Dissolution is a process which consists of adding a solute into a solvent to prepare a solution with a single phase (homogeneous mixture).
When a solute and a solvent are mixed, the solute molecules move around until they are evenly distributed in the solvent. The solute and solvent molecules will not change: there is therefore the same solute and solvent as those initially present.
When adding sugar to coffee, the sugar molecules will position themselves between the molecules of the solvent, which is the water in this case.

When too much solute is added to dissolve in a solvent, it is possible that part of the solute will not be able to dissolve. This solution is then said to be saturated.
Water is often used as a solvent. When a solute is dissolved in water, the resulting mixture is an aqueous solution.
There are certain factors which can affect the amount of solute that can be dissolved in a solvent. As the temperature of the solvent increases, it is possible to dissolve more solute than if the temperature is lower. Furthermore, the nature of the solute will alter the dissolution: for a given amount of water, it is not possible to dissolve the same amount of solute before obtaining a saturated solution. The amount of solute that can be dissolved in a determined volume of water is the solubility of that substance.
The concentration makes it possible to know the quantity of solute which has been dissolved in a volume of solution. The following sheets explain how to calculate the concentration of a substance.
Concentration and its Measurement Units
PPM (Parts per Million)
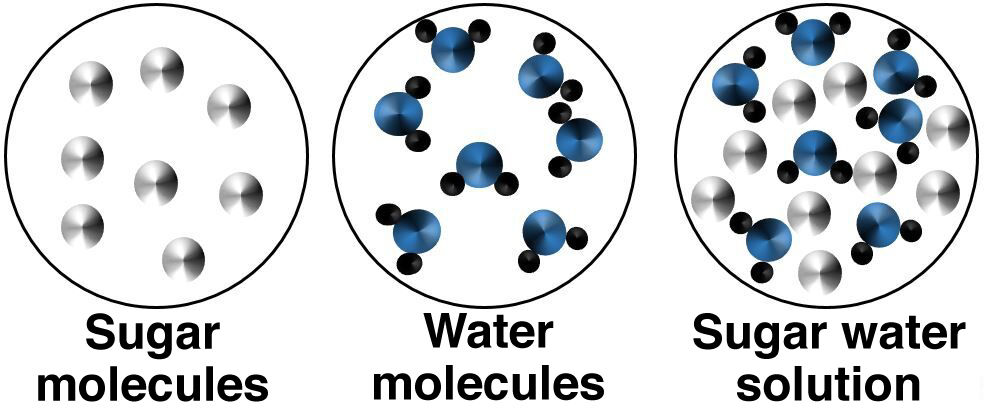
In a molecular dissolution, the dissolved molecules remain whole and do not separate into ions. Since there is no ion, this type of solution does not conduct electricity.
The bonds between the atoms of the solute molecule and those of the solvent do not break up.
When sugar is dissolved in water, the molecules of the solute will mix with that of the water without breaking down.
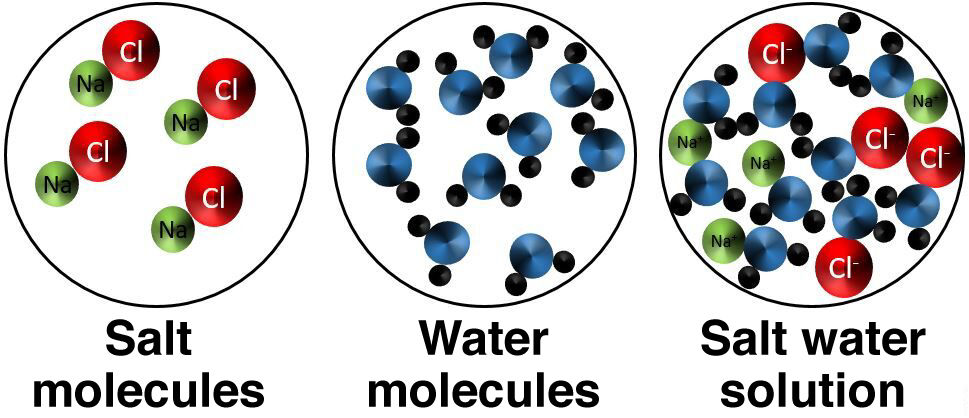
Ionic dissolution is the result of mixing a solvent and a solute that separate into ions. This type of solution therefore conducts electricity.
When table salt |(NaCl)| is dissolved in water, the salt separates and produces two ions, |Na^{+}| and |Cl^{-}|. The salt water solution is, therefore, an electrolyte, which is a solution that allows electric current to flow.