Lewis notation, sometimes called the electron dot structure, is used to represent the chemical symbol of an atom and its valence electrons.
In order to construct the Lewis notation of an atom, the number of valence electrons must be determined and precise rules must be followed. The resulting notation provides information about the chemical bonds that this atom can form with one or several other atoms.
Valence electrons are the electrons located on the last electron shell of an atom.
The number of valence electrons in an atom can be determined by referring to the Rutherford-Bohr atomic model: simply count the electrons located on the last electron shell, which is the shell farthest from the nucleus.
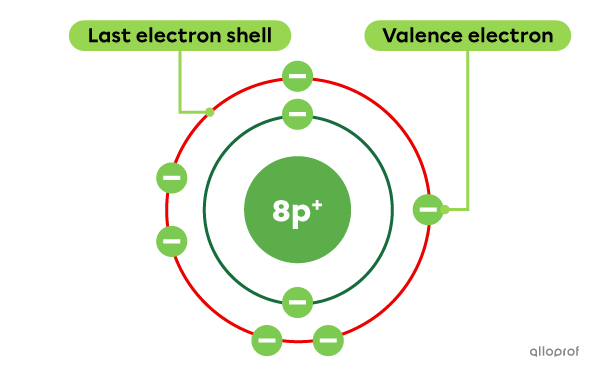
Oxygen |(\text{O})| is an element with a total of 8 electrons. Of these 8 electrons, 6 are located on the last electron shell. Therefore, oxygen has 6 valence electrons.
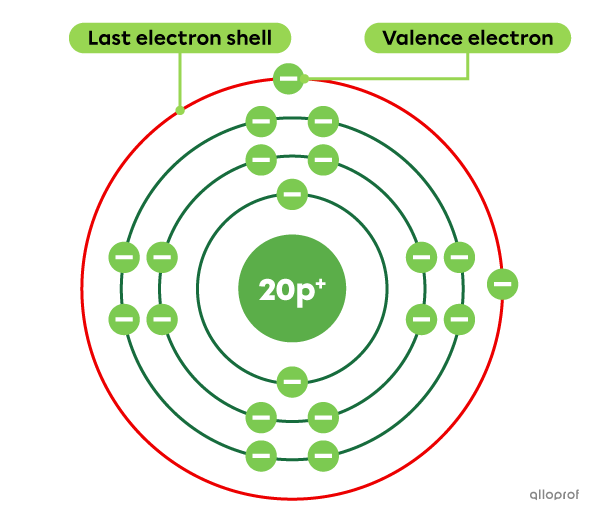
Calcium |(\text{Ca})| is an element with a total of 20 electrons. Of these 20 electrons, 2 are located on the last electron shell. Therefore, calcium has 2 valence electrons.
The number of valence electrons of an atom of a given element can also be determined by referring to the periodic table.
