Protection is an electrical function performed by any electrical component that interrupts the flow of current when the circuit is not operating normally.
The purpose of this function is to prevent damage to other electrical components in the circuit, to reduce the risk of fire and to protect the user from electric shocks or electrocution.
A fuse, a circuit breaker, a GFCI outlet and a surge protector power bar are examples of devices responsible for protection in an electrical circuit.
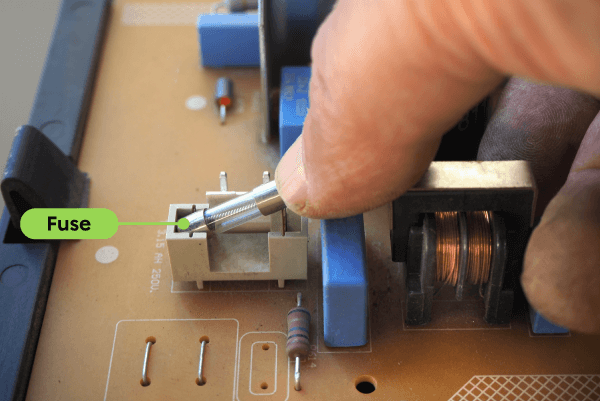
Source: Adapted from Hsyn20, Shutterstock.com
A fuse is an electrical component that contains a very thin metal wire. When a circuit is overloaded, this wire overheats and melts. This opens the circuit and the current can no longer flow.
A melted fuse, commonly referred to as a blown fuse, must be replaced with a new one.
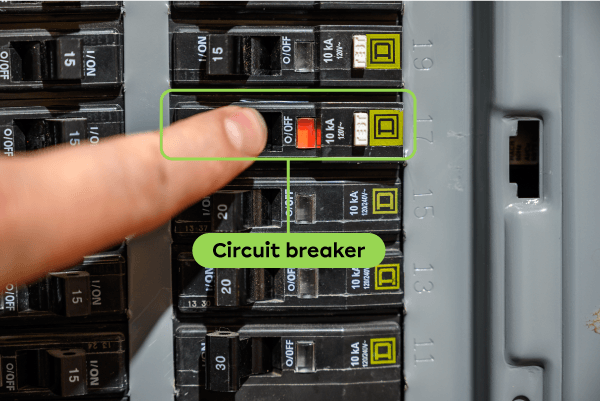
Source: Adapted from Lost_in_the_Midwest, Shutterstock.com
A circuit breaker is a device that contains two metal strips. When the circuit breaker overheats, the strips expand and bend away from each other. This opens the circuit and the current can no longer flow.
When the strips separate, the circuit breaker is said to have tripped, and it must be manually reset.

Source: Adapted from The Toidi, Shutterstock.com
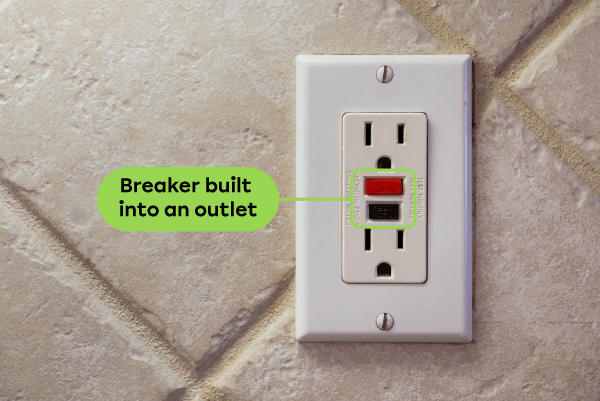
An GFCI is an electrical outlet with a built-in circuit breaker. It automatically cuts off the current in the event of a short-circuit.
In a house, this type of outlet is installed near sinks. This prevents electric shocks and electrocutions that could be caused by contact between electric current and water.

Source : Bacho, Shutterstock.com
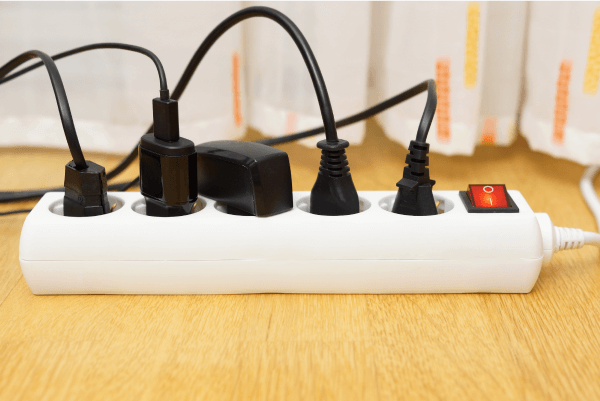
A surge protector power bar is a device with several outlets that is itself connected to a power outlet. Appliances connected to the power bar are protected from sudden changes in current, because the excess energy is channelled to the ground.
-
A short circuit is an electrical issue that causes a sudden increase in current. It can damage the electrical components of a circuit and presents a fire hazard.
-
Earthing, also known as grounding, is the redirection of excess electrical charge to the ground. It is used to protect people from electrocution or serious injury caused by a poorly insulated electrical circuit.