To find the intersection point(s) between a parabola and a conic, we solve one or more system(s) of second-degree equations.
-
Use the appropriate method (comparison, substitution, or elimination) to obtain an equation with one variable.
-
Manipulate the equation so that it equals |0.|
-
Solve the equation to find the value(s) of the isolated variable.
-
Replace the value(s) obtained in one of the original equations to obtain the value(s) of the other variable.
-
Write the coordinates of the point(s) of intersection.
Unlike the intersection between a line and a conic, there are five possible cases regarding the number of solutions:
-
the parabola and the conic do not intersect;
-
the parabola and the conic intersect only at one place, called the point of tangency; or
-
the parabola and the conic intersect in two, three, or four distinct places.
In the following interactive video, select a conic section and drag the cursor to study possible cases.
-
Use the appropriate method to obtain a one-variable equation
Use the substitution method since |y^2| in the parabola’s equation is already isolated.||\begin{align}x^2+\color{#3a9a38}{y^2}&=36\\x^2+\color{#3a9a38}{-16x}&=36\end{align}|| -
Manipulate the equation so that it equals |0|
||\begin{align}x^2-16x&=36\\ \color{#3B87CD}{1}x^2\color{#3A9A38}{-16}x\color{#EC0000}{-36}&=0\end{align}|| -
Solve the equation
Use the quadratic formula to obtain:||\begin{align} x&=\dfrac{-\color{#3A9A38}{b}\pm\sqrt{\color{#3A9A38}{b}^2-4\color{#3B87CD}{a}\color{#EC0000}{c}}}{2\color{#3B87CD}{a}}\\\\ &=\dfrac{-(\color{#3A9A38}{-16})\pm\sqrt{(\color{#3A9A38}{-16})^2-4(\color{#3B87CD}{1})(\color{#EC0000}{-36})}}{2(\color{#3B87CD}{1})}\\\\ &=\dfrac{16\pm\sqrt{400}}{2}\\\\ x&\in\{-2,18\} \end{align}||The equation shows that the parabola is horizontal and open to the left. Thus, reject |x=18,| since the function does not exist at this value.||x=-2|| -
Substitute the values obtained in one of the starting equations
