Certain properties that chemical elements have in common allow them to be grouped into three categories:
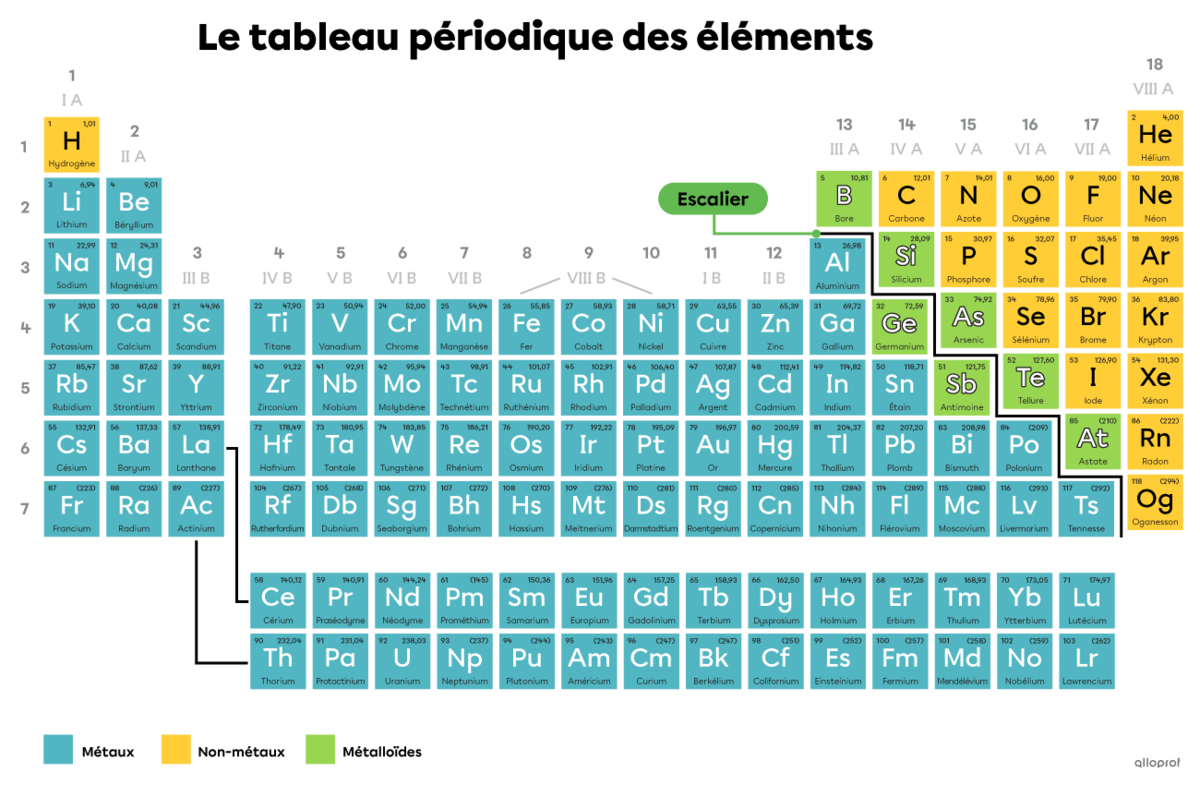
In a periodic table, a legend is generally used to clearly identify which elements are metals, non-metals and metalloids. In addition, a thicker line in the form of a staircase separates the metals from the non-metals and makes it easier to identify the metalloids.
Note: An image in English is coming soon!
Metals are the largest category of chemical elements. In a periodic table, they are found to the left of the staircase line.
Note: An image in English is coming soon!
Metals share the following main characteristics.
-
They are generally brightly coloured and have a shiny luster.
