Matter can be in the form of a pure substance or in the form of a mixture.
Mixtures are obtained when two or more substances are combined. They can be homogeneous or heterogeneous.
A heterogeneous mixture is a mixture in which several components can be identified with the naked eye or under a microscope.
Heterogeneous mixtures have the following characteristics:
-
They have more than one visible phase. These phases are generally gaseous, liquid, or solid.
-
The substances in these mixtures are not uniformly distributed.
-
The properties are not identical at any point.
This heterogeneous mixture comprises two visible phases: water and oil. The phase comprising water (aqueous phase) does not have the same properties as the oily phase. For example, oil has a lower density than water, which explains why it floats on water.
In addition, the particles of this mixture are distributed non-uniformly.
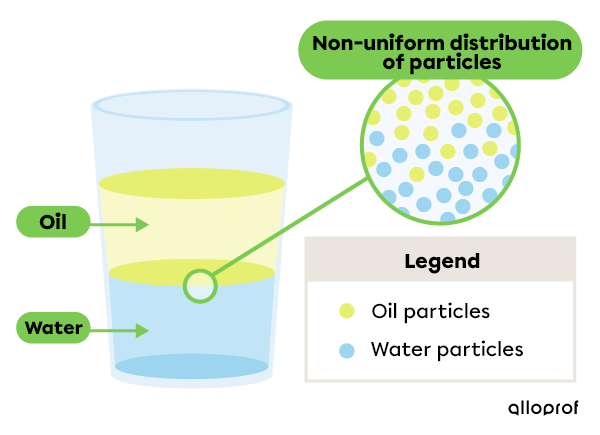
When two substances cannot mix at all, they are said to be immiscible. Thus, water and oil are immiscible, which means that oil is not soluble in water.
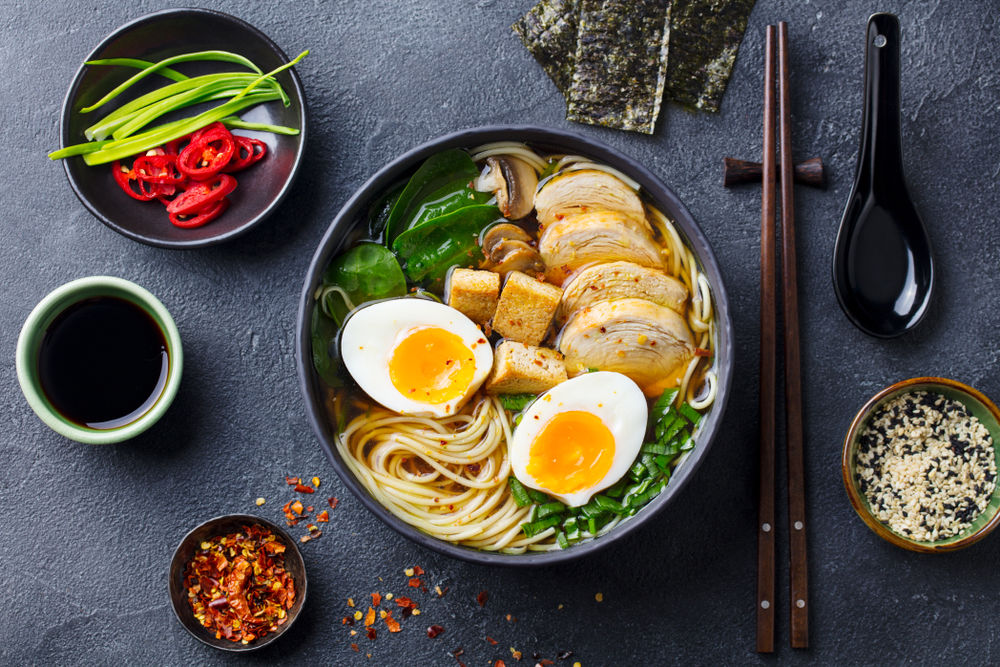
Ramen soup is a heterogeneous mixture. It has several visible phases. For example, the soup base is in a liquid state, while the meat is in a solid state.