||\begin{align} y^2&=-16\color{#3A9A38}{x}\\ &=-16(\color{#3A9A38}{-2})\\ &=32\\ y&=\pm\sqrt{32}\\\\ y_{\small{A}}&\approx5{.}66\\ y_{\small{B}}&\approx-5{.}66 \end{align}|| -
Write the coordinates of the points of intersection
The coordinates of the two points of intersection between the parabola |y^2=-16x| and the circle |x^2+y^2=36| are |A(-2,5{.}66)| and |B(-2,-5{.}66).|

-
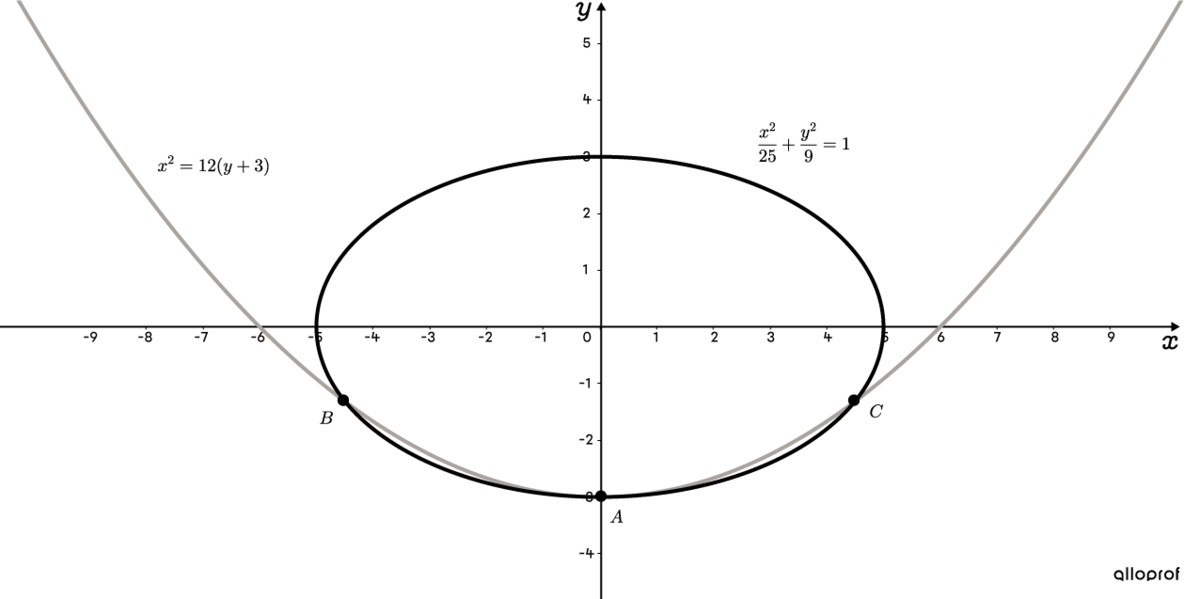
Use the appropriate method to obtain a one-variable equation
Use the substitution method, since |x^2| in the parabola’s equation is already isolated.||\begin{align} \dfrac{\color{#3a9a38}{x^2}}{25}+\dfrac{y^2}{9}&=1\\\\ \dfrac{\color{#3a9a38}{12(y+3)}}{25}+\dfrac{y^2}{9}&=1\end{align}|| -
Manipulate the equation so that it equals |0|
||\begin{align}\dfrac{12y+36}{25}+\dfrac{y^2}{9}&=1\\\\ \dfrac{9(12y+36)}{225}+\dfrac{25y^2}{225}&=1\\\\ \dfrac{108y+324+25y^2}{225}&=1\\\\ 25y^2+108y+324&=225\\ \color{#3B87CD}{25}y^2+\color{#3A9A38}{108}y+\color{#EC0000}{99}&=0\end{align}|| -
Solve the equation
Use the quadratic formula to obtain: ||\begin{align} y&=\dfrac{-\color{#3A9A38}{b}\pm\sqrt{\color{#3A9A38}{b}^2-4\color{#3B87CD}{a}\color{#EC0000}{c}}}{2\color{#3B87CD}{a}}\\\\ &=\dfrac{-(\color{#3A9A38}{108})\pm\sqrt{(\color{#3A9A38}{108})^2-4(\color{#3B87CD}{25})(\color{#EC0000}{99})}}{2(\color{#3B87CD}{25})}\\\\ &=\dfrac{-108\pm\sqrt{1\ 764}}{50}\\\\ y&\in\{-3,-1{.}32\} \end{align}|| -
Substitute the values obtained in one of the starting equations
For |y=-3|: ||\begin{align} x^2&=12(\color{#3a9a38}{y}+3)\\ &=12(\color{#3a9a38}{-3}+3)\\ &=0\\\\ x_{\small{A}}&=0
\end{align}||For |y=-1{.}32|:||\begin{align} x^2&=12(\color{#3a9a38}{y}+3)\\ &=12(\color{#3a9a38}{-1{.}32}+3)\\ &=20{.}16\\ x&=\pm\sqrt{20{.}16}\\\\ x_{\small{B}}&\approx-4{.}49\\ x_{\small{C}}&\approx4{.}49 \end{align}|| -
Write the coordinates of the points of intersection
The coordinates of the three points of intersection between the parabola |x^2=12(y+3)| and the ellipse |\dfrac{x^2}{25}+\dfrac{y^2}{9}=1| are |A(0,-3),| |B(-4{.}49,-1{.}32),| and |C(4{.}49,-1{.}32).|

-
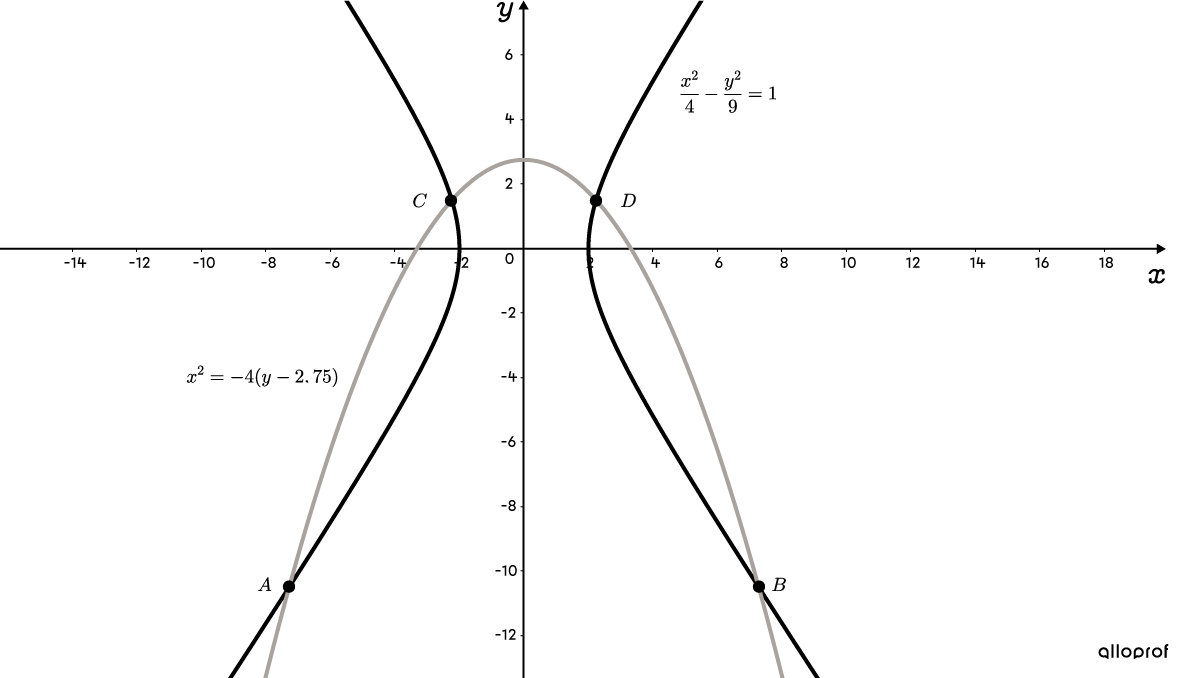
