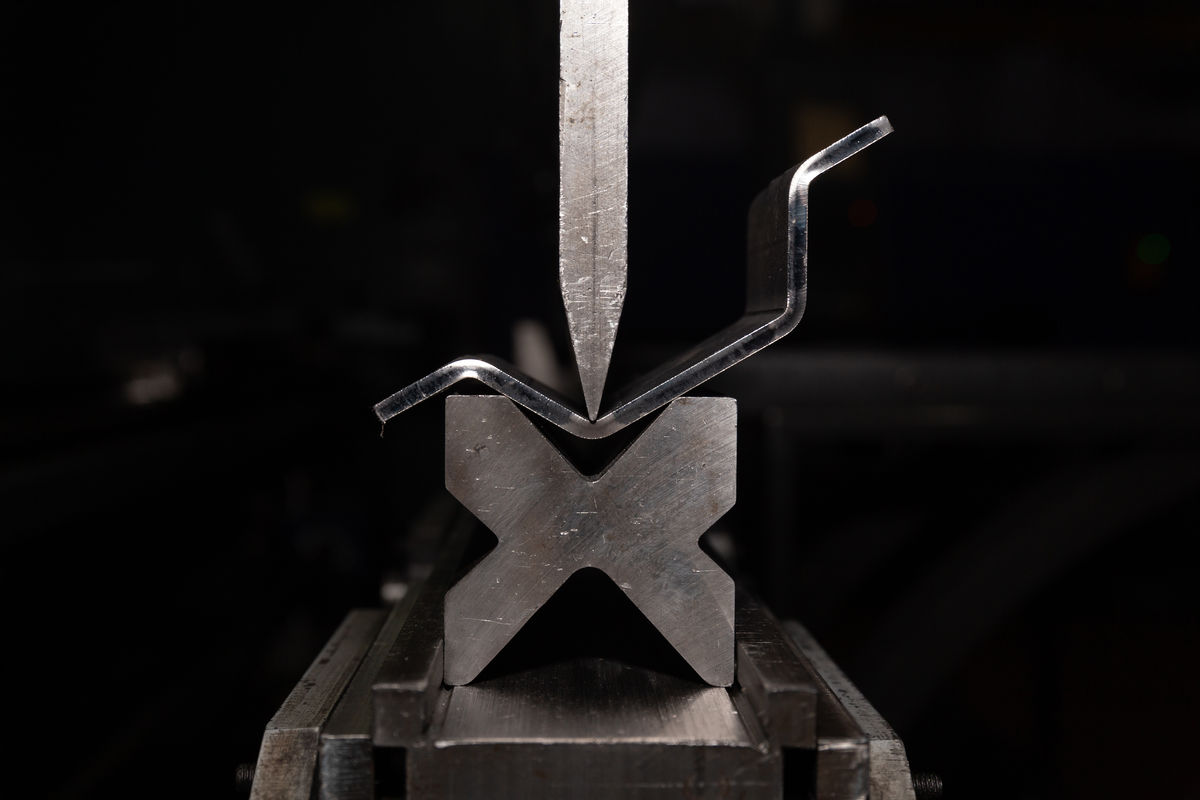
Cambering, sometimes called bending, is a technique where a material is permanently bent, changing its shape.
Materials most susceptible to bending are metals and thermoplastics, because they have good malleability. Cambering causes a plastic deformation of the machined material, because the bend is permanent.
A bending press can be used for cambering. Metal sheets are bent by the pressure exerted between the punch (the upper part of the press) and the die (the lower part of the press), which are V-shaped.

Zhak Yaroslav, Shutterstock.com
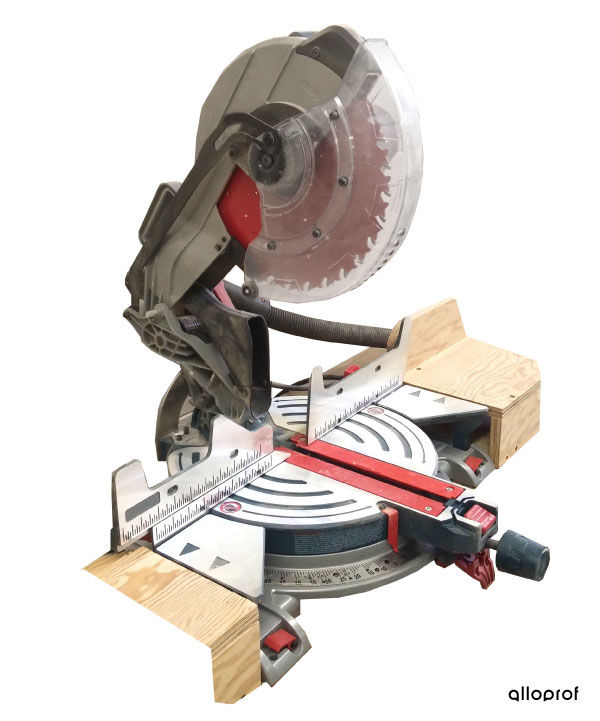
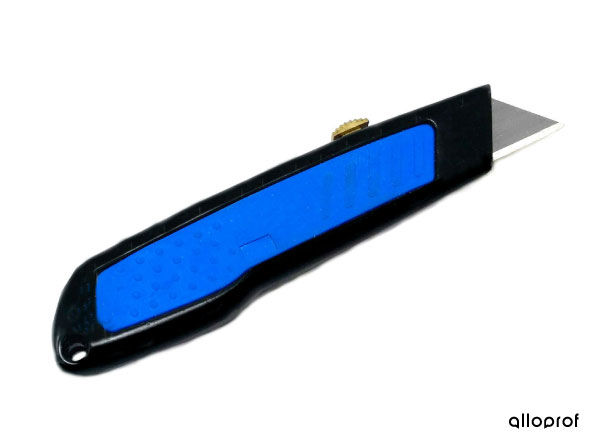
Cutting means to cut a material to the desired shape. When a material is cut using a saw, the technique is called sawing.
There are several tools for cutting parts. Tool selection is based on the nature of the material to be cut and its thickness.
Here are examples of tools and machine tools for cutting.




