A chemical group, sometimes referred to as a family, contains the elements that have similar chemical properties. Elements in the same group are placed in the same column in the periodic table of elements.
The groups in the periodic table are each numbered from 1 to 18. The groups studied in high school are 1, 2, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 and 18. They are also numbered with a Roman numeral from I to VIII, followed by the letter A.
The groups studied in high school are shown in colour in the following image while those that are not are shown in grey.
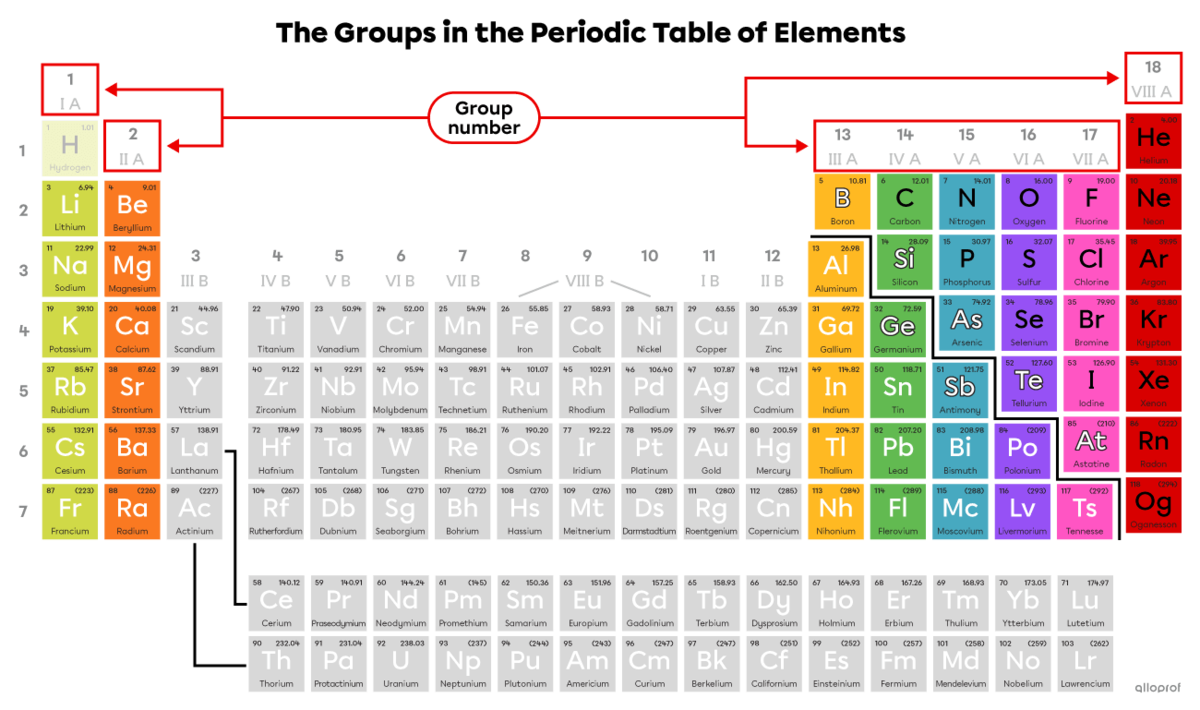
Note: Even though hydrogen |(\text{H})| is placed with the elements of Group 1 (IA), it does not belong to any chemical group.
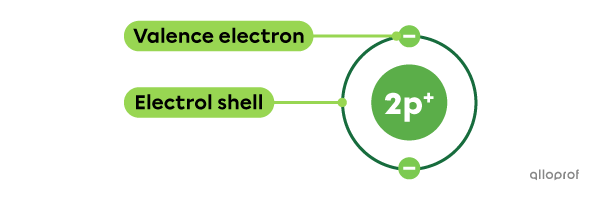
Valence electrons are electrons found on the outermost electron shell of an atom.
The number of valence electrons in an atom of a given group corresponds to its Roman numeral or the last digit of its Arabic numeral.
|
Arabic group numeral |
1 |
2 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Roman group numeral |
IA |
IIA |
IIIA |
IVA |
VA |
VIA |
VIIA |
VIIIA |
|
Number of valence electrons |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
Helium |(\text{He})| is in Group 18 (VIII A). However, it only has 2 valence electrons, not 8. Why was it classified in Group 18 and not 2 (II A)? Because it has a complete electron shell, like the other elements in Group 18. Helium's only electron shell can contain a maximum of 2 electrons. This characteristic gives it chemical properties similar to those of the other elements in Group 18.
The first two and last two groups on the periodic table are of interest because of their particular chemical properties. These groups have a specific name, given to them according to a property common to the elements they group together.