Use the appropriate method to obtain a one-variable equation
Use the substitution method, since |x^2| in the equation of the parabola is already isolated.||\begin{align} \dfrac{\color{#3a9a38}{x^2}}{4}-\dfrac{y^2}{9}&=1\\\\ \dfrac{\color{#3a9a38}{-4(y-2{.}75)}}{4}-\dfrac{y^2}{9}&=1\end{align}|| -
Manipulate the equation so that it equals |0|
||\begin{align}\dfrac{-4y+11}{4}-\dfrac{y^2}{9}&=1\\\\ \dfrac{9(-4y+11)}{36}-\dfrac{4y^2}{36}&=1\\\\ \dfrac{-36y+99-4y^2}{36}&=1\\\\ -36y+99-4y^2&=36\\ \color{#3B87CD}{4}y^2+\color{#3A9A38}{36}y\color{#EC0000}{-63}&=0\end{align}|| -
Solve the equation
Use the quadratic formula to obtain: ||\begin{align} y&=\dfrac{-\color{#3A9A38}{b}\pm\sqrt{\color{#3A9A38}{b}^2-4\color{#3B87CD}{a}\color{#EC0000}{c}}}{2\color{#3B87CD}{a}}\\\\ &=\dfrac{-(\color{#3A9A38}{36})\pm\sqrt{(\color{#3A9A38}{36})^2-4(\color{#3B87CD}{4})(\color{#EC0000}{-63})}}{2(\color{#3B87CD}{4})}\\\\ &=\dfrac{-36\pm\sqrt{2\ 304}}{8}\\\\ y&\in\{-10{.}5,1{.}5\} \end{align}|| -
Substitute the values obtained in one of the starting equations
For |y=-10{.}5|:||\begin{align} x^2&=-4(\color{#3a9a38}{y}-2{.}75)\\ &=-4(\color{#3a9a38}{-10{.}5}-2{.}75)\\ &=53\\ x&=\pm\sqrt{53}\\\\ x_{\small{A}}&\approx-7{.}28\\ x_{\small{B}}&\approx7{.}28 \end{align}||For |y=1{.}5|:||\begin{align} x^2&=-4(\color{#3a9a38}{y}-2{.}75)\\ &=-4(\color{#3a9a38}{1{.}5}-2{.}75)\\ &=5\\ x&=\pm\sqrt{5}\\\\ x_{\small{C}}&\approx-2{.}24\\ x_{\small{D}}&\approx2{.}24 \end{align}|| -
Write the coordinates of the points of intersection
The coordinates of the four points of intersection between the parabola |x^2=-4(y-2{.}75)| and the hyperbola |\dfrac{x^2}{4}-\dfrac{y^2}{9}=1| are |A(-7{.}28,-10{.}5),| |B(7{.}28,-10{.}5),| |C(-2{.}24,1{.}5),| and |D(2{.}24,1{.}5).|
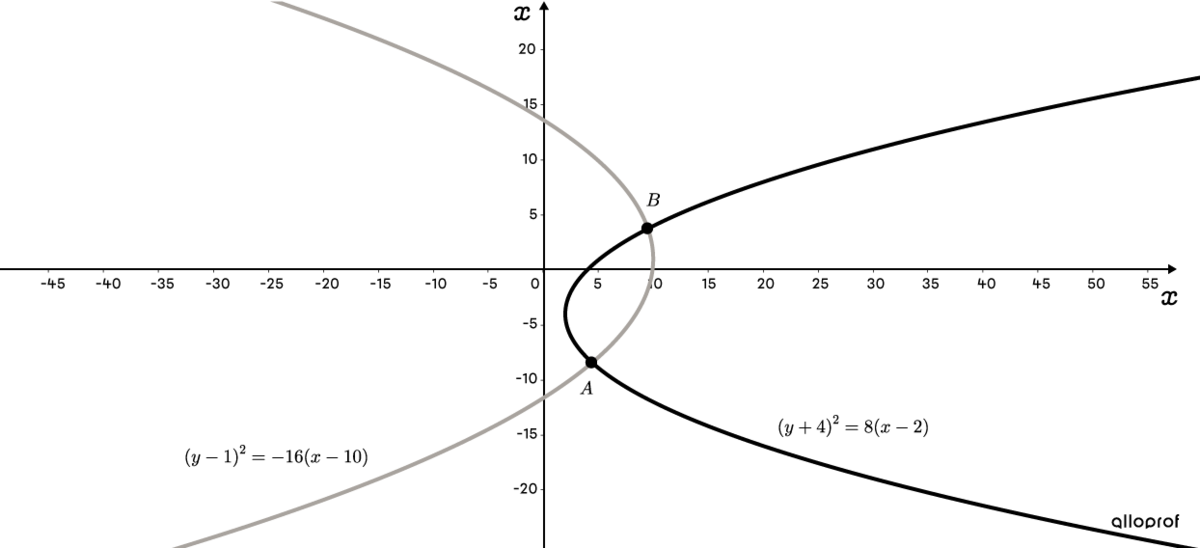
Determine the coordinates of the point(s) of intersection between the parabolas |(y+4)^2=8(x-2)| and |(y-1)^2=-16(x-10).|
-
Use the appropriate method to obtain a one-variable equation