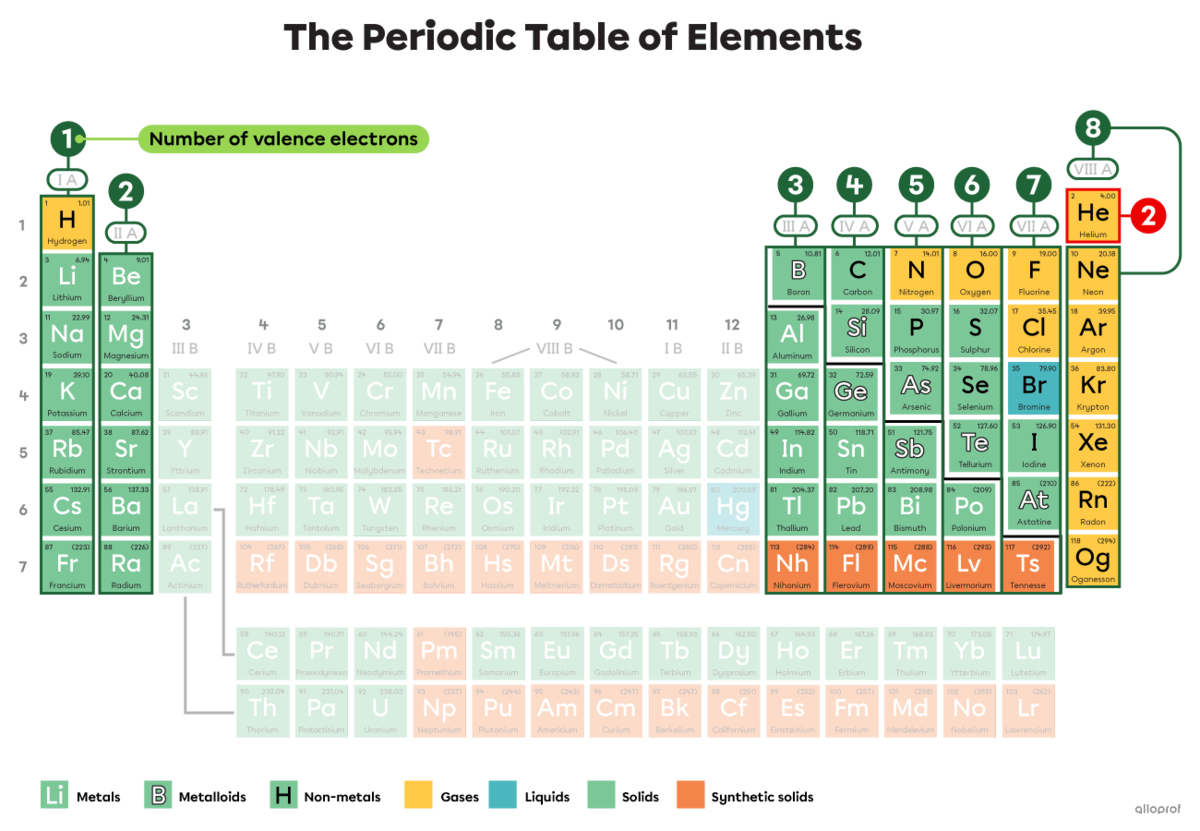
In this periodic table, some elements are highlighted. The number of valence electrons of these elements corresponds to the roman numeral indicating the group number to which they belong. For example, atoms in Group IA have 1 valence electron. Atoms in Group IIA have 2 valence electrons. Atoms in Group IIIA have 3, and so on.