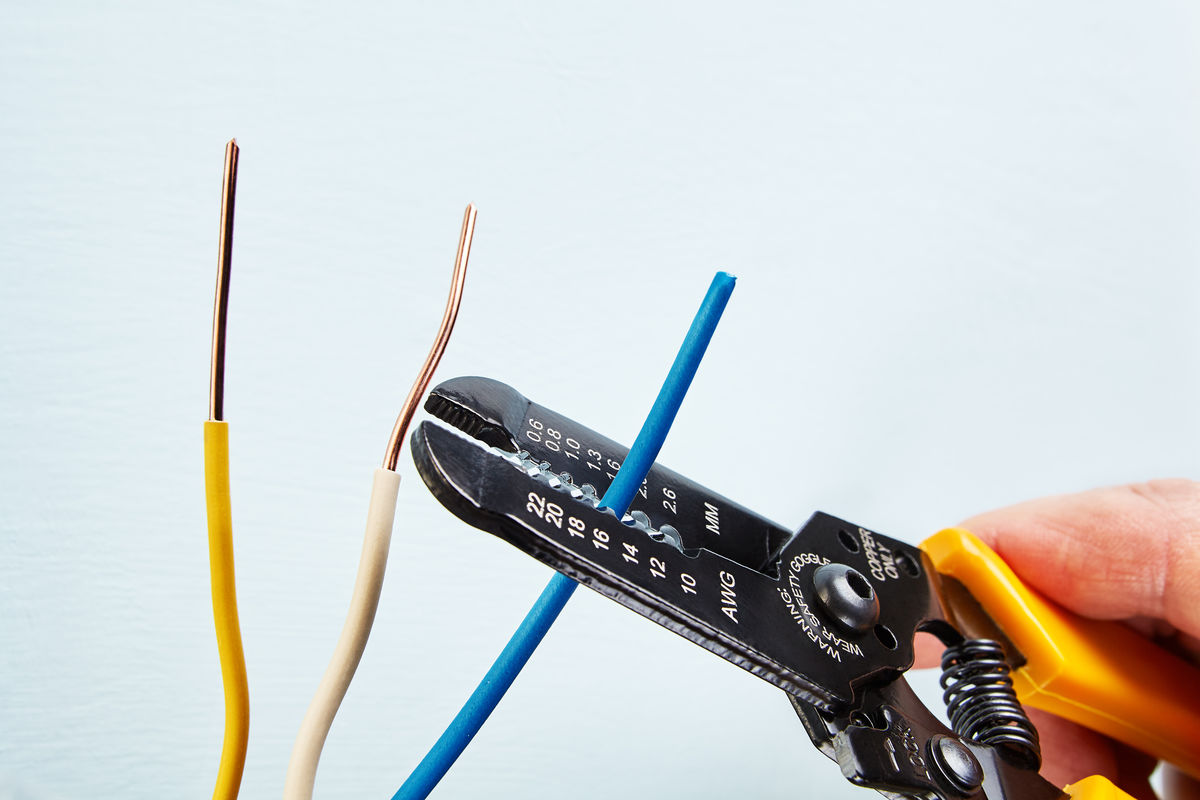
Stripping is a technique for removing the insulating sheath from the end of a conductive wire.
When building an electrical circuit, conductive wires must be connected. For the conductive materials to make contact, the insulating sheath at the end of the wires must be removed first. This technique can be performed using wire strippers.

pokchu, Shutterstock.com
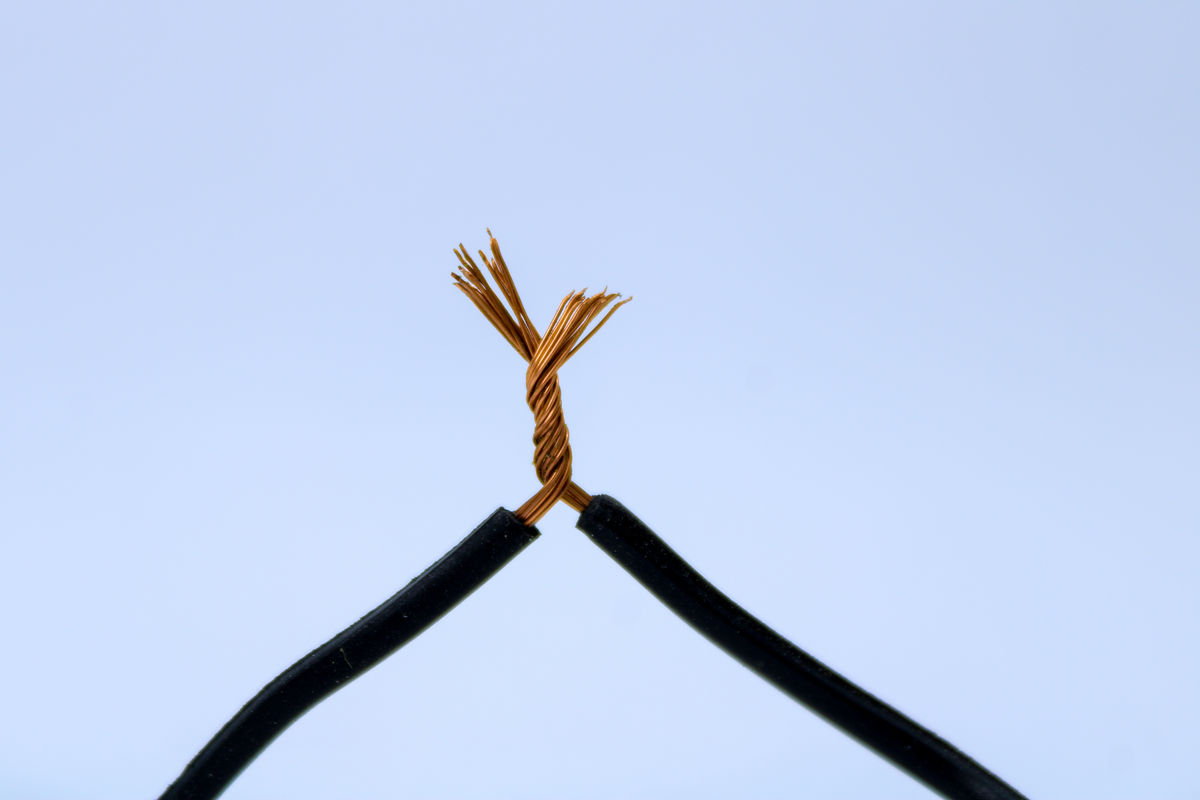
Splicing consists of twisting together the metal strands of two conductive wires to ensure a good connection.
When building an electrical circuit, it is sometimes necessary to join conductive wires. Once the insulating sheath is removed from the ends of the wires, it is important to ensure that the conductive materials are joined. It is done by splicing—twisting the strands of the two wires together to form a helix. It ensures that the two wires stay attached.