Anna_Pustynnikova, Shutterstock.com
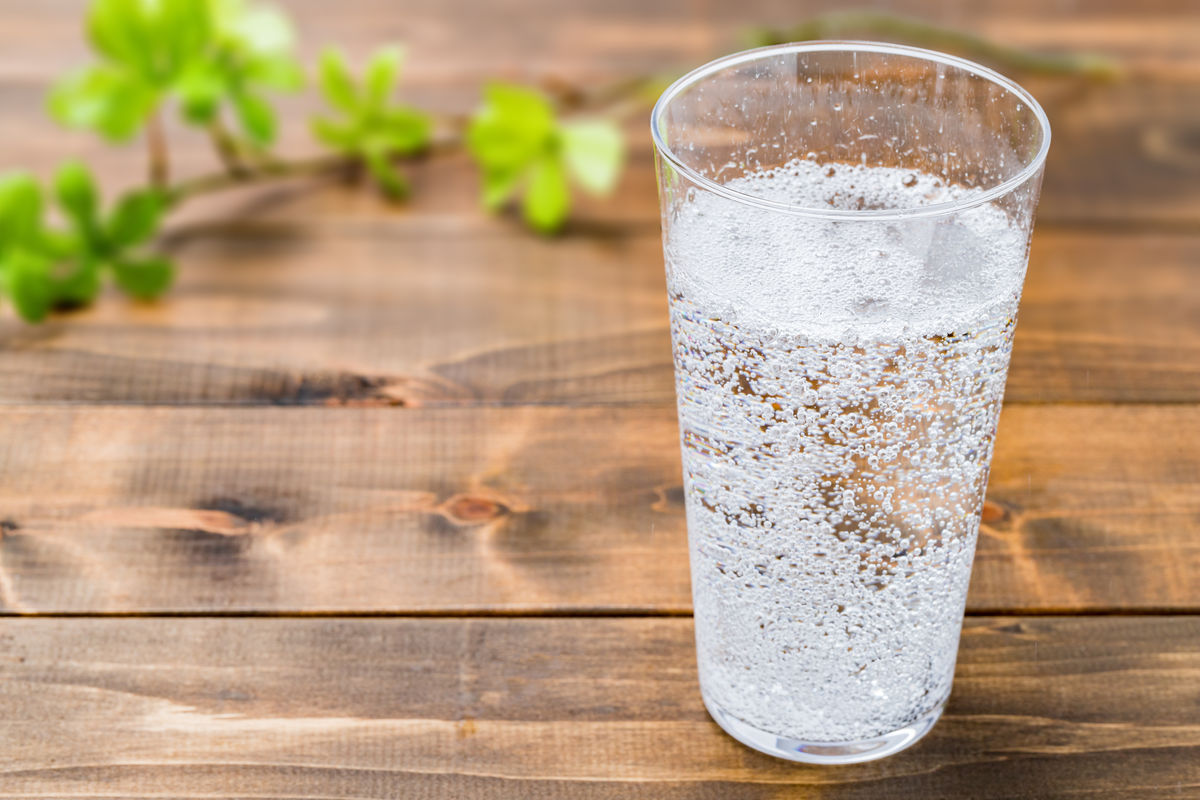
Carbonated water is a heterogeneous mixture that includes water, minerals, carbon dioxide (gas bubbles), and other ingredients.

flyingv3, Shutterstock.com
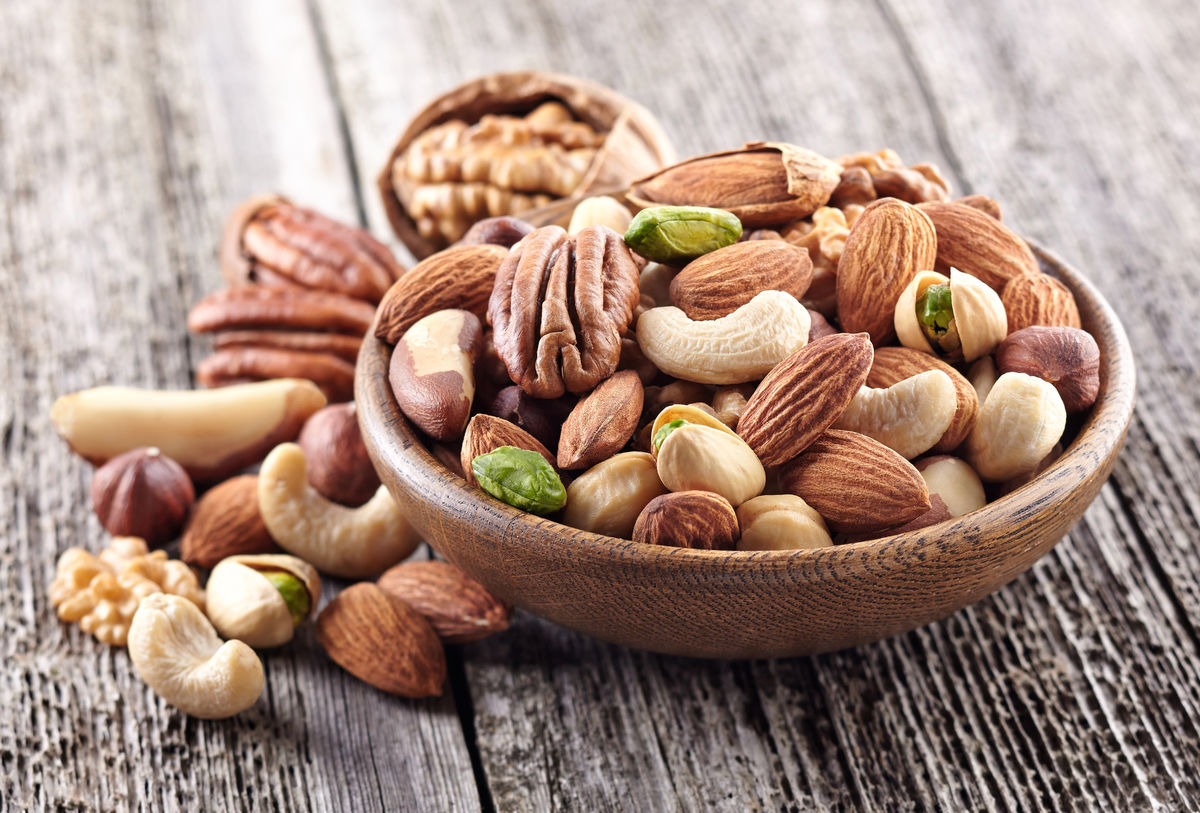
In this mixture of nuts, we can easily identify almonds, pistachios, cashews, and pecans. Since we can identify four solid phases, this is a heterogeneous mixture.