-
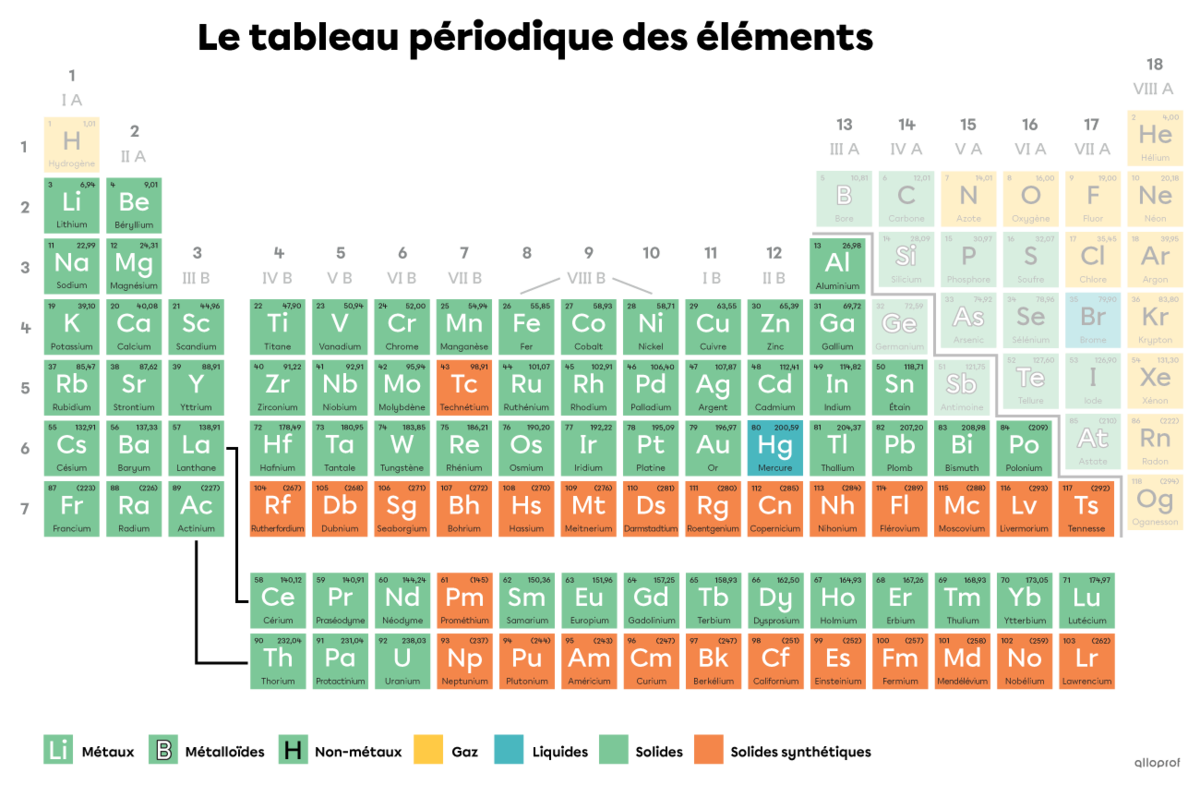
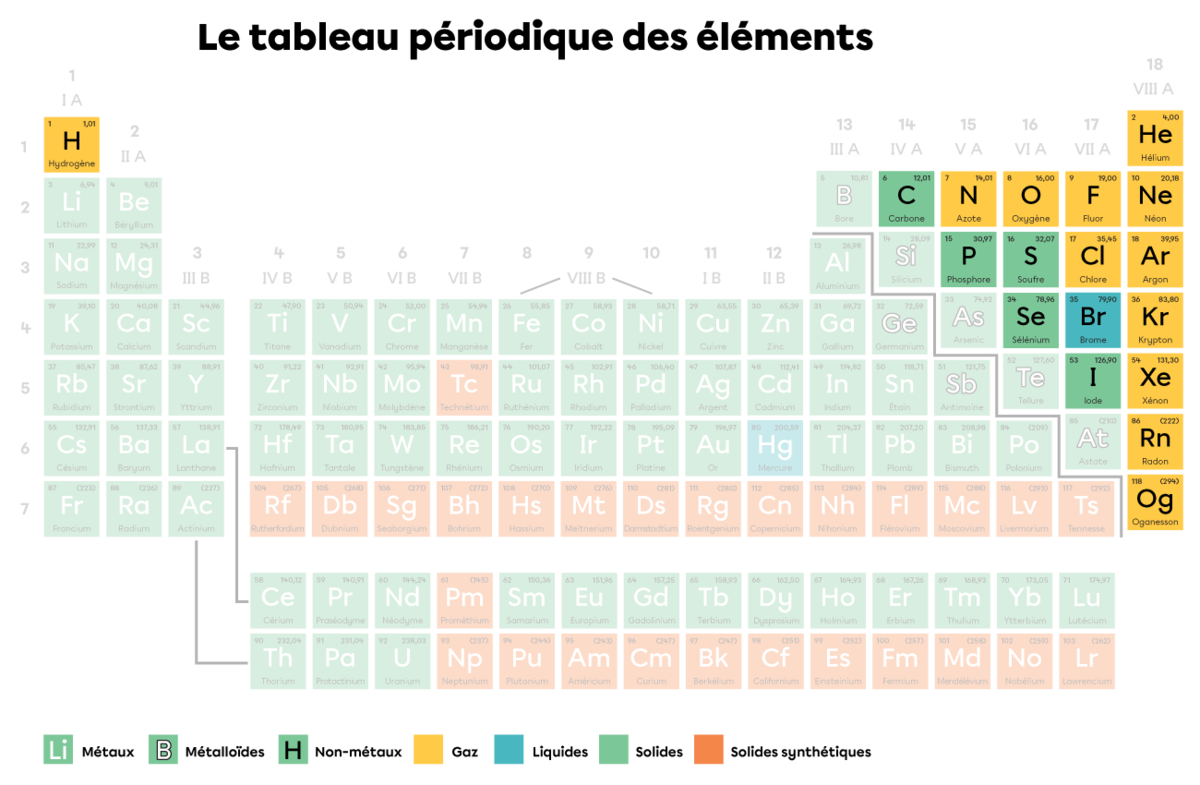
They are all solid at room temperature, except for mercury (Hg), which is a liquid.
-
They are good electrical and thermal conductors.
-
They generally form compounds with non-metals.
-
They tend to form positive ions. They are electron donors when they form compounds.
-
They generally react with acids.
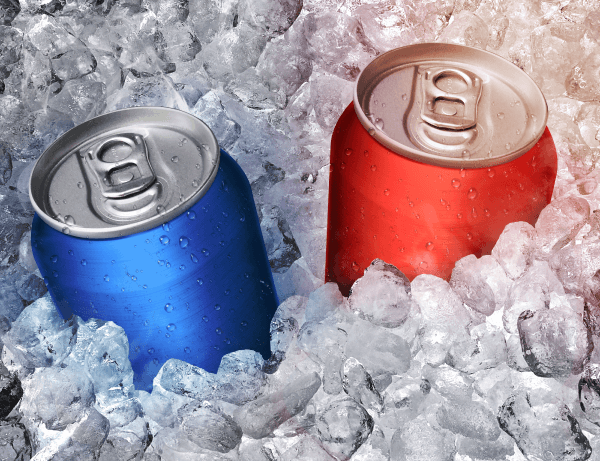

Source : aresunteanu, Shutterstock.com
Aluminum is a metal. Because it is so malleable, it is easy to shape into cans for beverages. Also, its good thermal conductivity allows beverages to cool quickly when placed in cold storage.
