An energy resource is a naturally occurring source of energy used to address the needs related to human activity.
The generation of electricity, heating and transportation are the main needs satisfied by exploiting energy resources. Here are the main energy resources.
This table summarizes the impact that commonly exploited natural resources have on the environment. However, the installation of the infrastructure required for the consumption of the energy resources has an additional impact on the environment, for example, the pollution associated with the construction of a power plant.
| Biomass | Wind | Solar Radiation | Hydroelectricity | Fossil Fuels | Uranium | Geothermal Energy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | |||||||
| Origin | Biosphere | Atmosphere | Space (the Sun) | Hydrosphere | Lithosphere | Lithosphere | Lithosphere |
| Form of Energy | Chemical | Mechanical | Radiant | Mechanical | Chemical | Nuclear | Thermal |
| Impacts | |||||||
| Nonrenewable Energy | x | x | |||||
| GHG Emissions | High | Negligible1 | None | Negligible1 | High | Negligible1 | Negligible1 |
| Emission of |\text{NO}_x| and |\text{SO}_x| | x | x | |||||
| Intensive Agriculture Impact | x | ||||||
| Mining and Oil Drilling Impact | x2 | x | x | ||||
| Flooding | x | ||||||
| Disruption of Ecosystems | x | x | x | x | x | x | Not well understood |
Notes:
-
The GHG emissions produced by these energy resources are so low that textbooks often label them as nonexistent.
-
The impact is due to the extraction and processing of minerals required for building photovoltaic cells in the solar panels.
Choosing the energy resource to use depends on many factors. The availability of the resource, geographic location, energy efficiency, financial constraints and environmental impact are generally considered.
A renewable energy resource generally has a less negative impact on the environment than a nonrenewable energy resource. Therefore, the renewable property of an energy resource is considered to be an advantage.
|
Renewable Energy Resources |
Nonrenewable Energy Resources |
|---|---|
|
Biomass |
Fossil fuels |
-
A renewable resource is an energy resource that replenishes at least as quickly as it is consumed.
-
A nonrenewable resource is an energy resource that does not replenish or replenishes at a slower rate than consumed.
The greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions caused by the consumption of an energy resource is considered to be a disadvantage because it has a negative impact on the environment.
|
Energy Resources with Zero or Negligible GHG Emissions |
Energy Resources with High GHG Emissions |
|---|---|
|
Wind |
Biomass |
Greenhouse gas emissions refer to the emission of certain gasses, such as carbon dioxide |(\text{CO}_2)|, methane |(\text{CH}_4),| nitrous oxide |(\text{N}_2\text{O})| and ozone |(\text{O}_3).| The gases have the ability to retain heat in the atmosphere and intensify the greenhouse effect.
Additionally, the emission of carbon dioxide |(\text{CO}_2)| and methane |(\text{CH}_4)| into the atmosphere disrupts the carbon cycle.
Biomass is all organic matter that can be used as fuel to produce energy, such as heat or electricity.
|
Origin |
Form of Energy |
|---|---|
|
Biosphere |
Note: Some textbooks categorize biomass as an energy resource originating from the lithosphere.
Examples of biomass energy resources include wood and wood residue, organic waste originating from animals and/or food, corn, wheat, canola and soybeans. The main products of biomass are as follows.
Wood → Firewood
Wood residue → Wood pellets
Organic waste → Biogas
Corn, wheat, canola, soybeans → Biofuel
The chemical energy from biomass is released during a combustion reaction (i.e., by burning biomass products).
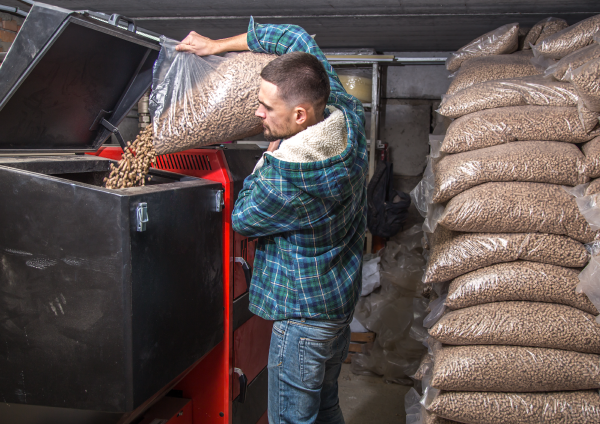
Wood, wood pellets, and biogas are mainly used as an energy resource for heating systems in certain buildings. Their combustion releases heat.
The heat released during the combustion of biogas can also be used to generate electricity at a thermal power plant. These power plants operate similarly to coal-fired power stations.

