The Rutherford-Bohr atomic model represents the atom by indicating the number of protons in the nucleus as well as the number of electrons in each electron shell (also called energy levels or orbitals).
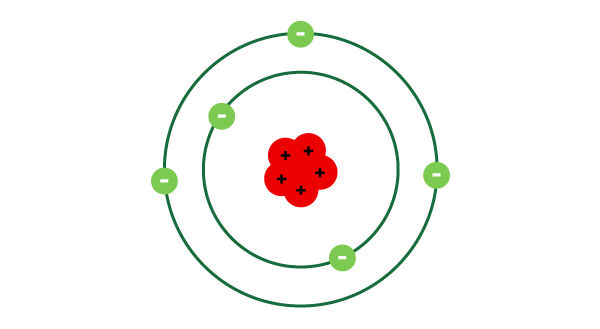
- The atom is represented as mostly empty space with a massive and dense nucleus containing protons in the center.
- Electrons orbit the atom’s nucleus in paths called electron shells, orbitals or energy levels.
- There can be more than one electron per electron shell.
- An electrically neutral atom has as many electrons as there are protons.
- The number of protons, like the number of electrons, corresponds to the element’s atomic number.
To put the Rutherford-Bohr atomic model in its historical context and to learn more about the different atomic models, refer to the concept sheet on the history of the atomic model.
To represent an atom according to the Rutherford-Bohr model, draw the nucleus indicating the number of protons, as well as the correct number of electrons in each electron shell according to the following 4 steps:
The number of protons in an atom corresponds to its atomic number (Z). This information can be found in the periodic table.
Protons are located in the nucleus of an atom. To draw the nucleus, simply draw a circle with the number of protons written in it, that is to say the atomic number, accompanied by "p+", which stands for proton.
The atomic number of boron is 5. Its nucleus, therefore, contains 5 protons.

The number of electrons in an electrically neutral atom is equal to the number of protons. It is, therefore, the same as the atomic number.
Boron has 5 protons. Since it is neutral, it also has 5 electrons.
The electrons must be distributed by first filling the layer closest to the nucleus, then continuing with the other layers.
Three rules must be followed when distributing electrons in the electron shells:
- The first layer can contain a maximum of 2 electrons.
- The following layers can contain a maximum of 8 electrons (this is valid for elements with atomic numbers less than or equal to 20).
- All layers must be filled to the maximum, except the last one, the outermost layer, which may be incomplete.
Boron has 5 electrons in total. The first electronic layer contains a maximum of 2 electrons. So now there are 3 electrons left to be placed.
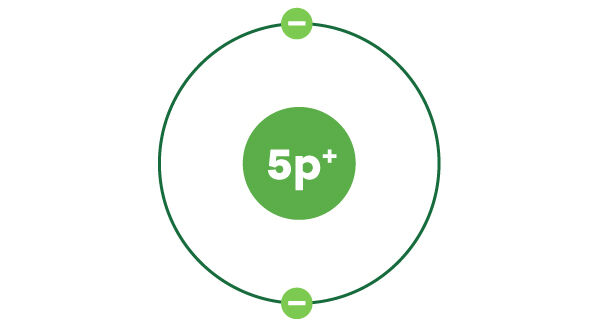
The second shell, which can contain a maximum of 8 electrons, is where the remaining 3 electrons are placed.
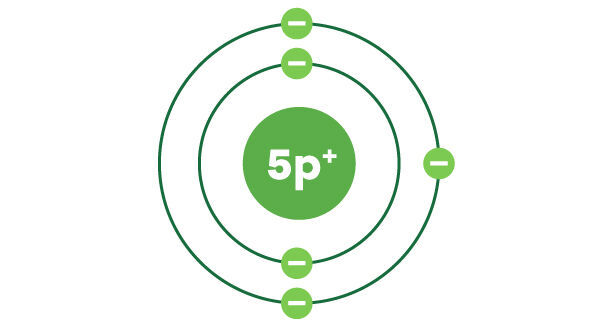
In the first electron shell, the first electron is usually placed at the top of the nucleus and the second electron, at the bottom of the nucleus.
For the second and other electron shells, the first four electrons are placed at the top, right, bottom and left of the nucleus. The remaining electrons are distributed to form electron pairs, as shown in the picture.

It is possible to check whether the electrons have been correctly placed in the electron shells by using the periodic table. The period number represents the number of electron shells for the atom.
As for the family (or group) number, it determines the number of valence electrons, which are the electrons located in the last electron shell.
Pour valider ta compréhension à propos du tableau périodique de façon interactive, consulte la MiniRécup suivante :

Bensaada, A., Bolduc, A., Claude, V., Meziane, M., Rhéaume, C. et Tardif, K. (2012). Kaléidoscope ST-STE - 2e cycle (2e année) (2e éd.). Chenelière Éducation.
Couture, I. et Peyronnet, O. (2009). Synergie, 2e cycle (2e année). [Manuel de l'élève]. Chenelière Éducation.
Khan Academy. (2020). Discovery of the electron and nucleus.
Doud, T. (2014). The 2,400-year search for the atom [video]. TED-Ed.