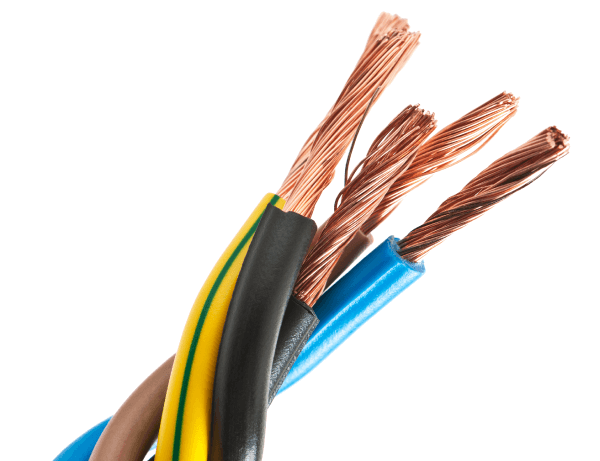
Source : TADDEUS, Shutterstock.com
Copper is a metal. In addition to being a good electrical conductor, it is ductile, which means it can be stretched to make electrical wires.
In a periodic table, the non-metals are all located to the right of the staircase line, except for hydrogen |(\text{H}).|
Note: An image in English is coming soon!
Non-metals have properties that are the opposite of metals. Here are the main common characteristics of non-metals:
-
They are generally dull in colour.