Dionisvera, Shutterstock.com
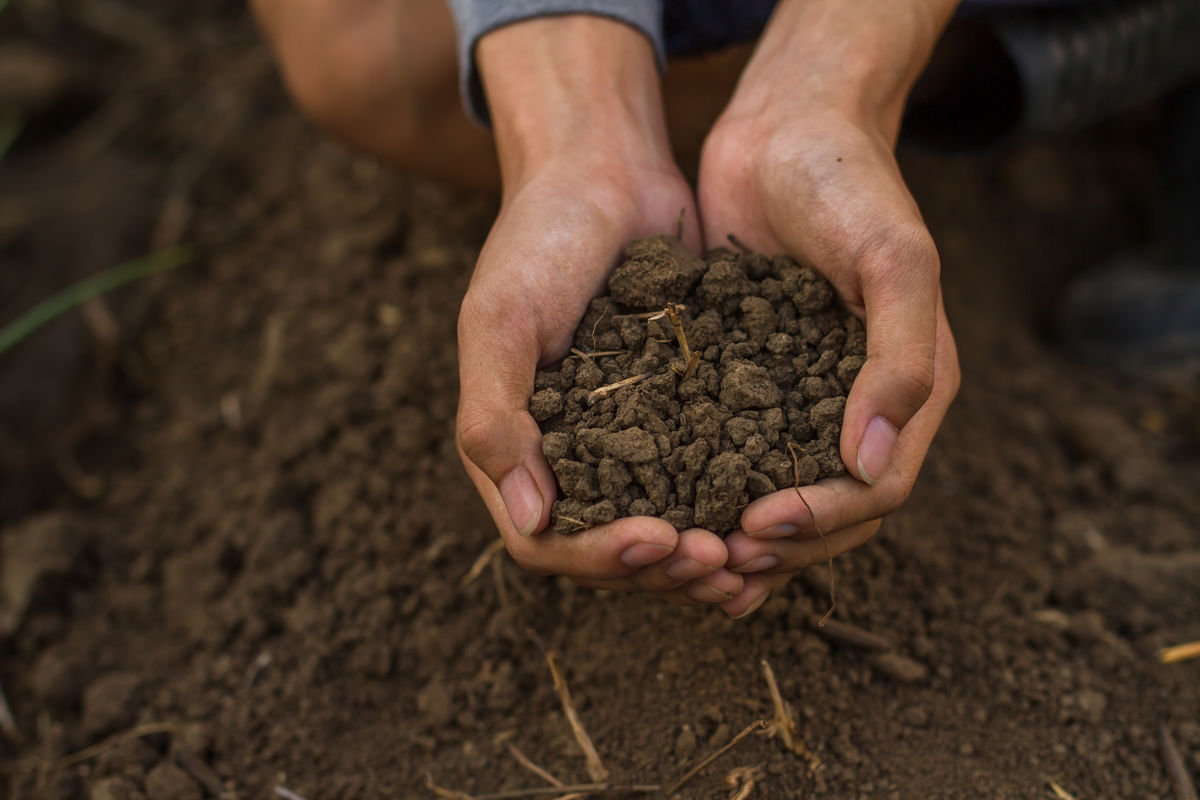
A humic soil is a heterogeneous mixture comprising several solid phases. Indeed, it contains a variety of organic and mineral matter. Certain components of the soil can be identified by observing it closely.

Piyaset, Shutterstock.com
A homogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the constituent substances cannot be identified.
Homogeneous mixtures have the following characteristics:
-
They have a single visible phase. This phase is generally in the gaseous, liquid, or solid state.
-
The substances are evenly distributed in these mixtures.
-
The properties of the mixture are identical at all points of the mixture since the particles are distributed uniformly.
Sugar water is made up of water and sugar. When these two substances are mixed together, the sugar cannot be identified. Only one phase is visible.
The sugar particles are evenly distributed in the water. Therefore, the properties of sugar water are the same in the middle of the glass and in the bottom of the glass. For example, sugar water has a uniform density throughout the mixture.
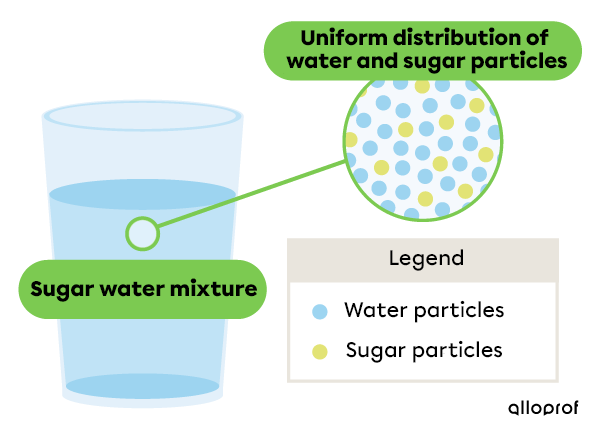
Since substances mix uniformly in a homogeneous mixture, these substances are said to be miscible. Thus, sugar and water are miscible, which means that sugar is soluble in water.
Sulphuric acid and water mix to form a homogeneous liquid mixture.