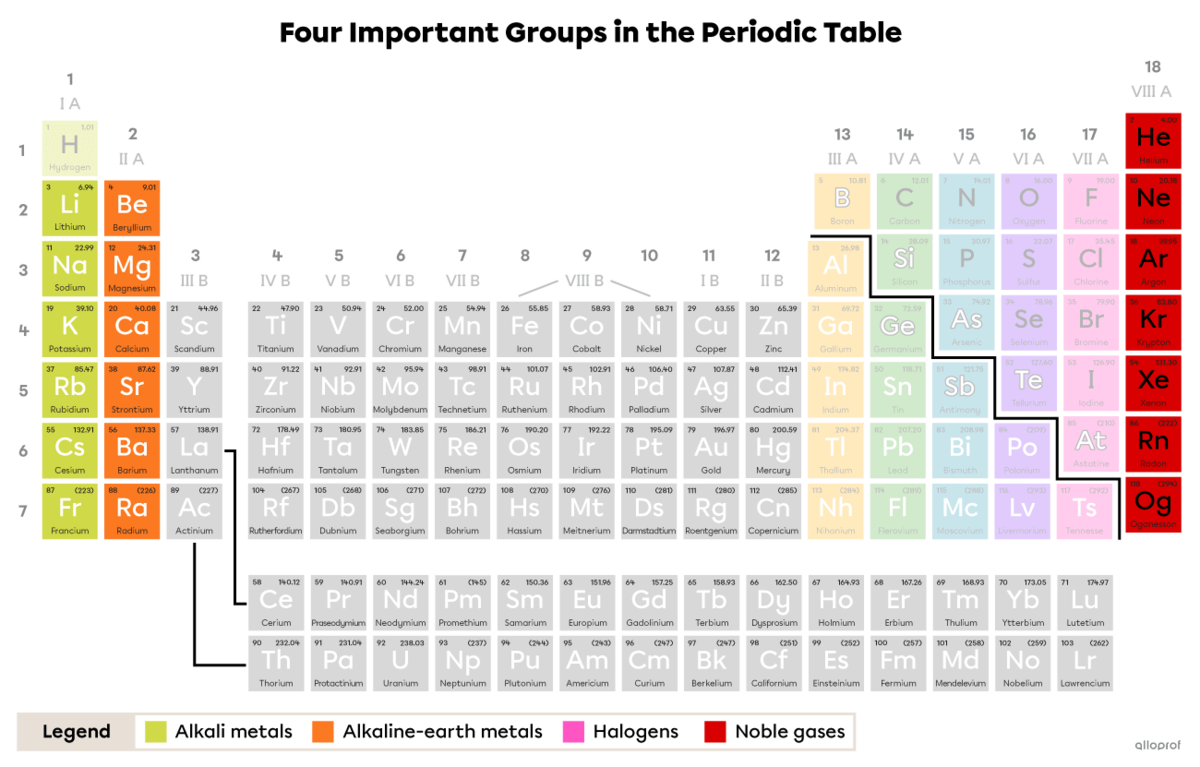
Although hydrogen |(\text{H})| is in the first column in the periodic table and has only one valence electron, it is not part of the alkali metals group. It is in a group of its own, sometimes behaving like an alkali element and sometimes like a halogen.
-
Group 1 or IA.
-
Alkali metals have 1 valence electron.
-
They are highly reactive, especially with halogens. They also react with water to form bases, which explains the root of the group’s name. Alkaline is a synonym for basic.
-
They are stored in oil to prevent reactions with the water vapour in the air.
-
They are soft, highly malleable and ductile metals with good electrical conductivity.
-
Hydrogen is not a member of the alkali family, even though it is in the same column in the periodic table.
-
Group 2 or IIA.
-
Alkaline-earth metals have 2 valence electrons.
-
They are reactive, especially with halogens. They also react with water to form bases, which explains the first part of the group’s name. Alkaline is a synonym for basic.
-
These metals are less soft than alkalis. They are malleable, ductile and very good conductors of electricity.
-
They are found in large quantities in the Earth's crust, which explains the second part of the group’s name.
-
Group 17 or VIIA.
-
Halogens have 7 valence electrons.
-
They are very reactive. They react with metals to form salts, which explains the origin of the group's name. Halogen comes from the Greek hals gennân, which means to generate a salt. Halogen gases also react with hydrogen |(\text{H})| to form acids.
-
Halogens have disinfectant properties. Chlorine, for example, is used to disinfect water.
-
Group 18 or VIIIA.
-
In noble gases, the electron shell furthest from the nucleus is complete. Helium has 2 valence electrons, while neon, argon, krypton and xenon have 8 valence electrons.
-
Noble gases are not very reactive. They do not tend to react unless they are subjected to special conditions in the laboratory. This is why they are sometimes called inert gases. They are also referred to as rare gases because of their low relative abundance in the air.
-
They are in a gaseous state under ambient conditions.
-
They emit light when an electric current is passed through them. This is why they are used in light signs.

Source: Neon [Online image], Pslawinski, Wikimedia Commons, (https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:NeTube.jpg). Rights reserved*[1]
Pour valider ta compréhension à propos du tableau périodique de façon interactive, consulte la MiniRécup suivante.

-
Pslawinski (Octobre 22, 2005). Neon [Online image]. Wikimedia Commons. (https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:NeTube.jpg). *Content used by Alloprof in compliance with the Copyright Act in the context of fair use for educational purposes. [https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/c-42/page-9.html].