Helium |(\text{He})| belongs to Group VIIIA, but it has only 2 valence electrons.
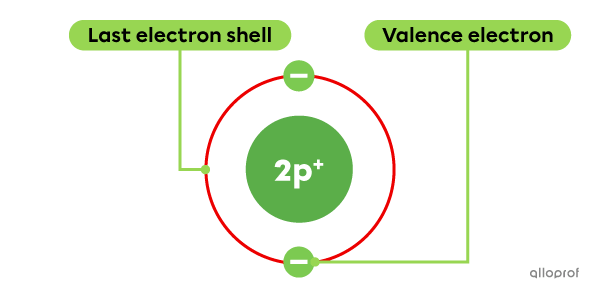
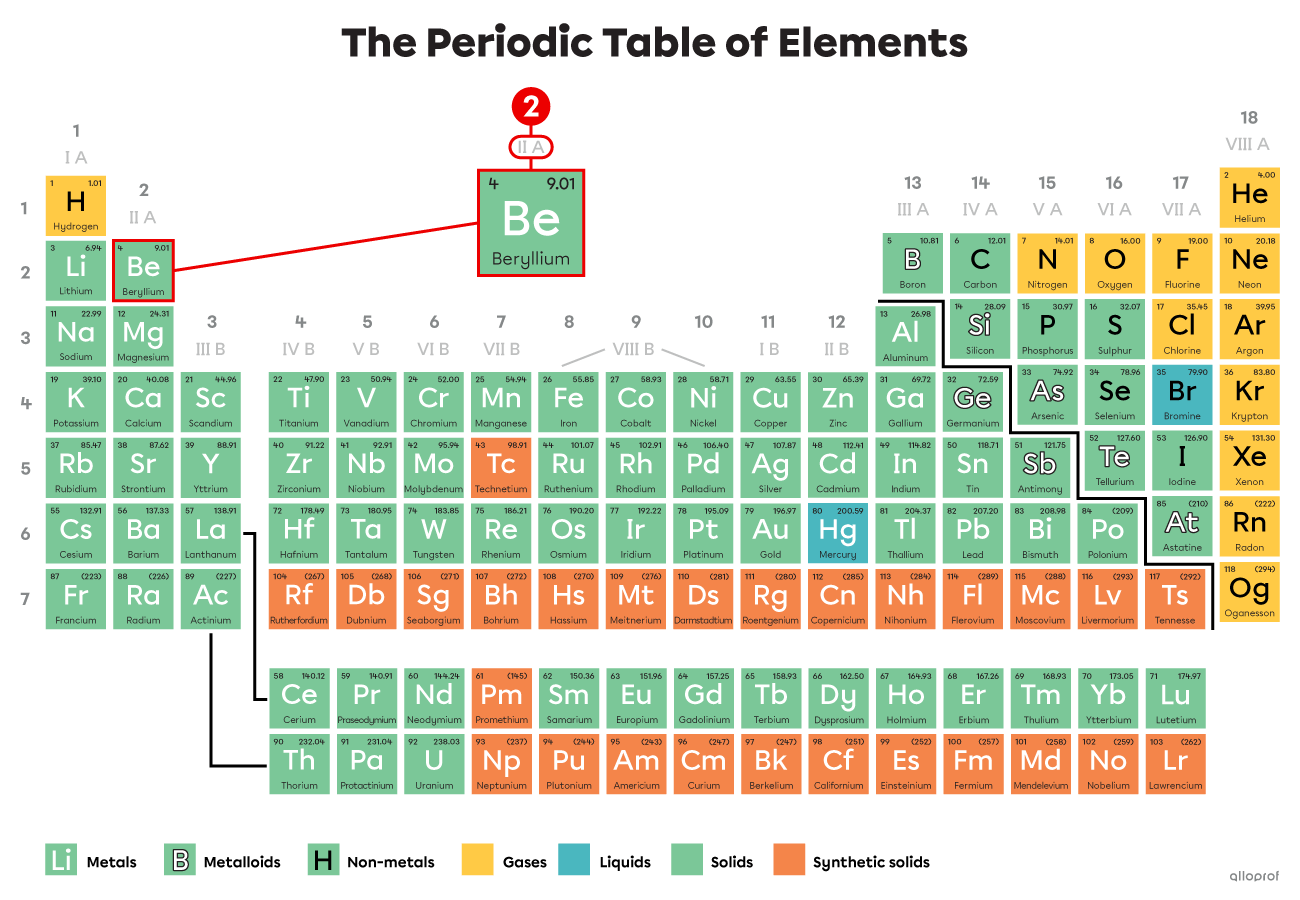
How many valence electrons does beryllium |(\text{Be})| have?
Beryllium |(\text{Be})| belongs to Group IIA. Therefore, it has 2 valence electrons.