Adapté de Ggw, Shutterstock.com
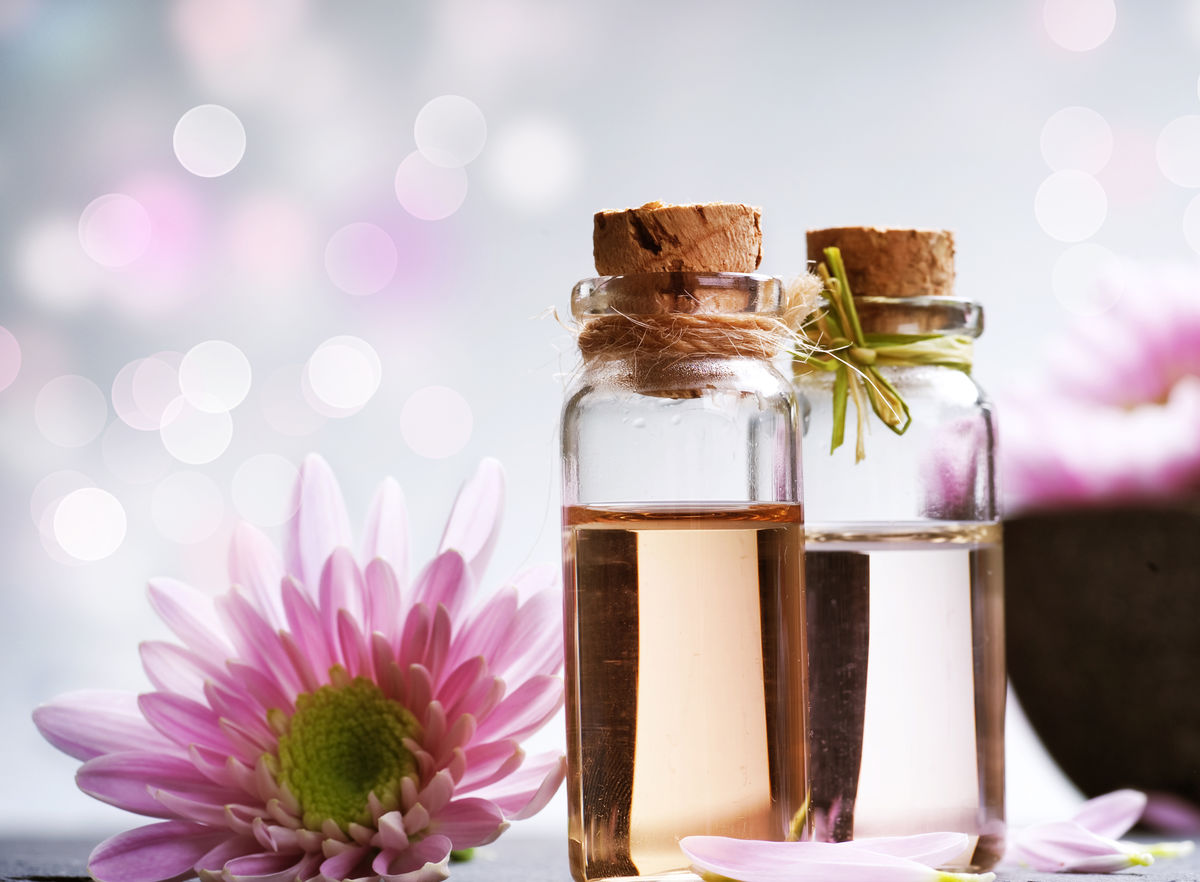
Essential oils are oils extracted from various plants. They are a homogeneous mixture comprising different substances found in plants.

Subbotina Anna, Shutterstock.com
Diamonds are pure, colourless substances. When they contain impurities, they can be coloured.
For example, blue diamonds are solid homogeneous mixtures composed mainly of carbon, but also of boron.

Sararwut Jaimassiri, Shutterstock.com
Steel is an alloy of iron, carbon, and sometimes other metals. This mixture is homogeneous since there is only one visible phase.

FabrikaSimf, Shutterstock.com
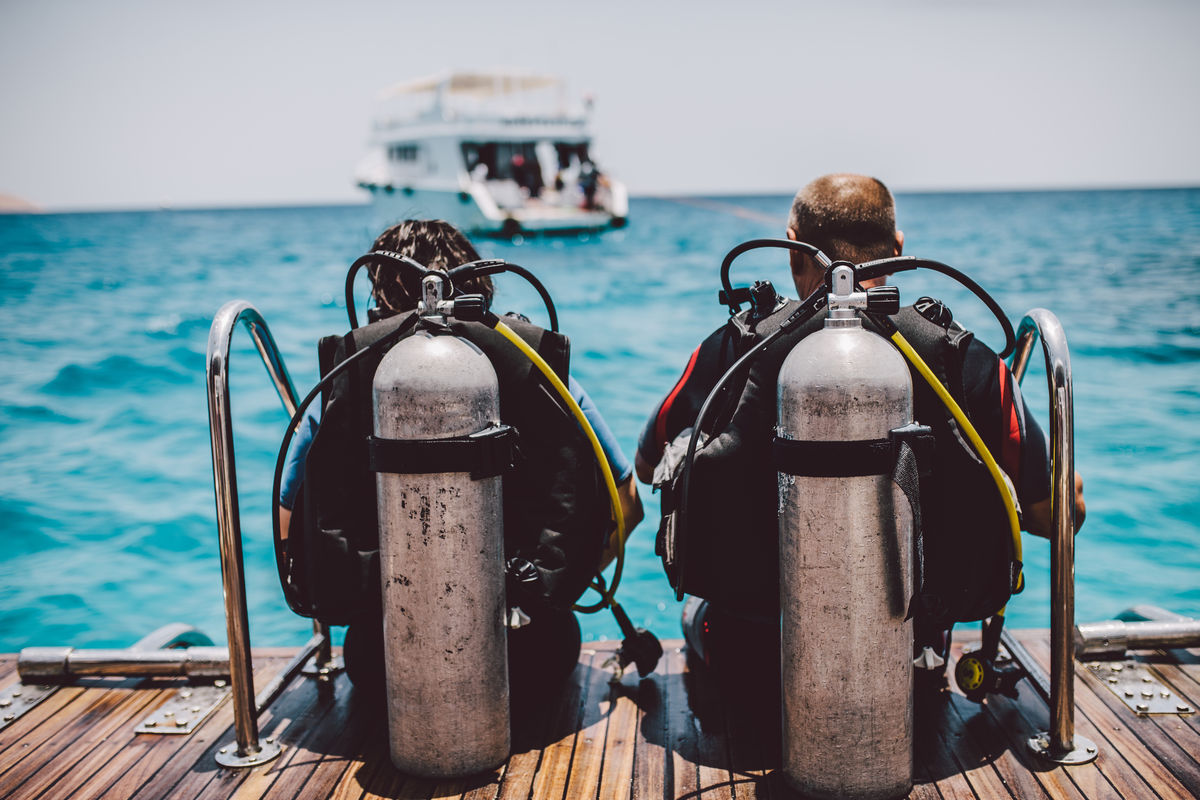
In scuba diving, divers are equipped with compressed air cylinders. Air is a homogeneous gaseous mixture composed of nitrogen, oxygen, and other substances. We can also say that it is a gaseous solution.