-
The majority of non-metals are gaseous at 0°C. In fact, 12 of them are gaseous, five are solid and one is liquid.
-
In their solid state, they are fragile, brittle and non-ductile.
-
They are good insulators, because they are poor electrical and thermal conductors.
-
They can form compounds with metals.
-
They tend to form negative ions. They receive electrons when they form compounds.
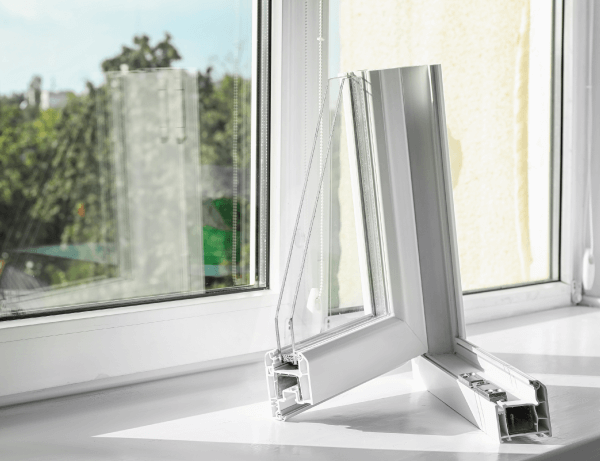

Source : New Africa, Shutterstock.com
Argon is a gaseous non-metal at room temperature. Since it is a good insulator, it is used in the manufacture of insulated windows, where it is injected and trapped between two sheets of glass.
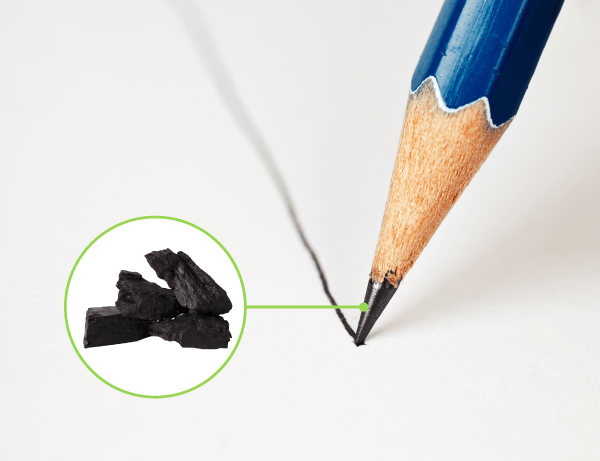
Sources : Adapté de Evgenii Ivanov, Shutterstock.com et de Kucher Serhii, Shutterstock.com
Carbon is a non-metal that is solid at room temperature. It is used in the form of graphite in the manufacture of pencil leads. Because it is brittle, it breaks off and leaves marks when pressed against paper.
In a periodic table, the metalloids are arranged around the staircase line.
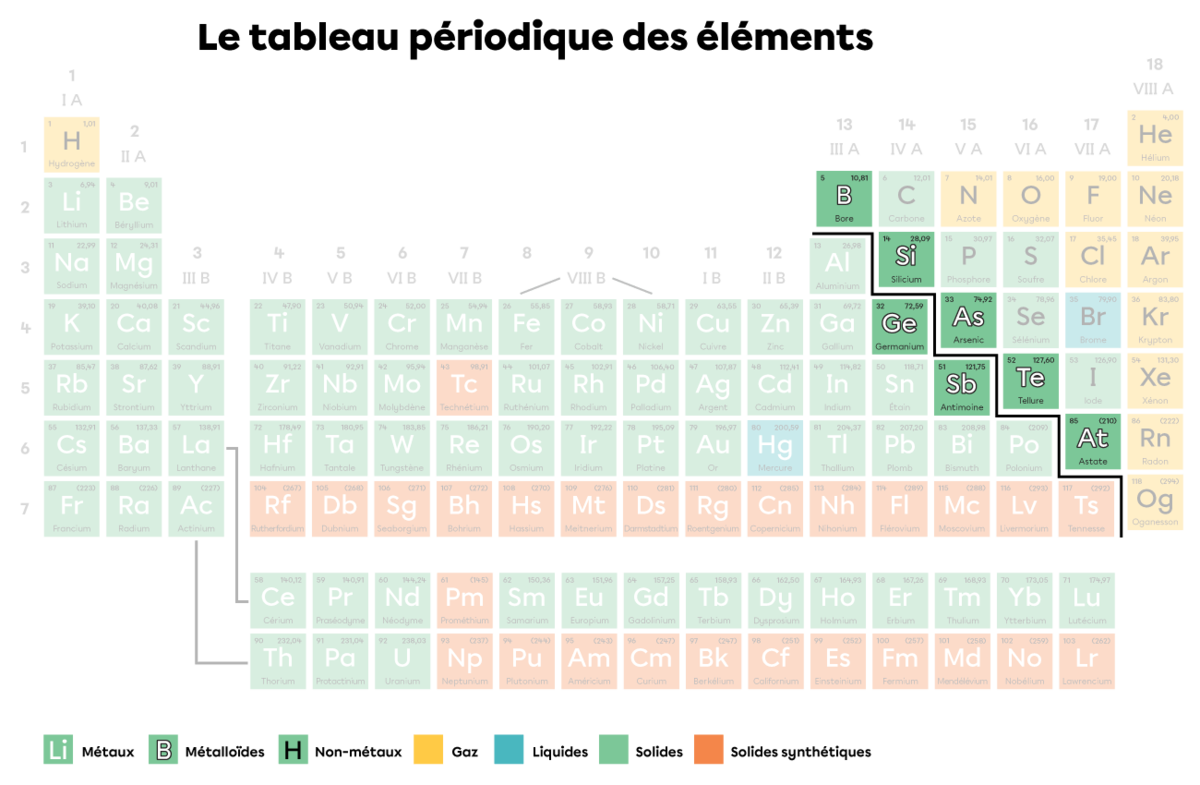