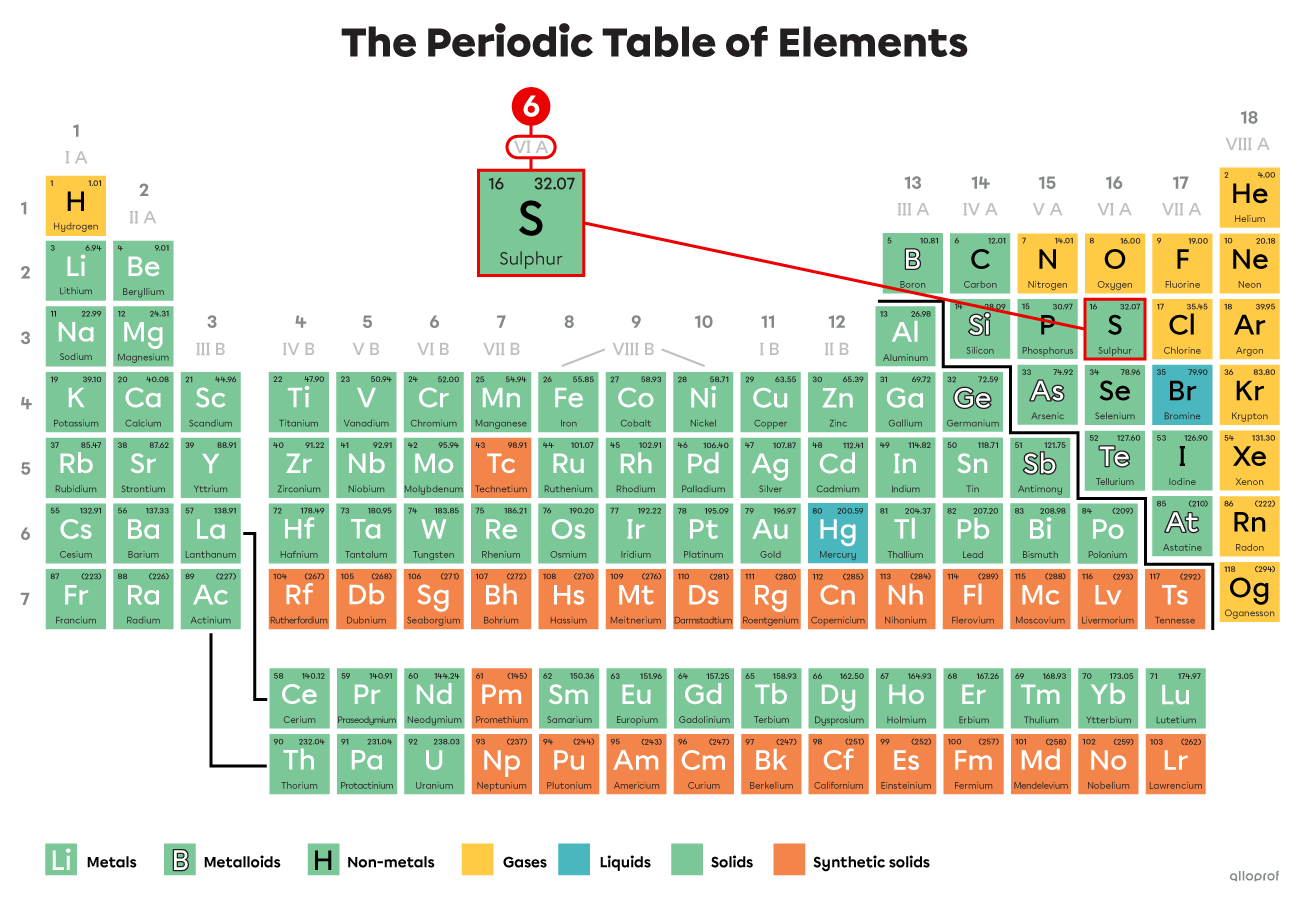
How many valence electrons does sulphur |(\text{S})| have?
Sulphur |(\text{S})| belongs to Group VIA. Therefore, it has 6 valence electrons.
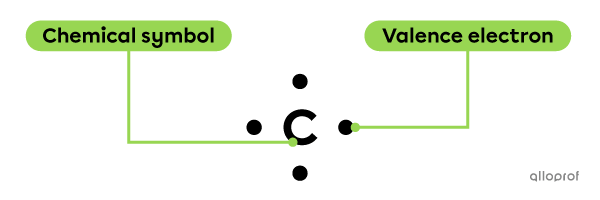
The Lewis notation of a given atom includes its chemical symbol and its valence electron(s), symbolized by dots.