San4ezz, Shutterstock.com
A solution is a homogeneous mixture. However, a saturated solution is a heterogeneous mixture. For example, salt is soluble in water. However, when we add too much salt to the water, it ends up no longer dissolving. The mixture is, therefore, salt water with a deposit of salt at the bottom. This saturated solution has two visible phases: the mixture is, therefore, heterogeneous.
A colloid is a mixture that appears homogeneous to the naked eye, but whose constituents can be identified with a microscope.
Colloids can have several phases in the gaseous, liquid and/or solid state. Observation of the mixture under a microscope is a technique used to determine whether it is indeed a colloid.
Depending on textbooks, colloids can be considered a separate category of mixtures or part of heterogeneous mixtures. On this page, we consider colloids as heterogeneous mixtures, since we can observe their heterogeneity under the microscope.
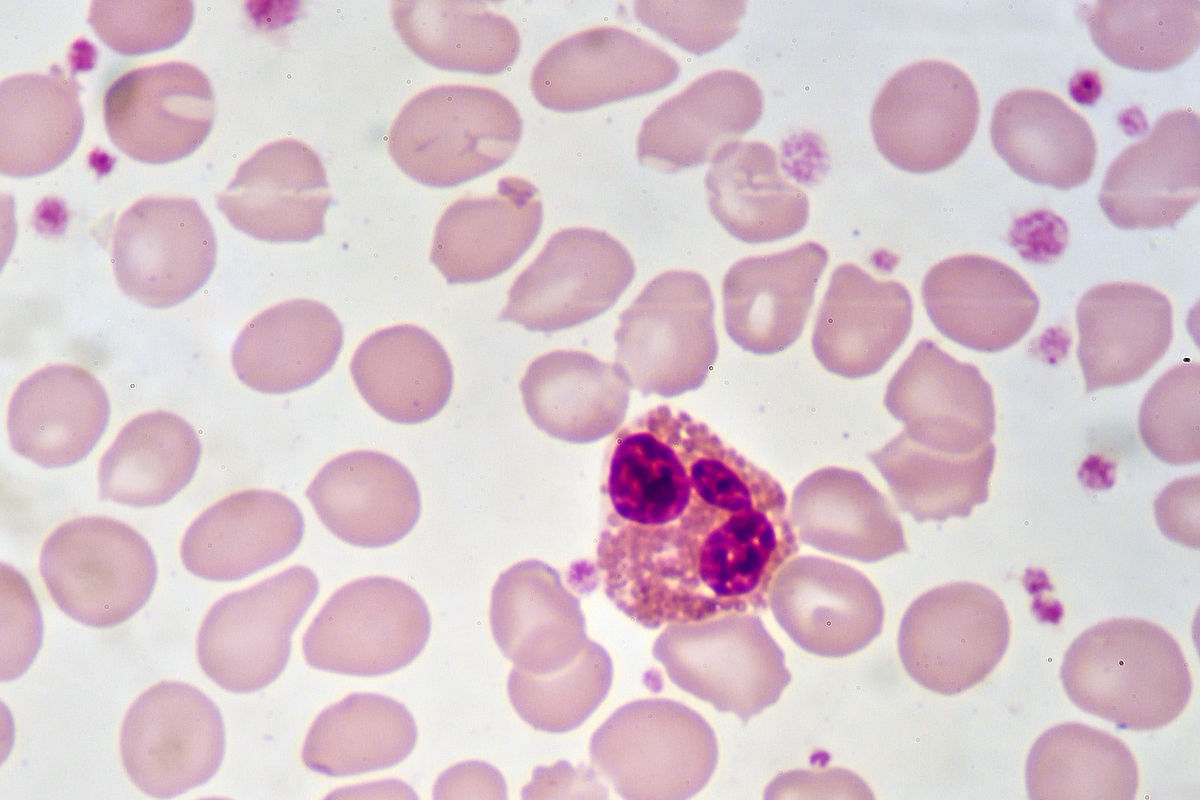
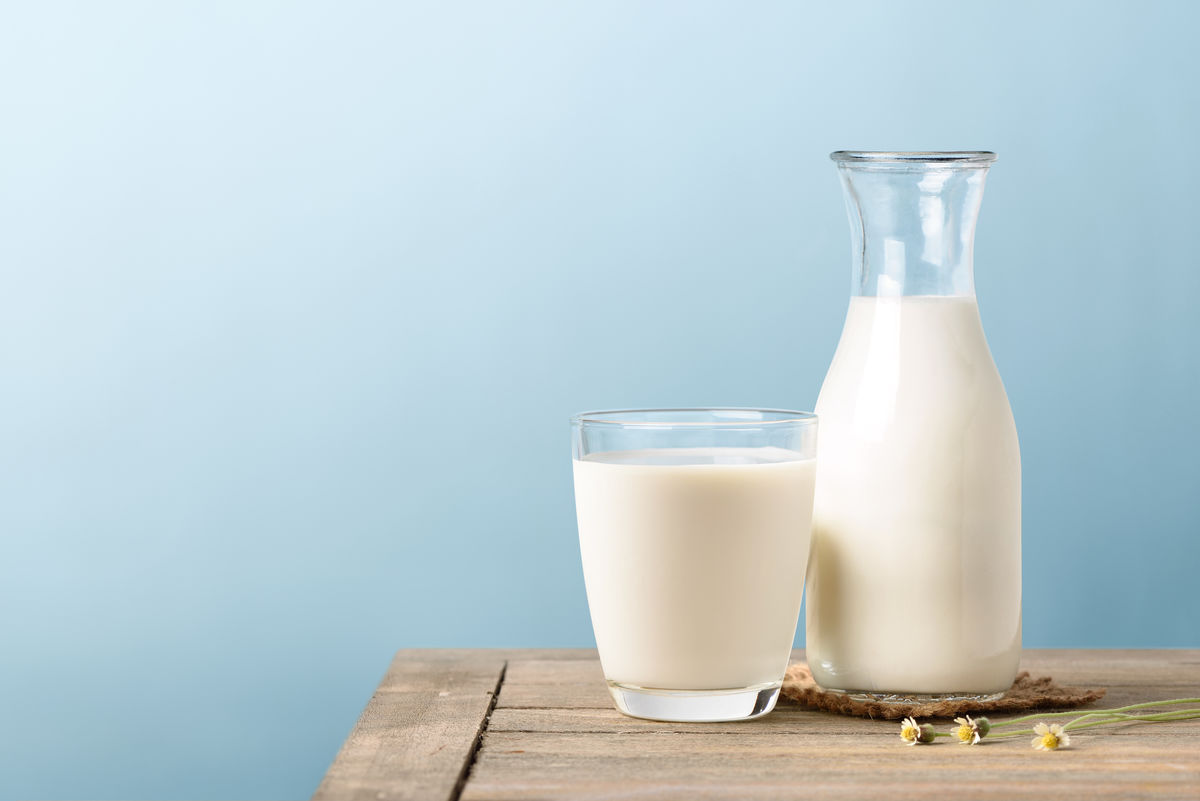
The fact that a liquid, gel, or foam is opaque can be an indication of its colloidal nature. This is the case with milk and blood.
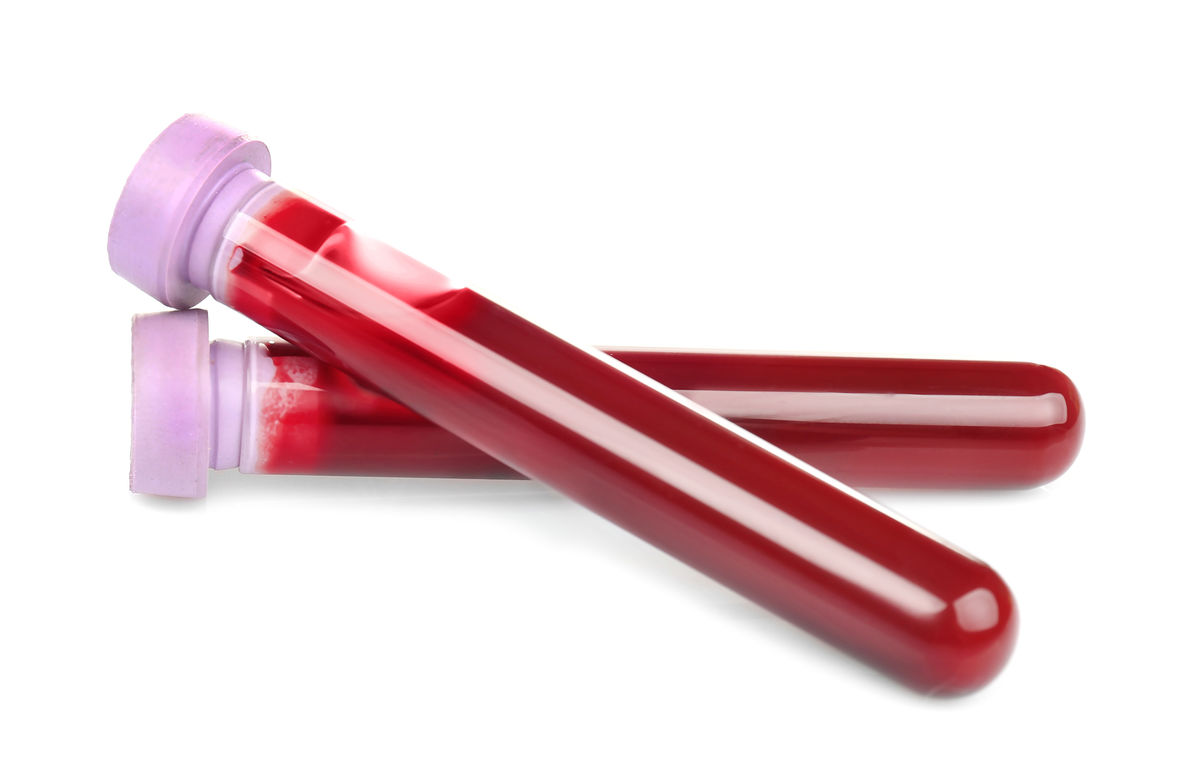

Africa Studio, Shutterstock.com
Jarun Ontakrai, Shutterstock.com
To the naked eye, blood appears as a homogeneous mixture. However, observation under a microscope makes it possible to see that the blood includes, among other things, heterogeneously dispersed cells. Thus, blood is a colloid.