Remarque : The elements belonging to metalloids sometimes differ from one textbook to another. Carbon |(\text{C}),| selenium |(\text{Se})| and polonium |(\text{Po})| are sometimes identified as metalloids.
Note: An image in English is coming soon!
Metalloids are a group of elements that share certain properties with metals and others with non-metals. The metalloids to the left of the staircase–germanium |(\text{Ge})| and |(\text{Sb})--| share more properties with metals than with non-metals. Conversely, the metalloids to the right of the staircase–boron |(\text{B}),| silicon |(\text{Si}),| arsenic |(\text{Ar}),| tellurium |(\text{Te})| and astatine |(\text{At})--| share more properties with non-metals than with metals.
Metalloids are also considered to be semiconductors, since their electrical conductivity varies according to certain parameters, such as temperature. They can therefore be insulators or conductors.
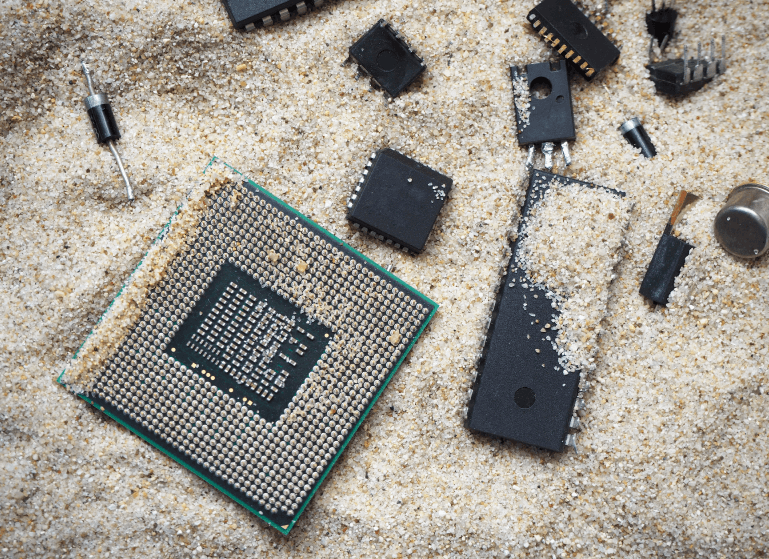

Source : Hsyn20, Shutterstock.com
Silicon is a metalloid. Once extracted from sand, it is used in the manufacture of many electronic components, such as processors, microchips, integrated circuits, transistors and diodes.