David Fadul, Shutterstock.com
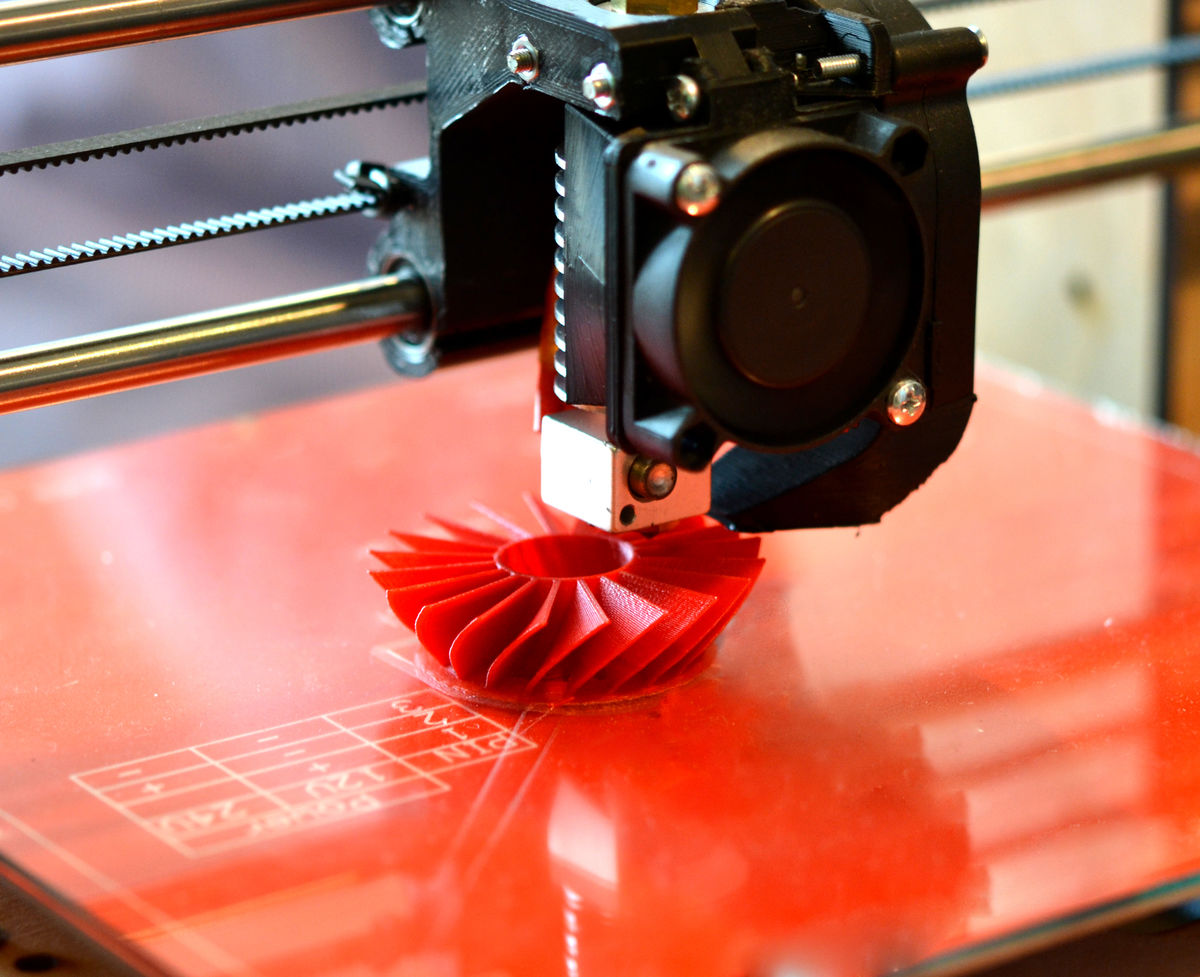
Additive manufacturing is a technique for building a three-dimensional part using a machine tool (3D printer) which controls, using software, the application of successive layers of materials.
Computer-aided design (CAD) software enables a file to be created where the technical object is modelled. The three-dimensional model is then read by the 3D printer which in turn deposits thin layers of plastic to manufacture the desired object.

Marina Grigorivna, Shutterstock.com
Threading is a technique that creates threads in a bar.
Threading is a complementary technique to tapping. Threading creates a helical thread around a cylindrical part. A screw is a common example of an object shaped by threading. The die used must be chosen according to the nature of the material, the size of the bar to be threaded, and the type of thread desired.
Here are examples of some threading tools.
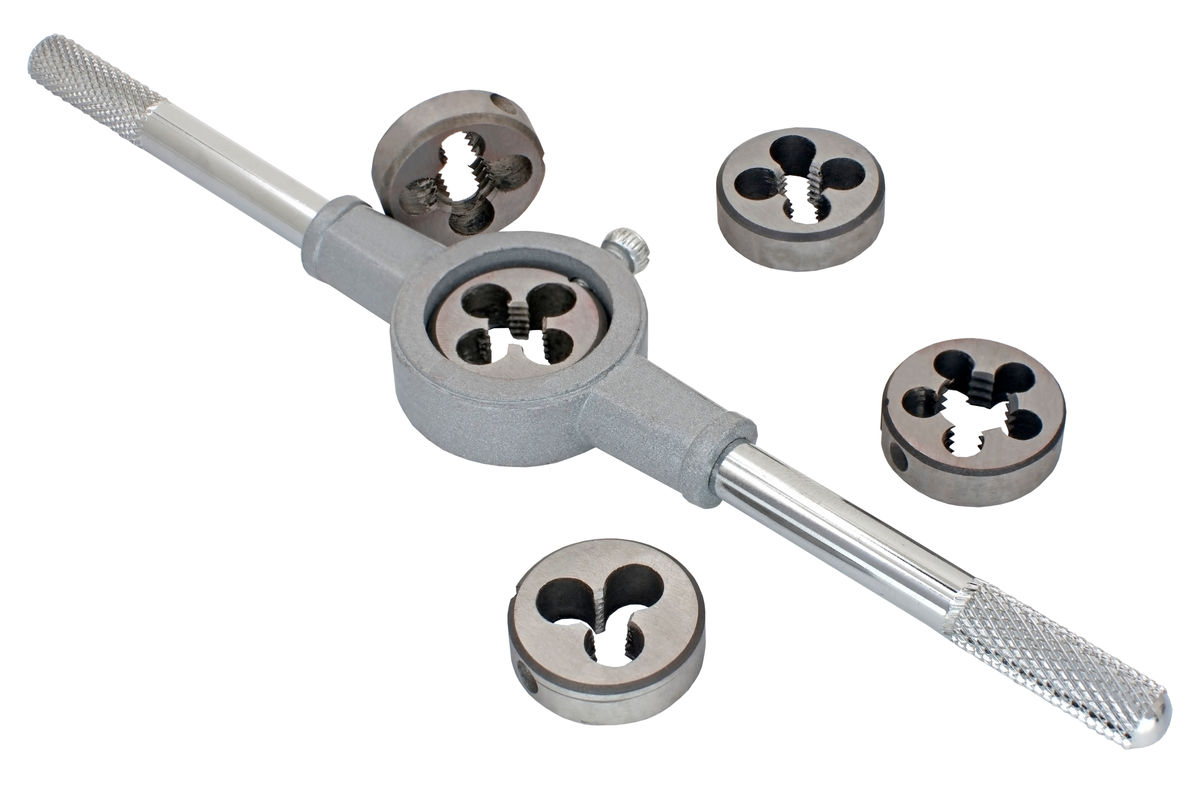