Photoongraphy, Shutterstock.com

Mr. Somluk Wanta, Shutterstock.com
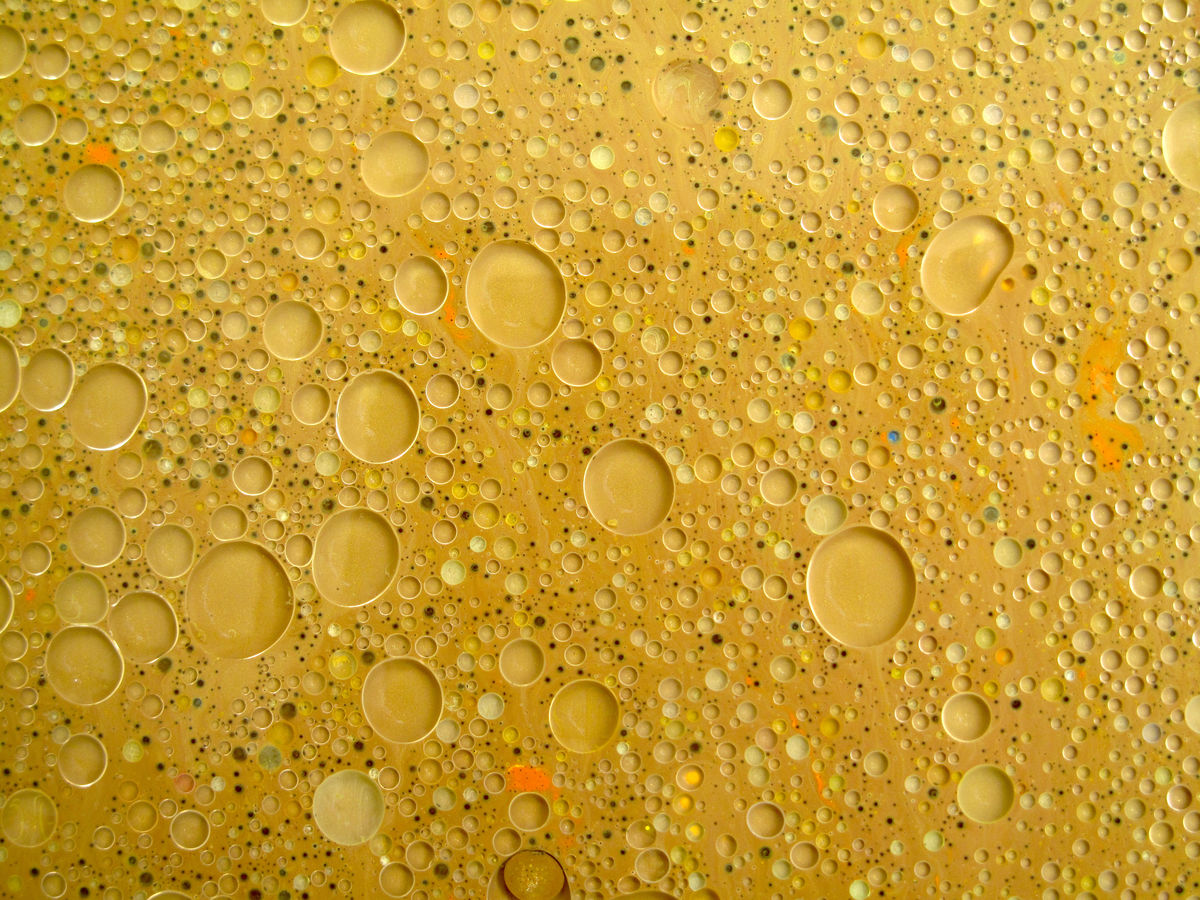
To the naked eye, the milk is white, opaque, and appears homogeneous. Under the microscope, bubbles of fat distributed heterogeneously can be observed in the aqueous medium. Milk is, therefore, a colloid.

