Occasionally, you may be asked to find one or more missing measurements from the perimeter or area of a figure. To solve problems related to area, it is useful to know the area formulas for different plane figures. Here are the steps to follow to solve this type of problem.
-
Determine the right area formula to be used.
-
Replace the variables with the known values.
-
Isolate the unknown variable.
-
Answer the question.
Here are a series of examples. The first are abstract geometry problems, while the last one is a word problem that includes a short scenario.
Find the measure of the side of the following square.
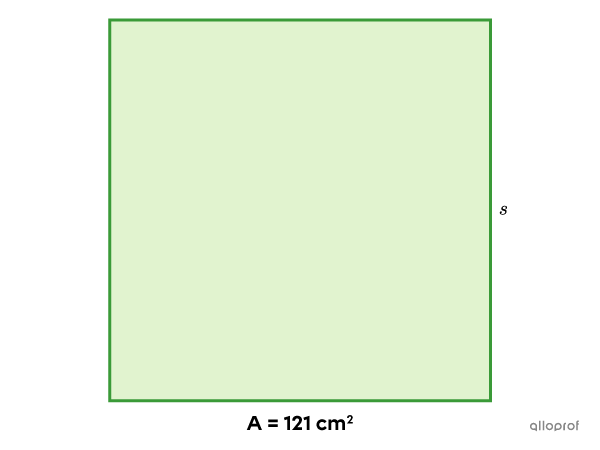
-
Determine the formula
We will use the formula for the area of a square.
||A= s^2|| -
Replace the variables with the known values
||\color{#3a9a38}{121}= s^2|| -
Isolate the unknown
||\begin{align}\color{#ec0000}{\sqrt{\color{black}{121}}}&=\color{#ec0000}{\sqrt{\color{black}{s^2}}}\\11&=s \end{align}|| -
Answer the question
The side of the square measures |11\ \text{cm}.|
Find the measure of the height of the following triangle.
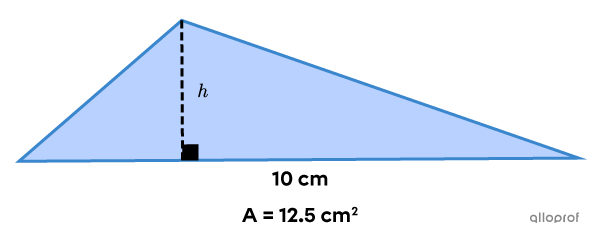
-
Determine the formula
Use the formula to calculate the area of a triangle.
||A=\dfrac{b\times h}{2}|| -
Replace the variables with the known values
||\color{#3a9a38}{12.5} =\dfrac{\color{#3a9a38}{10} \times h}{2}|| -
Isolate the unknown
||\begin{align}12.5\color{#ec0000}{\times 2}&=\dfrac{10h}{2} \color{#ec0000}{\times 2}\\25&=10h\\ \color{#ec0000}{\dfrac{\color{black}{25}}{10}}&=\color{#ec0000}{\dfrac{\color{black}{10h}}{10}}\\ 2.5 &= h\end{align}|| -
Answer the question
The height of the triangle is |2.5\ \text{cm}.|
Find the measure of the large base of the following trapezoid.
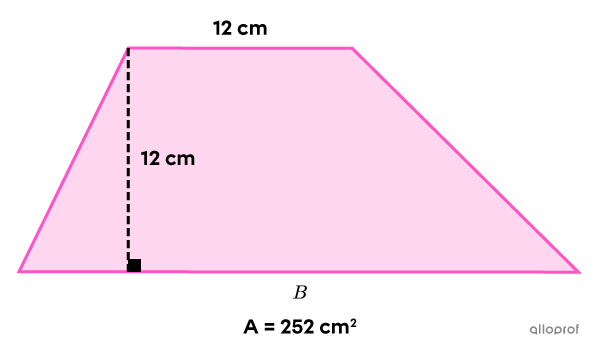
-
Determine the formula
Use the formula to calculate the area of a trapezoid.
||A=\dfrac{(B+b)\times h}{2}|| -
Replace the variables with the known values
||\color{#3a9a38}{252}=\dfrac{(B+ \color{#3a9a38}{12})\times \color{#3a9a38}{12}}{2}|| -
Isolate the unknown
||\begin{align}252&=\dfrac{12B+144}{2}\\252 \color{#ec0000}{\times 2}&= \dfrac{12B+144}{2}\color{#ec0000}{\times 2}\\ 504&= 12B+144\\ 504\color{#ec0000}{-144}&= 12B+ 144\color{#ec0000}{-144}\\360&=12B\\
\color{#ec0000}{\dfrac{\color{black}{360}}{12}}&= \color{#ec0000}{\dfrac{\color{black}{12B}}{12}}\\ 30&=B\end{align}|| -
Answer the question
Therefore, the large base measures |30\ \text{cm}.|
Find the measure of the apothem of the following regular hexagon.