a_v_d, Shutterstock.com
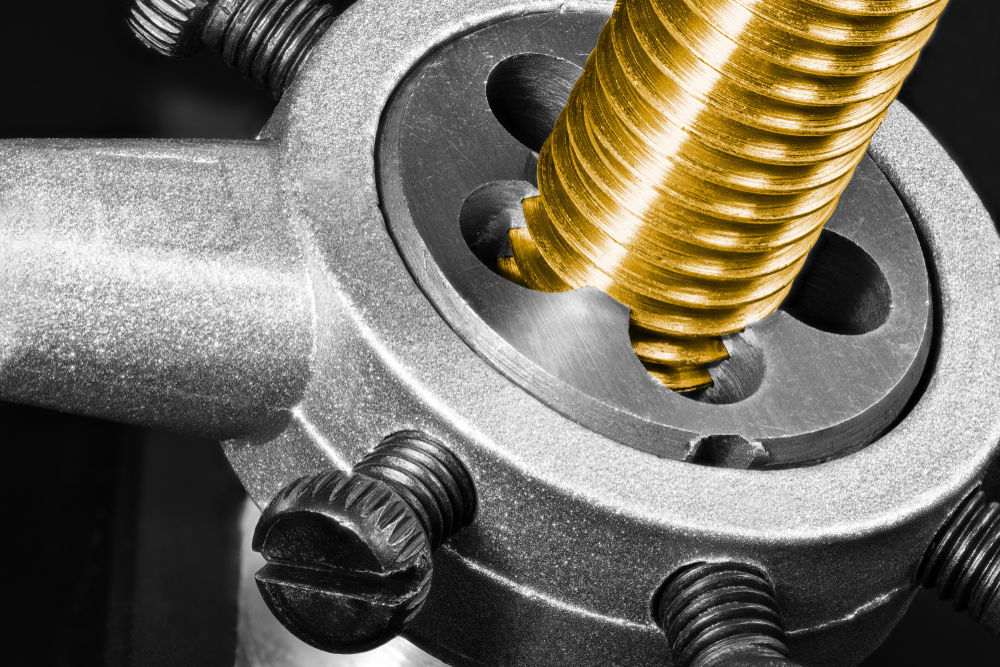

KPixMining, Shutterstock.com
Rolling is a machining technique involving permanently flattening a material by compressing it between two smooth cylinders.
Just like bending, rolling causes plastic deformation of the machined material. In addition, the technique is often used before cambering, because it can produce materials in sheets, making them more malleable for bending.
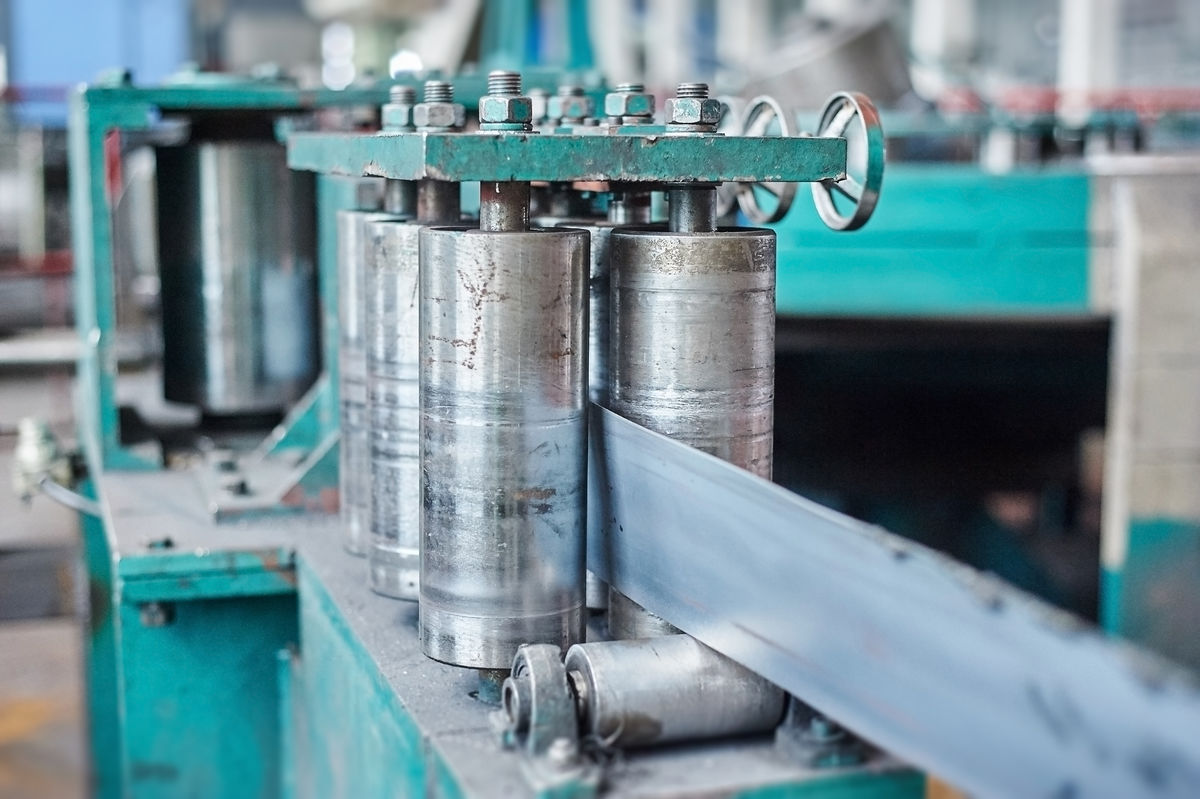

Vdovichenko Denis, Shutterstock.com
Moulding is shaping metal or plastic using a mould and heat.
Moulding occurs when a liquid material is poured into a hollow mould and after solidifying, it is removed. Plastics, glass, and aluminum are materials that are frequently shaped by moulding to produce an object.
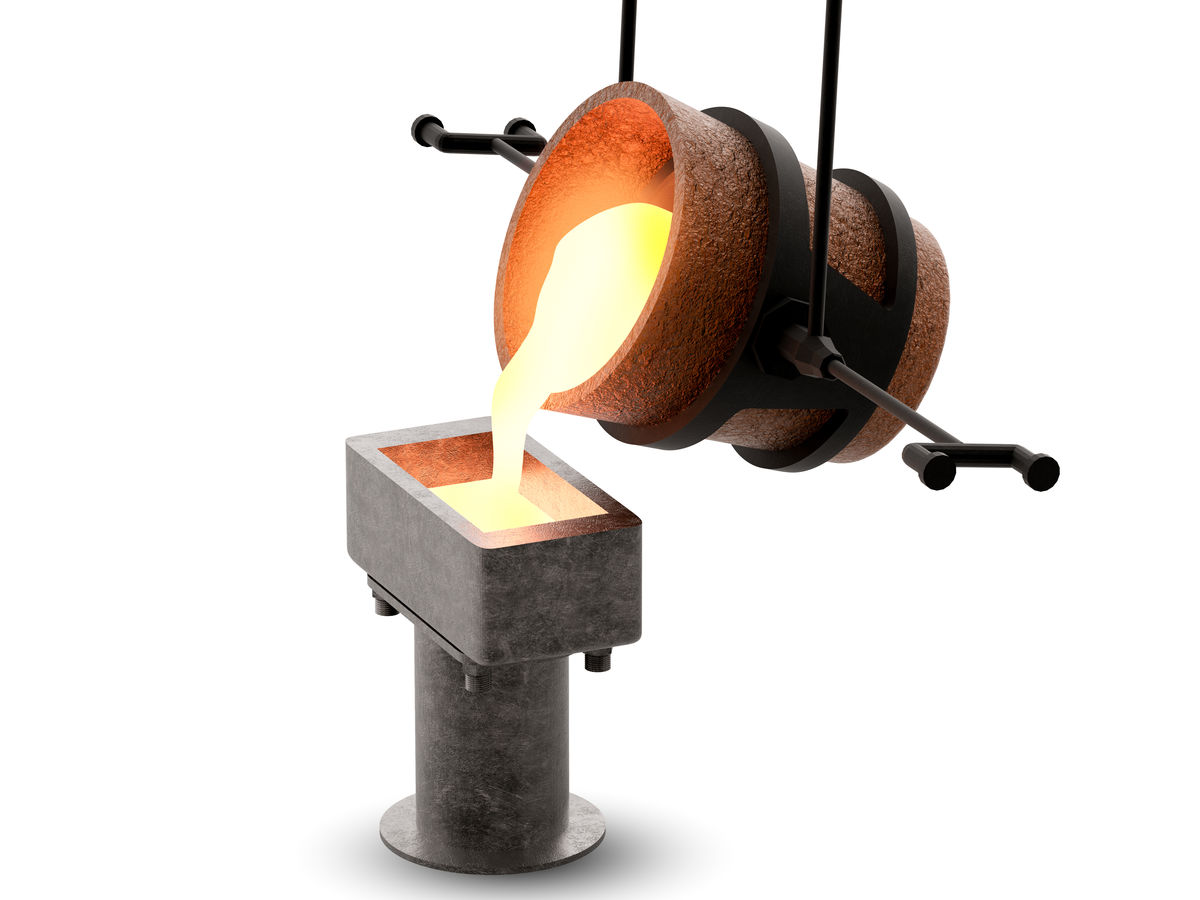