Mama_mia, Shutterstock.com
Alan Sau, Shutterstock.com
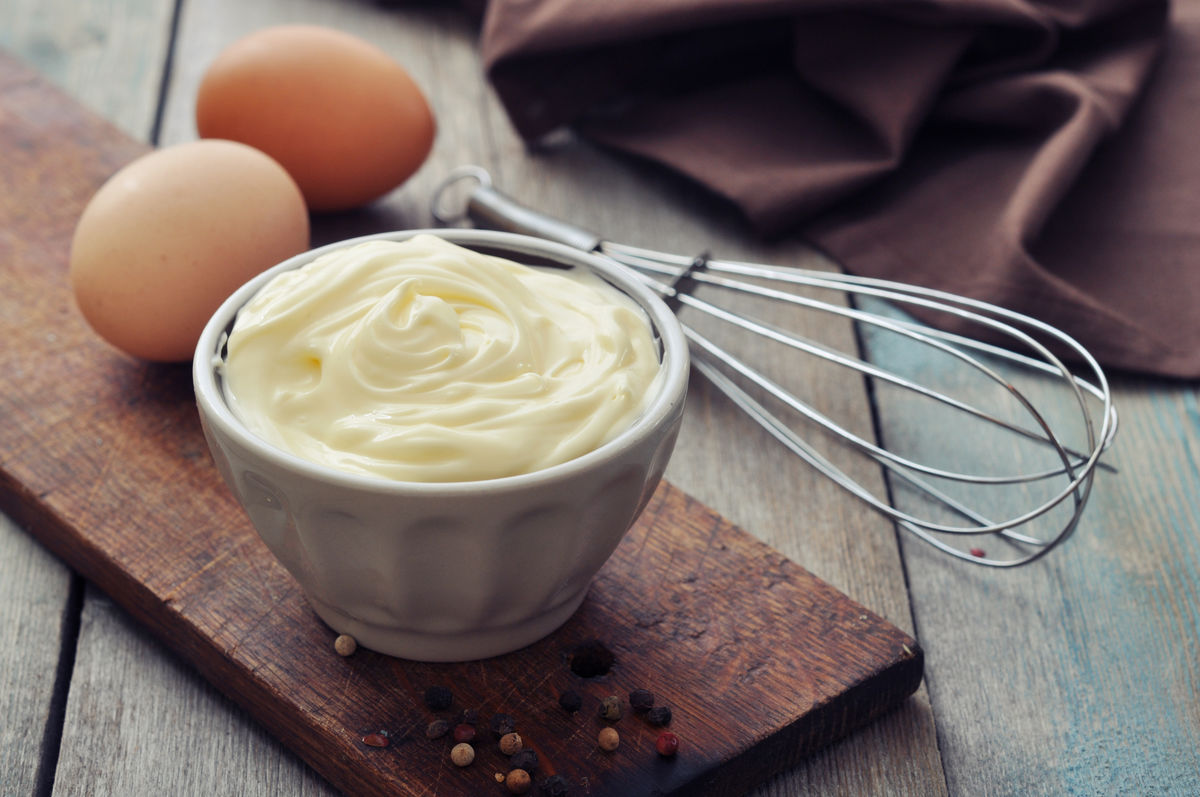
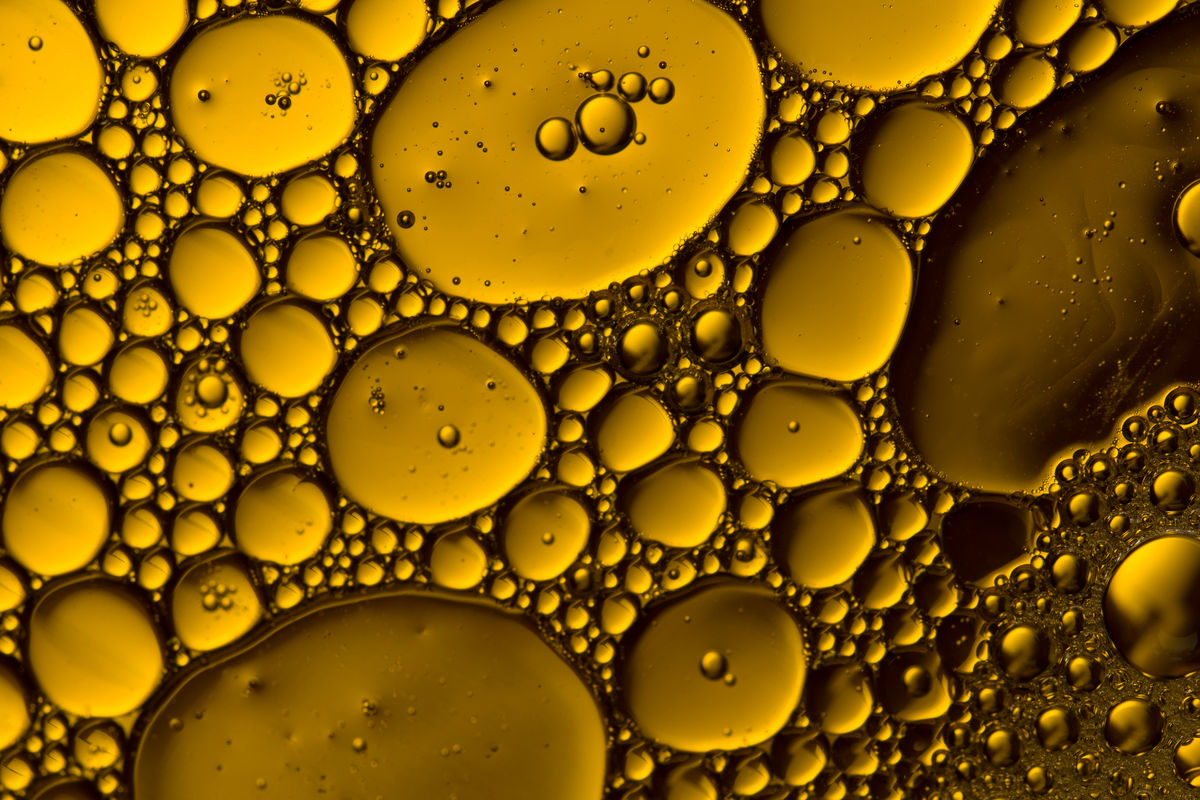
To prepare mayonnaise, its ingredients are mixed using a whisk, which allows air to be incorporated into the mixture. At first glance, the mayonnaise is homogeneous. Under the microscope, we can see the air bubbles trapped in the fat. Mayonnaise is, therefore, a colloid.
The human body comprises multiple mixtures. These can be homogeneous or heterogeneous. The following table shows examples of mixtures found in the body:
|
Homogeneous mixtures |
Heterogeneous mixtures |
|---|---|
|
Fecal matter |