Choose your level.
A molecule is a group of at least two chemically bonded atoms.
In reality, a molecule is a group of at least two non-metals that are chemically bonded together. Once the atoms featured in the following image are bonded, they form a molecule. Metals, due to their properties, do not form molecules but another type of substance. This concept is taught in more detail in Secondary 4, when the distinction between metals and non-metals is discussed.
Note: Cases involving metalloids are not explored in Secondary School (High School).
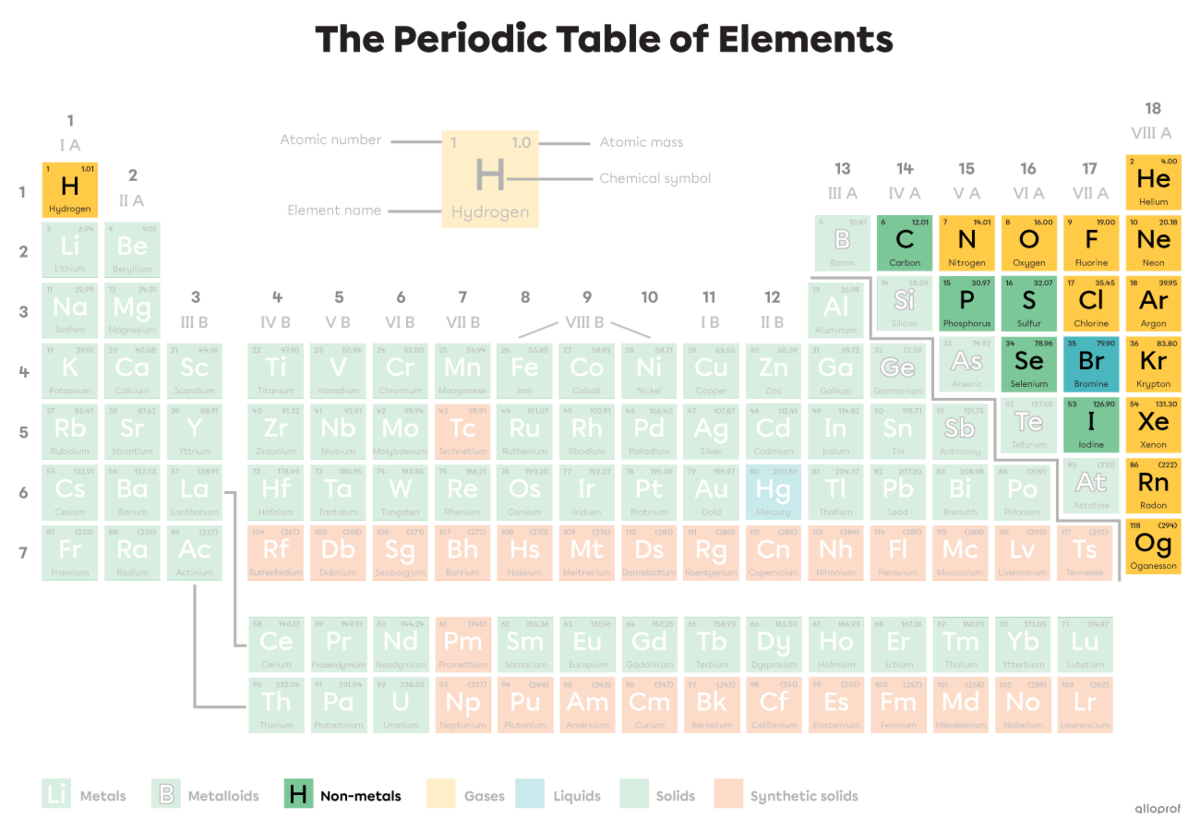
According to Dalton’s atomic model, atoms are represented by coloured balls. Therefore, a molecule is represented by a combination of at least 2 balls.
The molecule represented by the following model is a combination of three chemically bonded atoms.
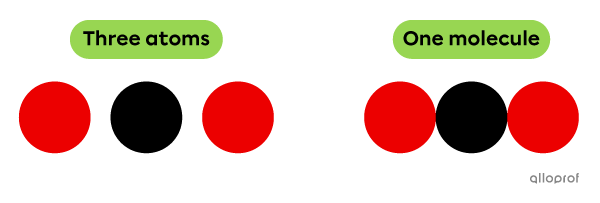
The periodic table of elements is where all elements are found, meaning all types of atoms. A molecule is a combination of at least two atoms that are found in the periodic table. They can be the same type or different types.