Shestakov Dmytro, Shutterstotck.com
Injection blow moulding involves pouring a material into a sealed mould. Air is then injected into the mould, pushing the material towards the walls of the mould.
This technique enables hollow parts such as plastic bottles to be manufactured.
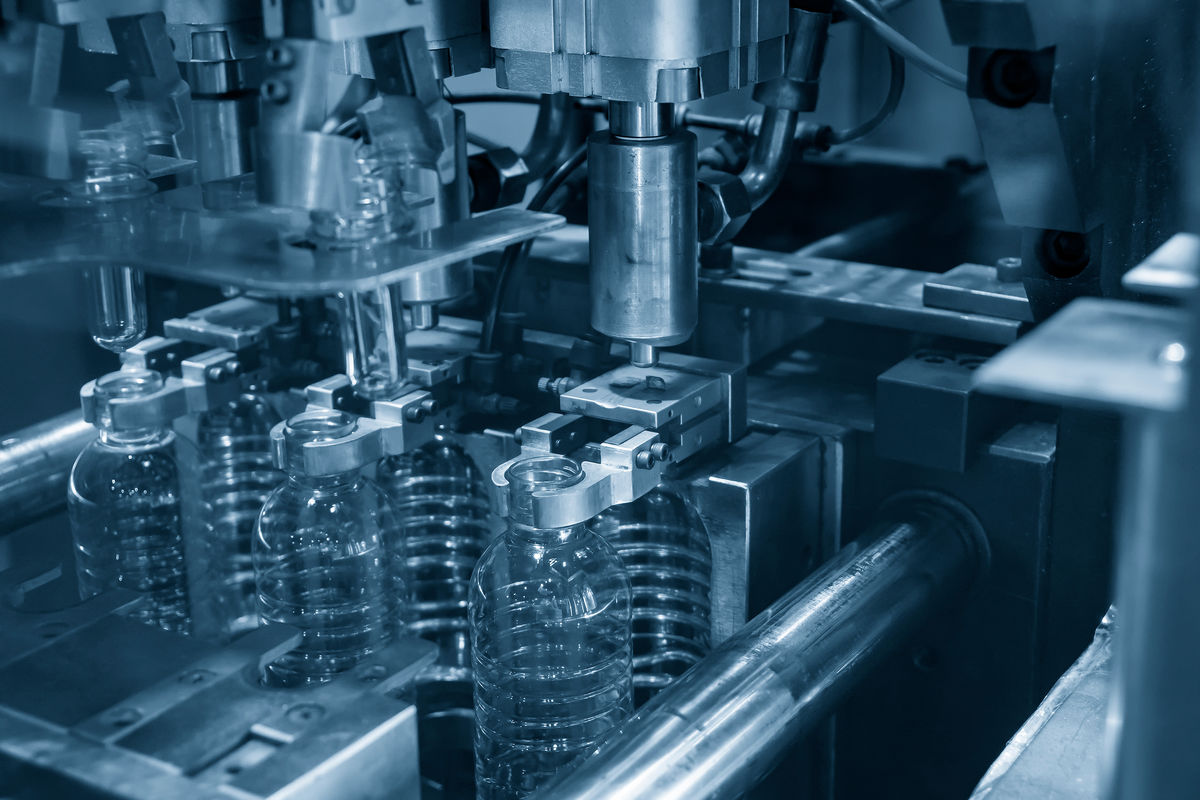

Pixel B, Shutterstock.com
Drilling consists of making a round hole in a material.
Here are examples of tools and machine tools for drilling.
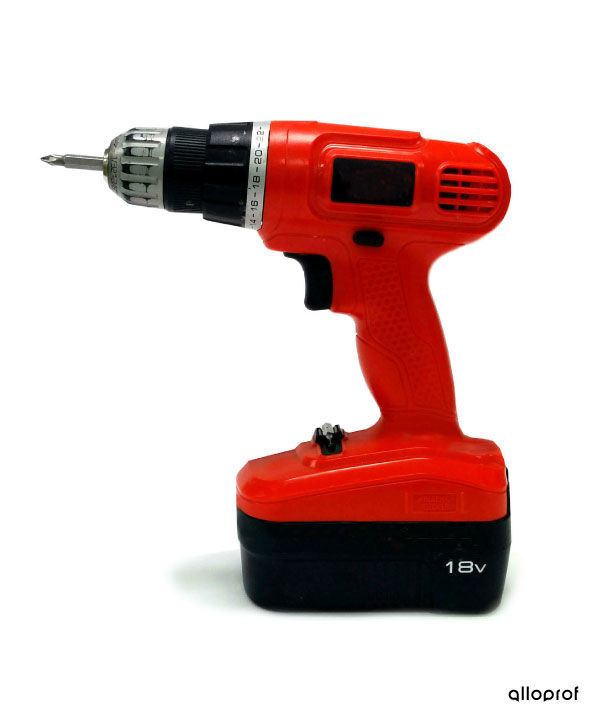
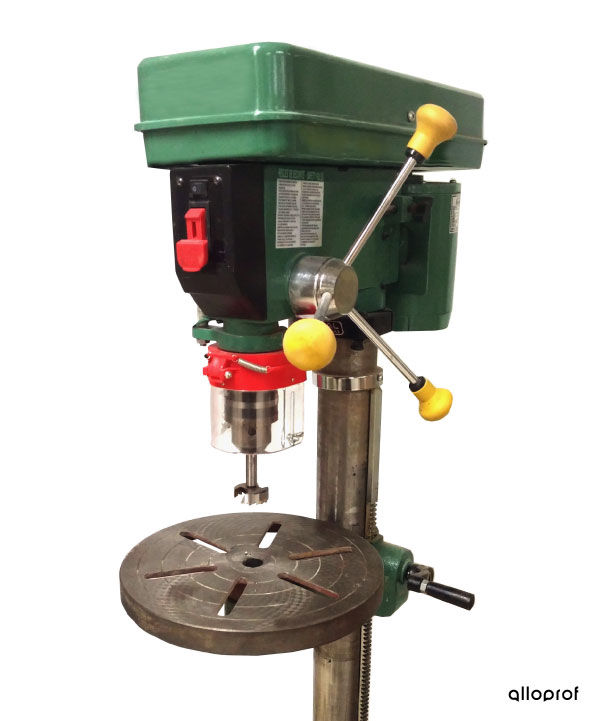