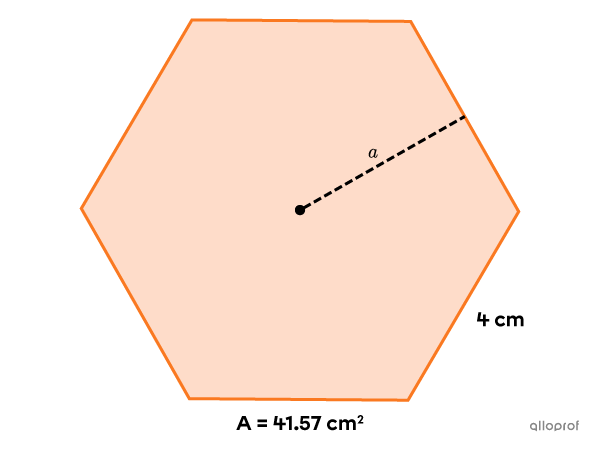
-
Determine the formula
Use the formula to calculate the area of a regular polygon.
||A=\dfrac{s\times a\times n}{2}|| -
Replace the variables with the known values
Since it is a hexagon, |n=6.|
||\color{#3a9a38}{41.57}=\dfrac{\color{#3a9a38}4 \times a \times \color{#3a9a38}6}{2}|| -
Isolate the unknown
||\begin{align}41.57&=\dfrac{24a}{2}\\41.57&=12a\\\color{#ec0000}{\dfrac{\color{black}{41.57}}{12}}&= \color{#ec0000}{\dfrac{\color{black}{12a}}{12}}\\ 3.46 &\approx a \end{align}|| -
Answer the question
The apothem of the regular hexagon measures about |3.46\ \text{cm}.|
Find the measure of the radius of the following circle.
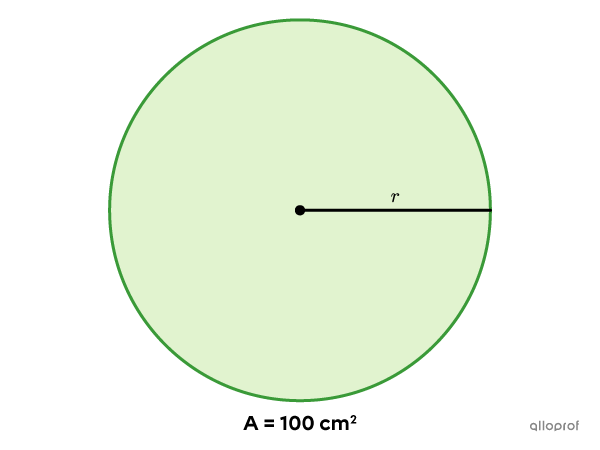
-
Determine the formula
Use the formula to calculate the area of a circle.
||A=\pi r^2|| -
Replace the variables with the known values
||\color{#3a9a38}{100}=\pi r^2|| -
Isolate the unknown
||\begin{align}\color{#ec0000}{\dfrac{\color{black}{100}}{\pi}} &= \color{#ec0000}{\dfrac{\color{black}{\pi r^2}}{\pi}}\\31.83&\approx r^2\\ \color{#ec0000}{\sqrt{\color{black}{31.83}}}&\approx \color{#ec0000}{\sqrt{\color{black}{r^2}}} \\ 5.64 &\approx r \end{align}|| -
Answer the question
The radius measures approximately |5.64\ \text{cm}.|
To ensure maximum safety, a school bus company wants to put glittering lights around the stop arm of its buses. This arm is formed by a rectangle and a regular octagon.
Knowing that the total area of this figure is |15.42\ \text{dm}^2,| determine how many lights can be installed on the contour of the stop arm if the company wants to install lights at every |5\ \text{cm}.|
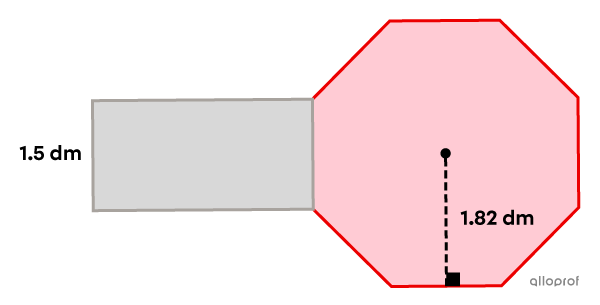
-
Determine the formula
Use the formulas to calculate the area of a rectangle and the area of a regular octagon.
||\begin{align}A_\text{total}&=A_\text{rectangle}+A_\text{octagon}\\A_\text{total}&=b \times h + \dfrac{s\times a\times n}{2}\end{align}|| -
Replace the variables with the known values
The measure of one side of the octagon is the same as the height of the rectangle. Also, since it is an octagon, there are |n=8| sides.
||\color{#3a9a38}{15.42}=b\times \color{#3a9a38}{1.5} + \dfrac{\color{#3a9a38}{1.5}\times \color{#3a9a38}{1.82} \times \color{#3a9a38}8}{2}|| -
Isolate the unknown
||\begin{align} 15.42&=1.5b+\dfrac{21.84}{2}\\15.42&=1.5b+10.92\\15.42\color{#ec0000}{-10.92}&=1.5b+10.92\color{#ec0000}{-10.92}\\4.5&=1.5b\\\color{#ec0000}{\dfrac{\color{black}{4.5}}{1.5}}&=\color{#ec0000}{\dfrac{\color{black}{1.5b}}{1.5}}\\3&=b \end{align}|| -
Answer the question
To find the length of the contour where there will be lights, we must determine the perimeter of the figure, that is, add the measure of each of its sides.
||\begin{align}\text{Perimeter} &= 8 \times 1.5 + 2 \times 3 \\
&= 18\ \text{dm} \\
&= 180\ \text{cm}\end{align}||
Since there are lights at every |5\ \text{cm},| we can install |36,| since |180 \div 5 = 36.|
Note: The side common to both the rectangle and the octagon should not be included in the perimeter since it is not part of the outline of the figure.
Pour valider ta compréhension des mesures manquantes dans les figures planes de façon interactive, consulte la MiniRécup suivante.