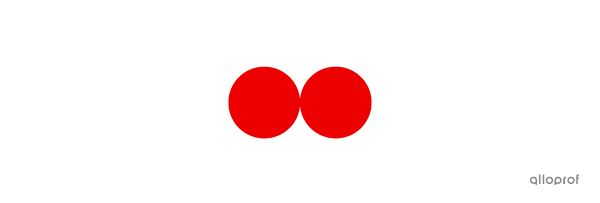
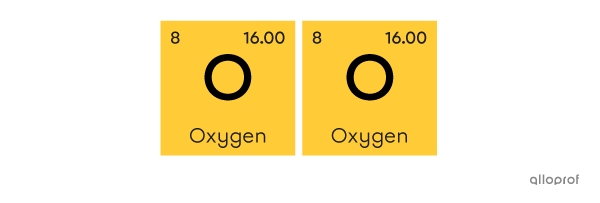
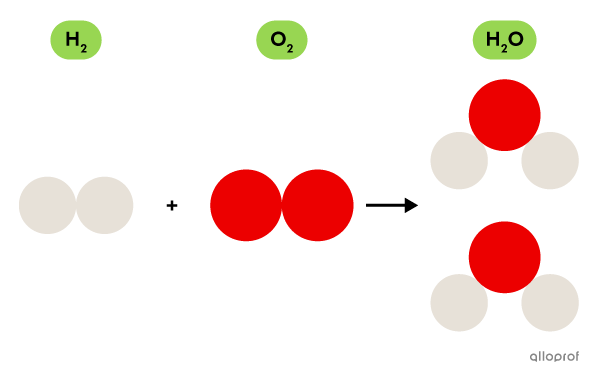
A molecule of oxygen |\text{(O}_2)| is made of two atoms of oxygen |(\text{O}).|
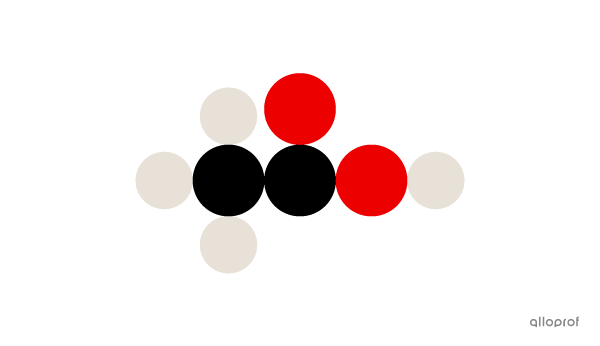
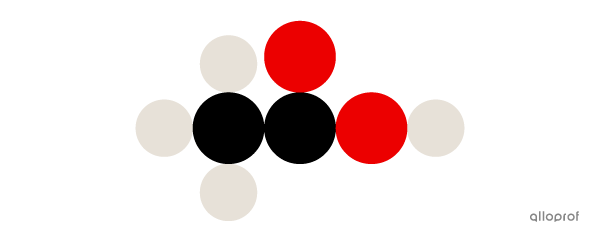
A molecule of acetic acid |(\text{CH}_3\text{COOH})| is made of four atoms of hydrogen |(\text{H}),| two atoms of carbon |(\text{C})| and two atoms of oxygen |(\text{O}).|
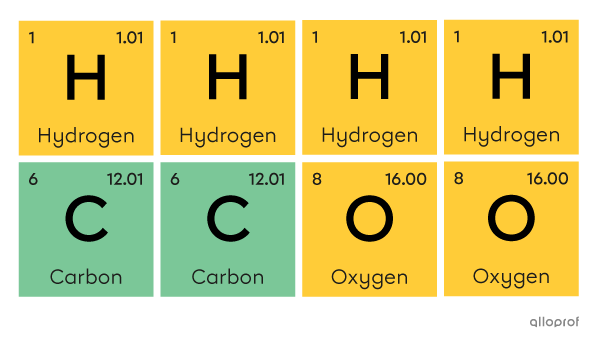
In order to recognize a molecule using its chemical formula, look at the types of capital letters and/or subscripts.