Drilling is performed with a drill bit inserted into a drill. It is important to choose a drill suitable for the hole to be drilled. The choice is made according to the diameter of the hole, but also the nature of the material to be drilled. The rotation speed of the drill must also be adjusted according to the two parameters. For example, the greater the hardness and the larger the diameter, the lower the rotational speed of the drill.
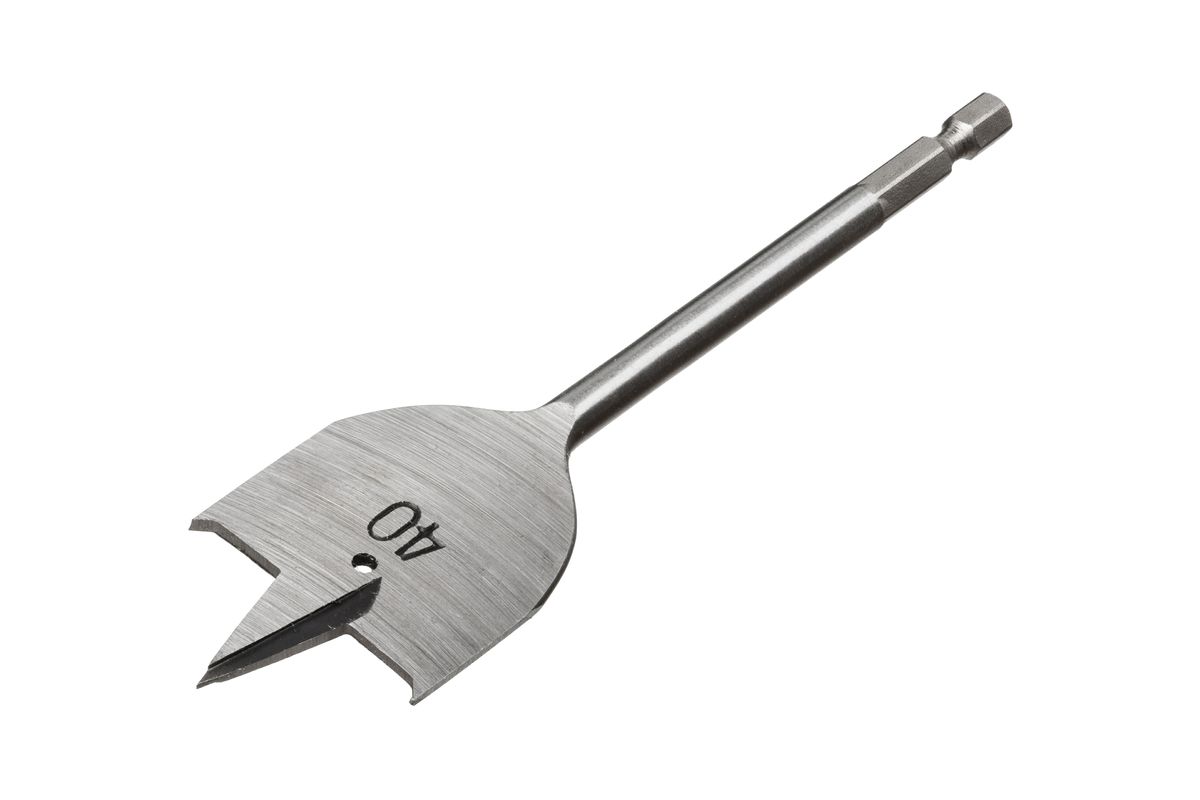



