A property of matter is a characteristic specific to a substance or group of substances.
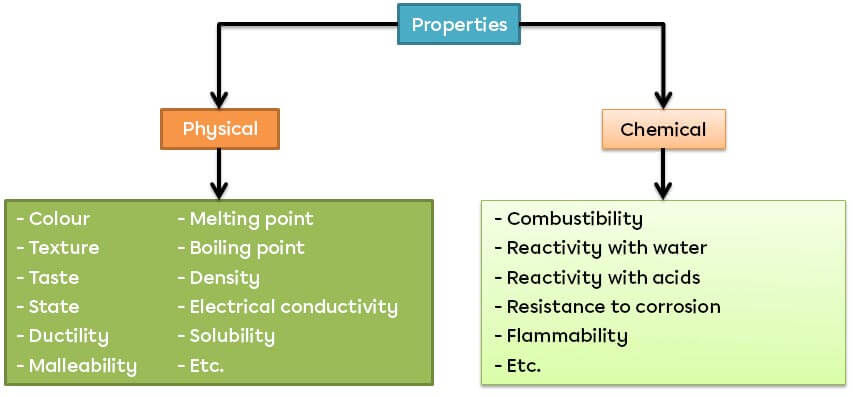
A property is either a physical or a chemical characteristic. A physical property occurs or is observed without changing the nature of the substance. A chemical property describes the behaviour of a substance when it undergoes a chemical reaction.
A property can be characteristic or non-characteristic. Non-characteristic properties can describe several substances while characteristic properties are specific to one substance.
The human body contains numerous mixtures, many of which are solutions. Their properties are very interesting to study.
Non-characteristic properties are not specific to a substance.
This type of property cannot be used to identify a substance, determine its use or predict its effect on the environment.
There are many non-characteristic properties:
-
shape
-
size
-
permeability
-
transparency
-
buoyancy
Only characteristic properties can be used to identify a substance.
A characteristic property can be used to differentiate a substance or a group of substances.
In everyday life, a substance can be described by its mass, volume or temperature. For example, when someone is thirsty, they might buy 1 L of liquid to drink. However, without specifying if the liquid is water, milk or a soft drink, the volume is not helpful in determining what type of beverage it is.
To accurately identify a substance, it is important to know the specific properties that do not change. For example, water always boils at 100°C no matter the amount. Using characteristic properties, it is possible to:
-
Identify a substance or an object.
-
Determine how to use a substance or an object.
-
Predict the effect of a substance or an object on the environment.
There are two categories of characteristic properties. Physical characteristic properties can be qualitative (observable using the senses) or quantitative (accurately measured using instruments). Chemical characteristic properties refer to the reaction of a substance when it comes into contact with another substance.
Many reference books and specialized websites contain data identifying the characteristic properties of various substances. This allows for an unknown substance to be identified by comparing its measured values with its theoretical values. Substances can be very similar, sometimes with only one characteristic that differs.
| Substances | Examples of characteristic properties |
 Water (Source) |
|
 Iron (Source) |
|
A substance is a transparent solid. Transparency is a non-characteristic property of this substance, because it cannot be used to determine whether the substance is ice, glass or plastic. However, if it is known that the substance has a melting point of 0°C and a boiling point of 100°C, it can be concluded with certainty that the substance is ice (water). Therefore, the melting point and boiling point are characteristic properties.
To identify a criminal from a composite sketch and fingerprints taken at a crime scene, the clues in the composite sketch must be identified first. There are physical properties to identify, such as hair colour, facial features, presence or absence of scars, jewelry or tattoos.
However, identifying a criminal by whether or not they were wearing jewelry is an unreliable method. It is important to use reliable methods, such as DNA sample analysis and fingerprints from the crime scene, and compare them with databases. These reliable methods are characteristic properties because they are unique to one person.
Characteristic properties are used both in science and technology. When selecting a material to use in the manufacturing of a technical object, it is important to consider the material’s properties to make sure it is suitable for the constraints it will face. These are a material’s mechanical properties. To find out more, refer to the following concept sheet:
Mechanical Properties of Materials
Shape is how matter appears or the way a substance occupies space (cube, pyramid, sphere, etc.).
Water is a liquid that takes the shape of a glass.
This rock is shaped like a cube.

Size is the height, width and length of a living being or object.
The Eiffel Tower is 324 metres high and 124.90 metres wide.
Absorption is the act of absorbing. In other words, it is a substance’s ability to retain another substance.
A sponge absorbs water.
If a substance is permeable, it can be penetrated by another substance.
Concrete is permeable because it allows water to pass through it.
If a substance is impermeable, it will not let other substances through.
A raincoat keeps water out and keeps a person dry.
If a substance is transparent, it allows light to pass through so a person can see clearly through that substance.
The opposite of transparency is opacity.
The glass in a window is transparent; it is possible to see through it. A window frame is opaque and does not let light through.

This glass is partially transparent, or translucent; it is impossible to see clearly through it.
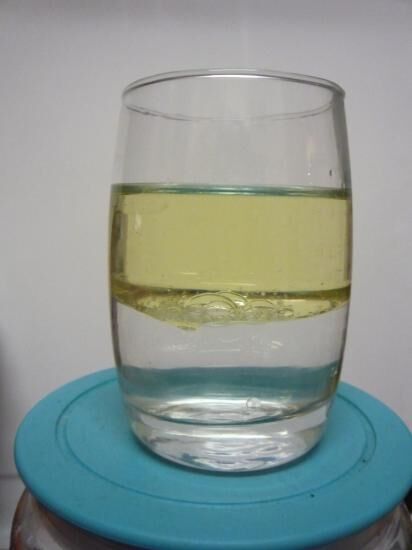
Buoyancy is the ability to float on the surface of a liquid, and it depends on the density of the substances in question.
A boat floats on water.

Oil has a lower density than water, so it floats on the water’s surface.