The valence electrons must be placed around the atom's symbol according to specific rules.
-
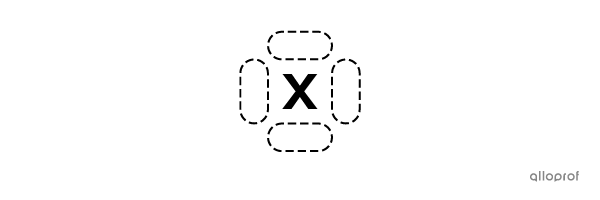
There are four sides around the chemical symbol of an atom where the valence electrons can be placed.
-
A maximum of 2 electrons can be placed on each side.
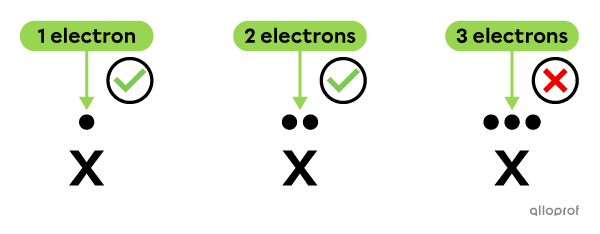
-
The valence electrons are distributed one at a time on each side, before being placed in pairs.
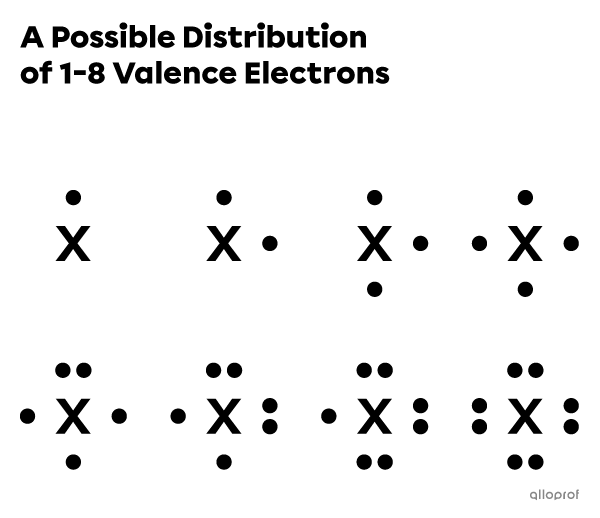

Helium |(\text{He})| has 2 valence electrons. It is an exception to the last rule, because these electrons must be placed together in the following way.

When representing the Lewis notation of an atom, some electrons can be found in pairs. They are called lone pairs of electrons. The other electrons are said to be unpaired.
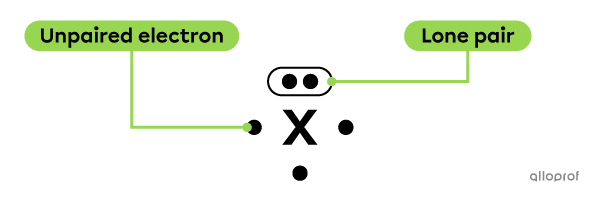
The lone pairs are placed parallel to the sides of the chemical symbol.