maksimee, Shutterstock.com
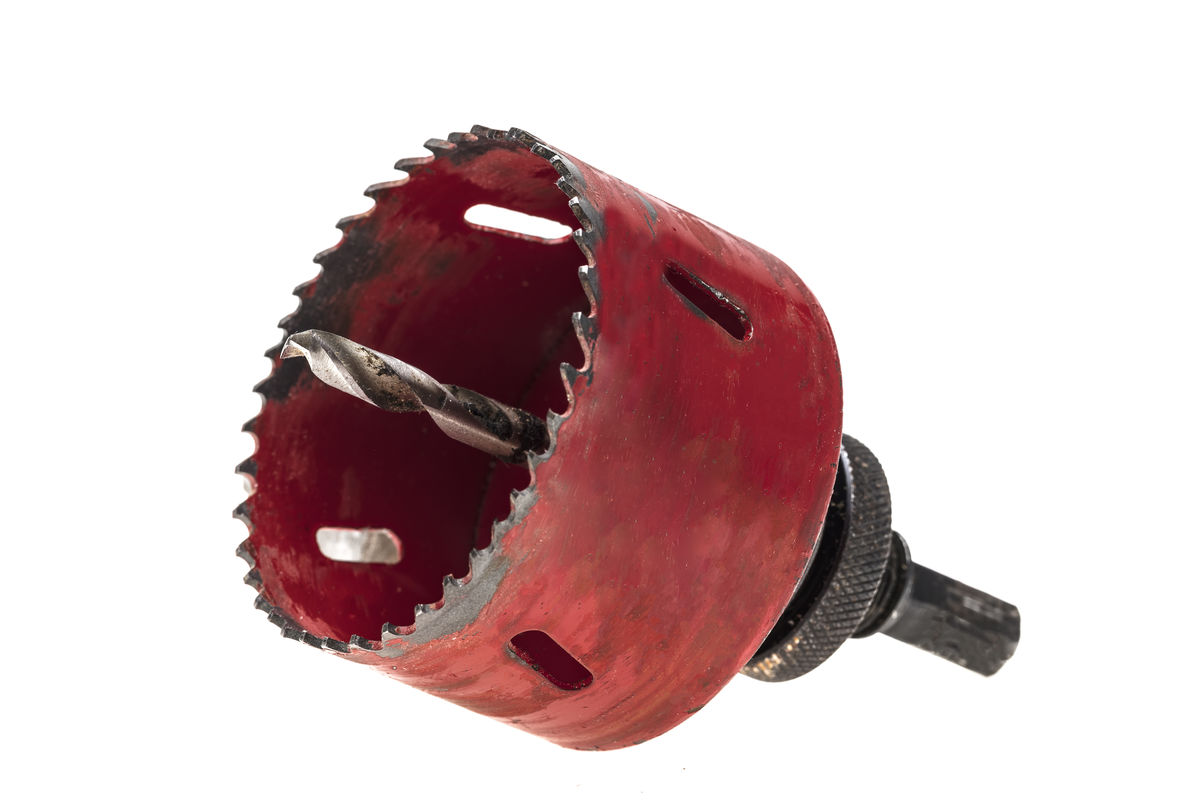

Mehmet Cetin, Shutterstock.com
Shaping is a technique for modifying the profile of a material by routing grooves in a generally long part.
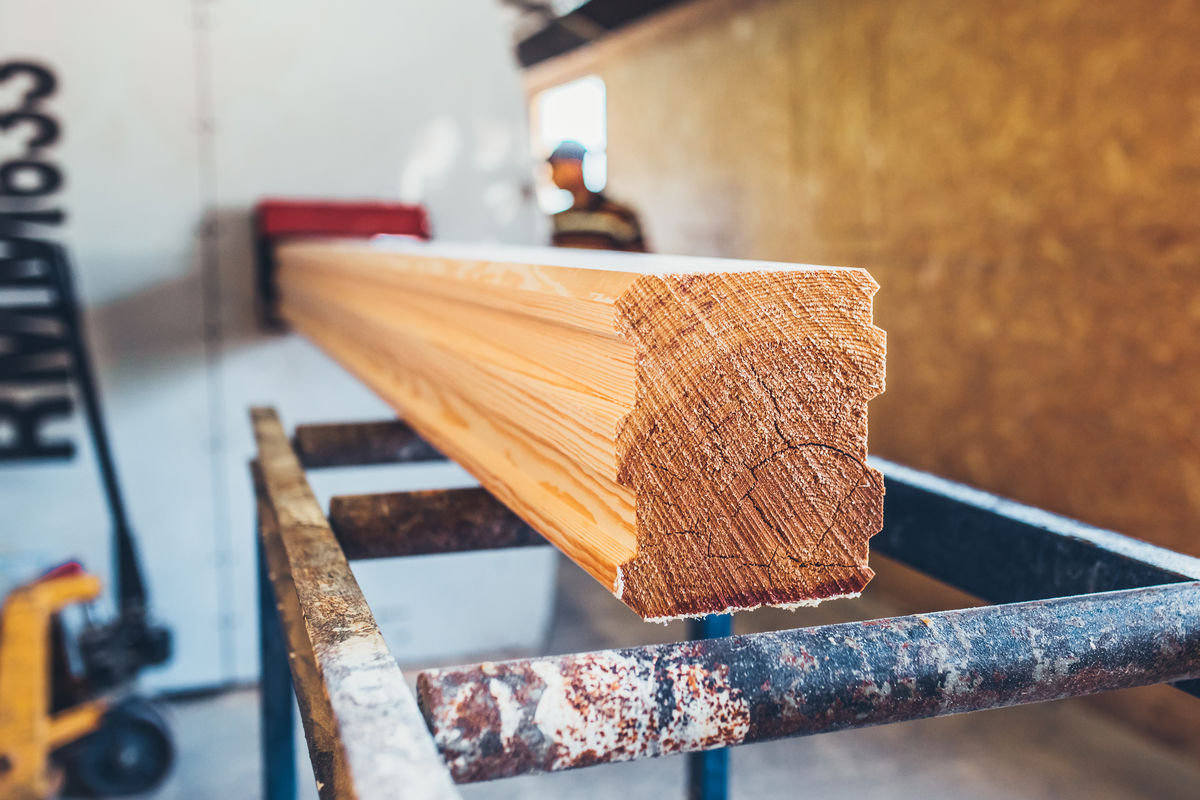

Vano Vasaio, Shutterstock.com
Soldering involves permanently joining metal parts by bonding them with tin.
Soldering is commonly used when working with electricity. It makes it possible to connect two conductive wires and to fix components on a printed circuit, among other things.
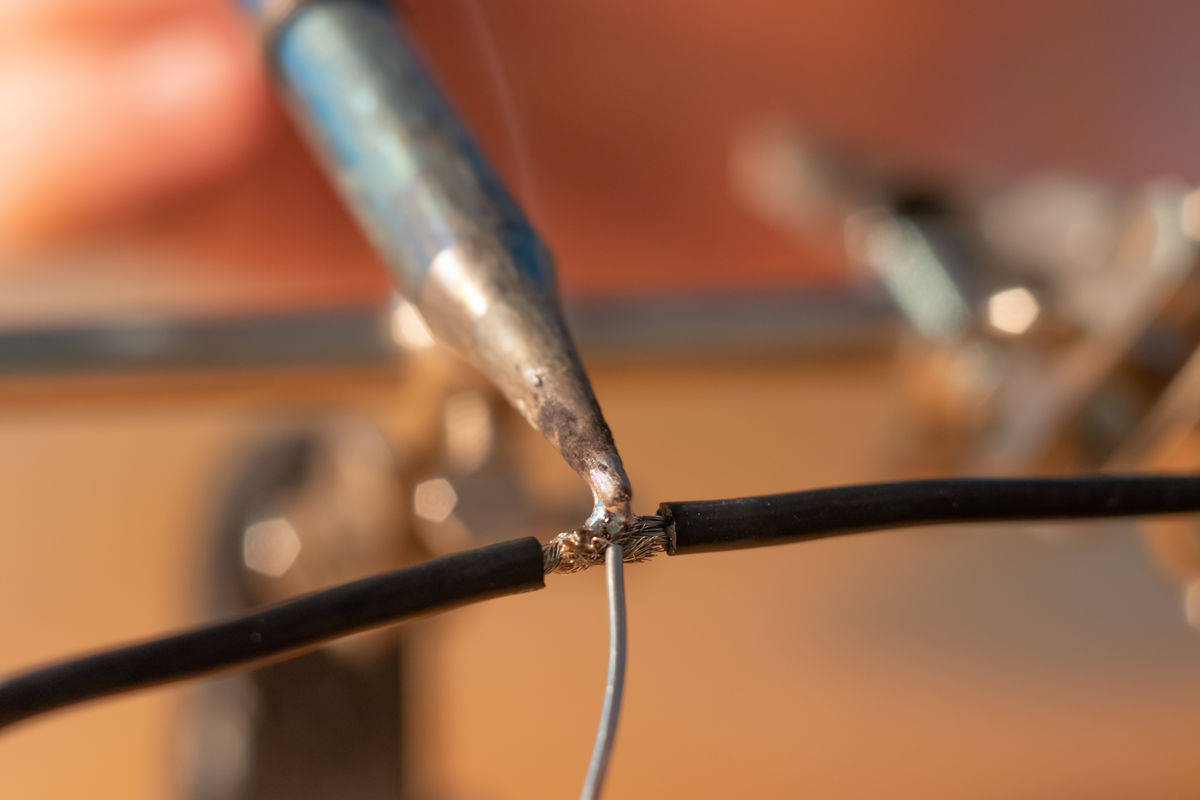
joelpapalini, Shutterstock.com
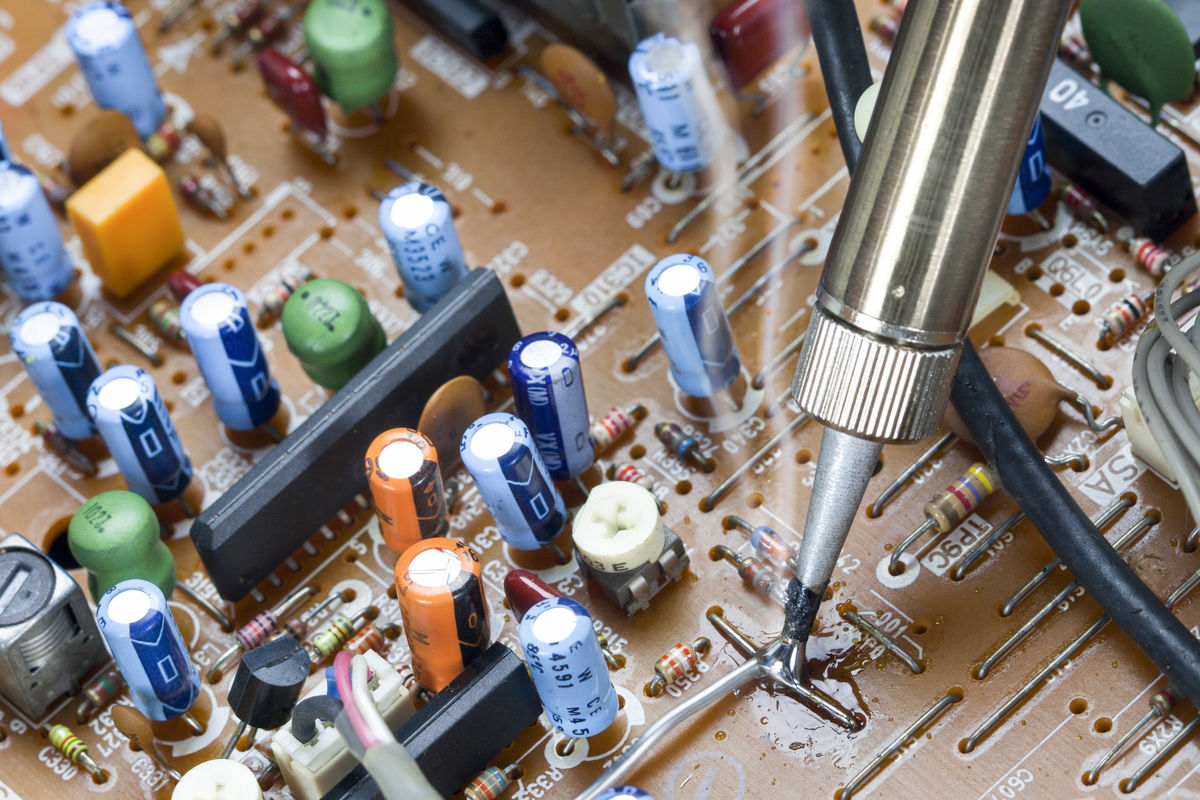
Toa55, Shutterstock.com
Tapping is a technique for making threads in preexisting holes.
A tap is fixed to a tap holder (also called a tap wrench) and is screwed inside the material to be tapped. It can also be done by attaching a tap to a drill chuck. The tap used must be chosen according to the type of thread required and the nature of the material to be tapped.
Here are examples of tools used for tapping.
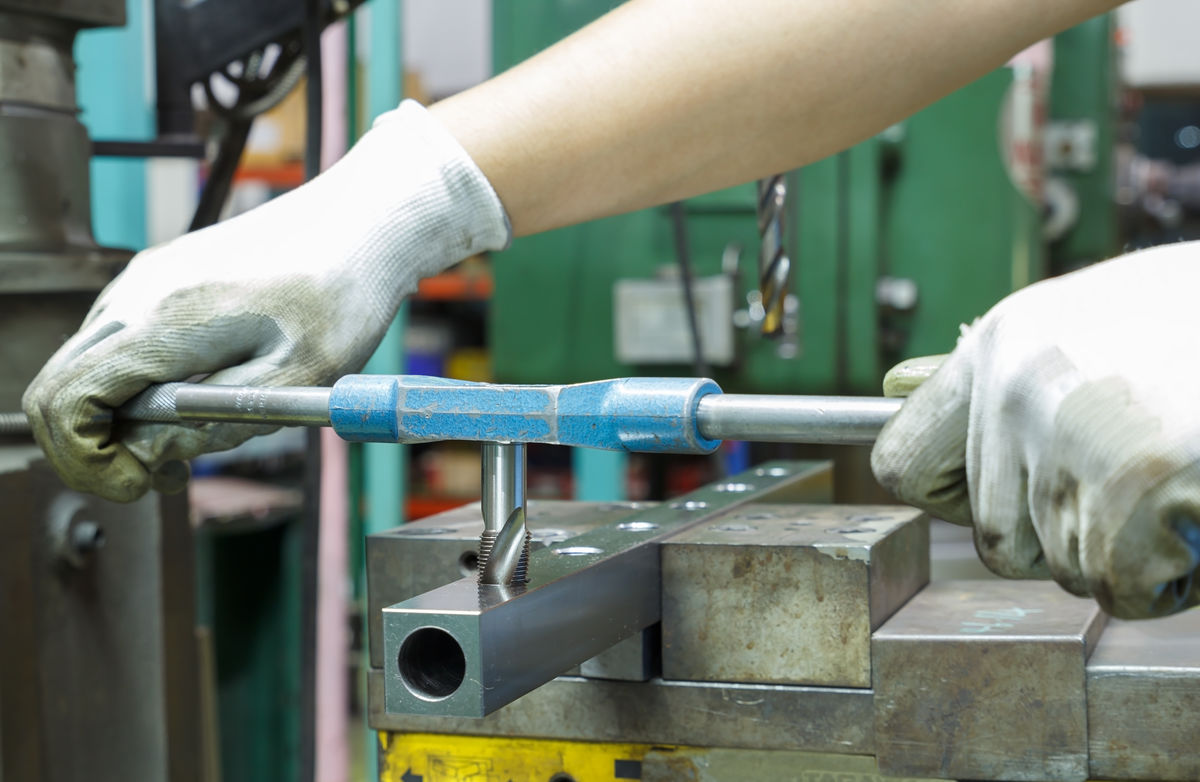