Every type of atom (element) has a unique symbol that contains only one capital letter. Therefore, a chemical formula that contains several capital letters indicates that there are several types of atoms. For example, |\text{HCl}| contains 2 capital letters. Therefore, this substance contains two types of atoms: hydrogen and chlorine. It’s a molecule.
In a chemical formula, a subscript indicates the number of atoms of a given type. The subscripts are written only when more than one atom of the same type is included. Remember, when there is a subscript, there is more than one atom. For example, |\text{I}_2| has a subscript of |2.| This substance contains two atoms of iodine |(\text{I}).| It is a molecule.
A molecule does not have the same properties as the elements that compose it.
Once the chemically bonded atoms separate and rearrange their bonds in a different way, they form new molecules. These new molecules do not have the same properties as the initial molecules despite the fact that they are made of the same atoms and a chemical reaction occurred.
A water molecule is formed from oxygen |(\text{O})| and hydrogen |(\text{H}).|
Molecular oxygen |(\text{O}_2)| made of oxygen atoms |(\text{O})| is a gas essential for respiration. Molecular hydrogen |(\text{H}_2)| made of hydrogen atoms |(\text{H})| is a combustible gas.
The water molecule |(\text{H}_2\text{O})| itself is neither essential for respiration nor combustible. Instead, one of its main properties is its ability to dissolve many substances, such as salt, sugar and carbon gas, for example.
Even if the molecule |\text{H}_2\text{O}| is formed by atoms that are found in the |\text{O}_2| molecule and in the |\text{H}_2| molecule, the properties of these three molecules are very different.
Pour valider ta compréhension à propos de l’organisation de la matière de façon interactive, consulte la MiniRécup suivante.

A molecule is a group of at least two chemically bonded non-metals.
When metals combine with non-metals, they form salts and not molecules. Salts are also called ionic compounds.
Metalloids are elements with properties that vary depending on the context. Metalloids can form molecules just as easily as salts (ionic compounds).
For example, borane |(\text{BH}_3)| is a molecule, while boron trifluoride |(\text{BF}_3)| is an ionic compound.
A molecule can be identified using its chemical formula or its name.
The chemical formula of a molecule is specifically referred to as the molecular formula. It contains the chemical symbols of all the atoms that make up the molecule. Each chemical symbol is accompanied by a subscript if there is more than one atom of this type present.
It is important to respect nomenclature rules when naming molecules.
The following molecule can be identified either by its common name, methane, or by its chemical formula, |\text{CH}_4.|
-
The |\text{C}| symbol indicates the molecule contains carbon.
-
The lack of subscript next to |\text{C}| means that the molecule only has one atom of carbon.
-
The |\text{H}| symbol indicates the molecule contains hydrogen.
-
The subscript 4 that follows the |\text{H}| means that there are 4 hydrogen atoms in the molecule.

A molecule can be represented using Dalton’s atomic model.
Here, a molecule of acetic acid |(\text{CH}_3\text{COOH})| is represented according to Dalton’s atomic model.
A molecule can also be represented according to Lewis notation and the Rutherford atomic model. Both topics are covered in the Environmental Science and Technology (EST) course.
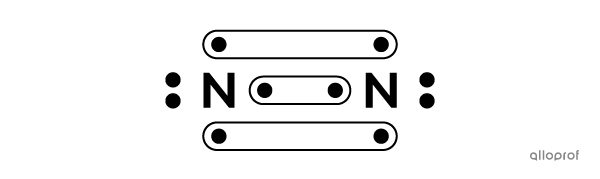
Here, molecular nitrogen |(\text{N}_2)| is represented using Lewis notation.
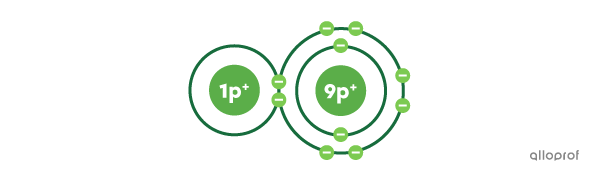
Here, a molecule of hydrofluoric acid |(\text{HF})| is represented using Rutherford-Bohr’s atomic model.