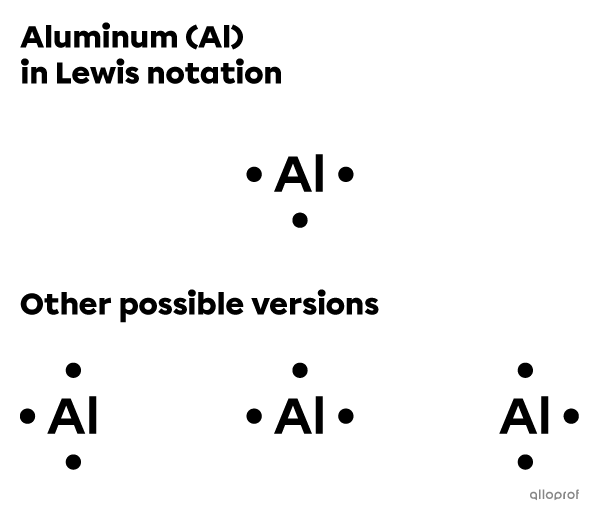
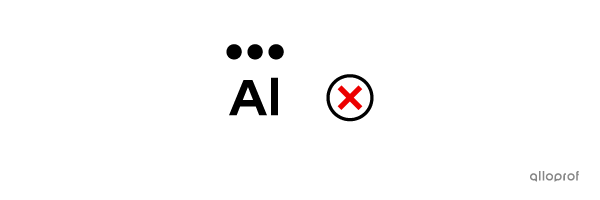
Represent the aluminum atom |(\text{Al})| using Lewis notation.
The aluminum atom |(\text{Al})| belongs to Group IIIA. Therefore, it has 3 valence electrons.
-
Write the chemical symbol of the element (Al).
-
Distribute the 3 valence electrons around the symbol one at a time on each side.
There are several ways to represent aluminum using Lewis notation. In all versions, there are 3 unpaired electrons.

Beware of common mistakes!
-
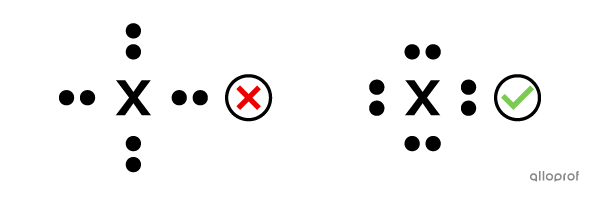
The electrons cannot be placed on one side of the symbol in groups of 3. According to the rules, each side can hold a maximum of 2 electrons.
-
The electrons should not be paired right away. They should be placed one at a time before forming lone pairs.

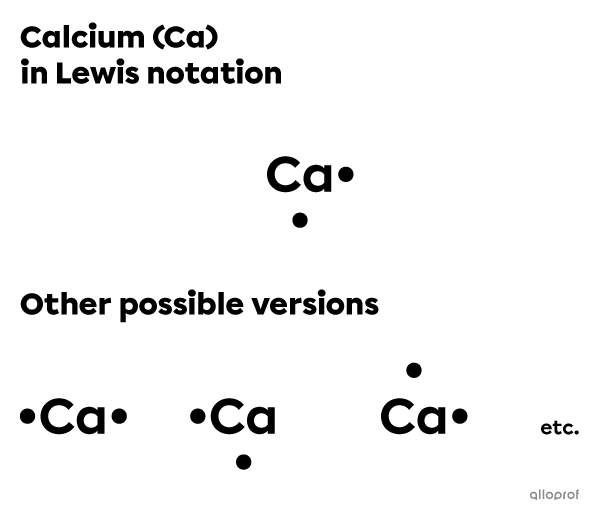
Represent the calcium atom |(\text{Ca})| using Lewis notation.
The calcium atom |(\text{Ca})| belongs to Group IIA. Therefore, it has 2 valence electrons.
-
Write the chemical symbol of the element (Ca).
-
Distribute the 2 valence electrons around the symbol one at a time on each side.
There are several ways to represent calcium using Lewis notation. In all versions, there are 2 unpaired electrons.

Beware of common mistakes!
The 2 electrons cannot be grouped on one side of the symbol. According to the rules, they should be placed one at a time before forming lone pairs.