In general, the methods of comparison or substitution are the most efficient for obtaining a one-variable equation. However, we notice that |8| is a factor of |-16.| Therefore, instead of isolating a variable, eliminate the terms in |x| using the elimination method by multiplying the equation |(y+4)^2=8(x-2)| by |-2|.Expand the two equations:||\begin{align} (y+4)^2&=8(x-2)\\ y^2+8y+16&=8x-16\\ \color{#EC0000}{-2}(y^2+8y+16)&=\color{#EC0000}{-2}(8x-16)\\ -2y^2-16y-32&=\color{#3B87CD}{-16}x+32\\\\ (y-1)^2&=-16(x-10)\\ y^2-2y+1&=\color{#3B87CD}{-16}x+160 \end{align}||Subtracting the two equations gives:||\begin{align} -2y^2-16y-32&=-16x+\ \ 32\\ ^{\huge{-}}\quad\quad (y^2-\ \ 2y+\ \ 1&=-16x+160)\\ \hline -3y^2-14y-33&= \ \ \ \ \ \color{#EC0000}{0x}-128 \end{align}||
-
Manipulate the equation so that it equals |0|
||\begin{align}-3y^2-14y-33&=-128\\ \color{#3B87CD}{3}y^2+\color{#3A9A38}{14}y\color{#EC0000}{-95}&=0\end{align}|| -
Solve the equation
Use the quadratic formula to obtain: ||\begin{align} y&=\dfrac{-\color{#3A9A38}{b}\pm\sqrt{\color{#3A9A38}{b}^2-4\color{#3B87CD}{a}\color{#EC0000}{c}}}{2\color{#3B87CD}{a}}\\\\ &=\dfrac{-(\color{#3A9A38}{14})\pm\sqrt{(\color{#3A9A38}{14})^2-4(\color{#3B87CD}{3})(\color{#EC0000}{-95})}}{2(\color{#3B87CD}{3})}\\\\ &=\dfrac{-14\pm\sqrt{1\ 336}}{6}\\\\ y&\in\{-8{.}43,3{.}76\} \end{align}|| -
Substitute the values obtained in one of the starting equations
Start by isolating |x| in one of the equations.||\begin{align}(y+4)^2&=8(x-2)\\ \dfrac{(y+4)^2}{8}&=x-2\\ \dfrac{(y+4)^2}{8}+2&=x\end{align}||For |y=-8{.}43|:||\begin{align}x_{\small{A}}&=\dfrac{(\color{#3A9A38}{y}+4)^2}{8}+2\\\\ &=\dfrac{(\color{#3A9A38}{-8{.}43}+4)^2}{8}+2\\\\ &\approx4{.}45\end{align}||For |y=3{.}76|:||\begin{align}
x_{\small{B}}&=\dfrac{(\color{#3A9A38}{y}+4)^2}{8}+2\\\\ &=\dfrac{(\color{#3A9A38}{3{.}76}+4)^2}{8}+2\\\\ &\approx9{.}53\end{align}|| -
Write the coordinates of the points of intersection
The coordinates of the two points of intersection between parabolas |(y+4)^2=8(x-2)| and |(y-1)^2=-16(x-10)| are |A(4{.}45,-8{.}43)| and |B(9{.}53,3{.}76).|