Aumm graphixphoto, Shutterstock.com

Aumm graphixphoto, Shutterstock.com
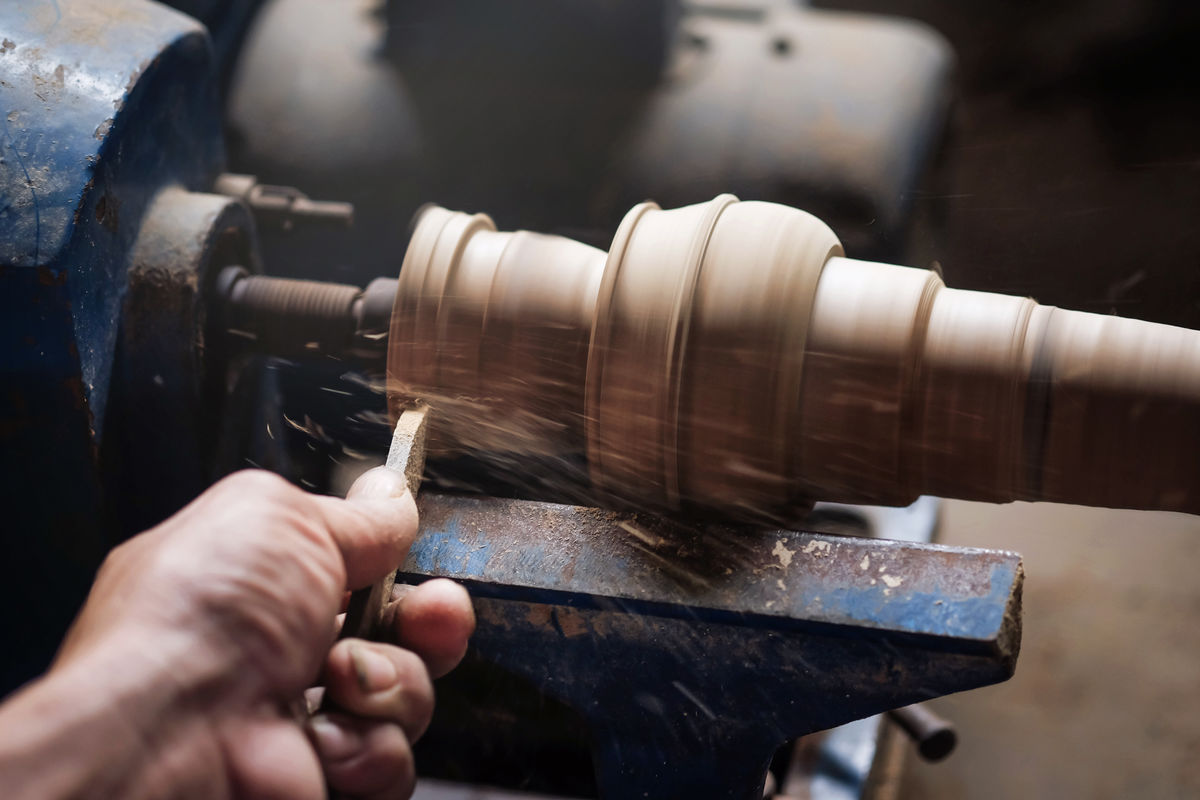
Turning is a technique for forming a material into a rounded shape. It is achieved by grooving a piece while it is rotating.