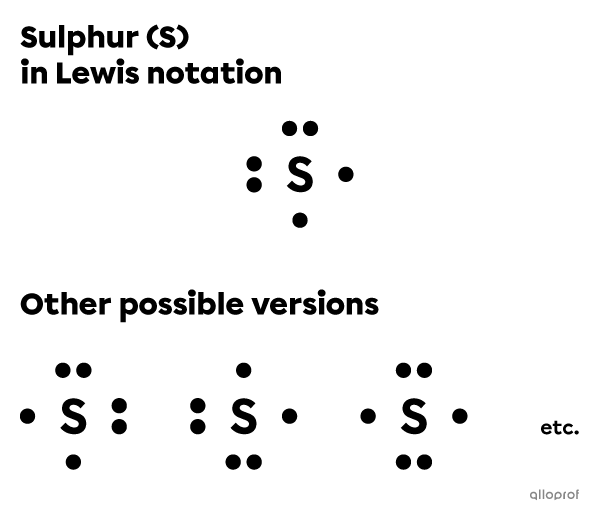
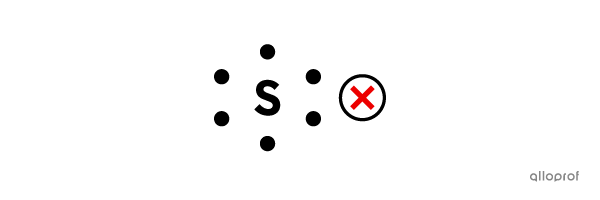
Represent the sulphur atom |(\text{S})| using Lewis notation.
The sulphur atom |(\text{S})| belongs to Group VIA. Therefore, it has 6 valence electrons.
-
Write the chemical symbol of the element (S).
-
Distribute the 6 valence electrons around the symbol one at a time on each side.
There are several ways to represent sulphur using Lewis notation. In all versions, there are 2 lone pairs and 2 unpaired electrons.

Beware of common mistakes!
-
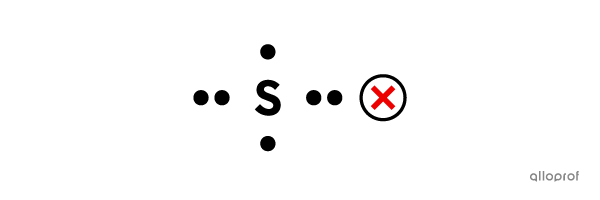
The 6 electrons cannot be spaced out evenly around the symbol. According to the rules, once an electron is placed on each of the four sides of the symbol, the following electrons should pair up with them to form lone pairs.
-
The electrons cannot be placed on one side of the symbol in groups of 3. According to the rules, each side can hold a maximum of 2 electrons.

-
The electrons should not be paired right away. They should be placed one at a time on each side before forming lone pairs.

-
The lone pairs cannot be placed as shown here. They are placed parallel to the sides of the chemical symbol.
In addition to representing individual atoms, Lewis notation is used to represent chemical bonds between atoms in molecules and in ionic compounds.
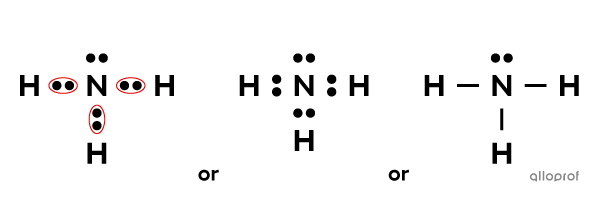
Ammonia |(\text{NH}_3)| is a molecule with one nitrogen atom |(\text{N})| bound to three hydrogen atoms |(\text{H}).| The atoms in this molecule are bound by covalent bonds.
The Lewis notation of ammonia looks as follows.
Sodium chloride |(\text{NaCl})| is an ionic compound composed of a sodium ion |(\text{Na}^+)| bound to a chlorine ion |(\text{Cl}^-).| The interaction between the positive charge of the sodium and the negative charge of the chlorine creates an ionic bond.
The Lewis notation for sodium chloride looks as follows.

To learn more about the Lewis notation of molecules and ionic compounds, you can consult the different sections of the concept sheet on ionic and covalent bonds.