Fabian Faber, Shutterstock.com
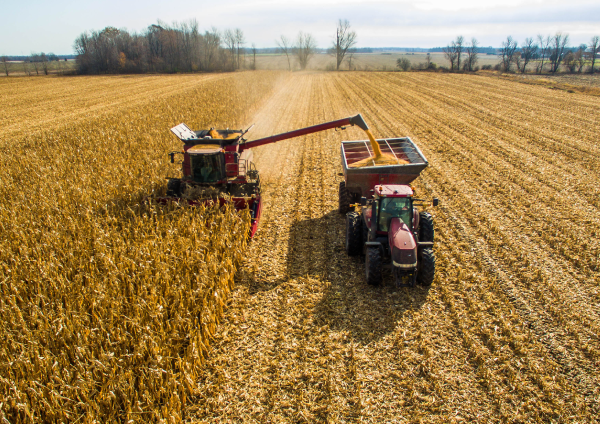
When corn, wheat, canola and soybeans are used as an energy resource, they are mainly transformed into biofuel. Biofuel is used in the transportation industry.
The consumption of biomass energy has a negative impact on the environment. For example:
-
The combustion of biomass products emits greenhouse gasses, which intensifies the greenhouse effect and the disruption of the carbon cycle.
-
The combustion of biomass products emits sulfur oxides |(\text{SO}_x)| and nitrogen oxides |(\text{NO}_x)| into the atmosphere. These gasses contribute to acid rain.
-
Biofuel production involves intensive agriculture of corn, wheat, canola and soybeans. It contributes to the following:
-
deforestation
-
use of large quantities of clean water
-
use of pesticides leading to the loss of biodiversity
-
accelerating erosion
-
fertilizer use causing the disruption of the nitrogen and phosphorus cycles as well as accelerating the eutrophication of bodies of water
-
heavy machinery use causing soil compaction
-
heavy machinery use causing a release of greenhouse gasses, sulfur oxides |(\text{SO}_x)| and nitrogen oxides |(\text{NO}_x)| due to fuel combustion.
-
Biogas is obtained by processing organic waste from animals and/or food. The combustion of biogas emits carbon dioxide |(\text{CO}_2),| a greenhouse gas.
However, the decomposition of organic waste emits methane |(\text{CH}_4)| which retains more heat in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide |(\text{CO}_2)|.
Overall, the transformation of organic waste into biogas replaces some methane |(\text{CH}_4)| emissions with carbon dioxide emissions |(\text{CO}_2)|.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
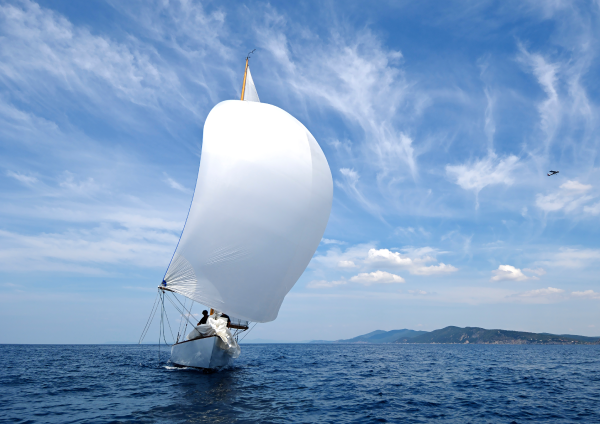
Wind is the movement of air masses through the atmosphere.
|
Origin |
Form of Energy |
|---|---|
|
Mechanical energy or wind power |
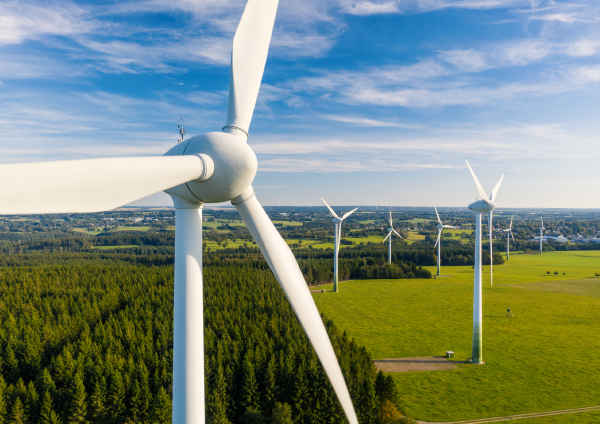
Wind energy is mostly used to generate electricity using wind turbines.
The consumption of wind energy has a negative impact on the environment. For example:
-
The presence of wind turbines located across a landscape can be considered a source of visual pollution.
-
The sound created by the moving blades of the wind turbines can be considered a source of noise pollution.
-
To generate a significant amount of electricity, multiple wind turbines have to be installed creating a wind farm. Wind farms generally require a large amount of land unoccupied by trees. This contributes to deforestation and wildlife displacement leading to the loss of biodiversity.
-
Wind turbines threaten flying animals with collisions, injuries and death.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
A windmill is another example of wind energy use.
A sailboat is also an example of wind energy use.
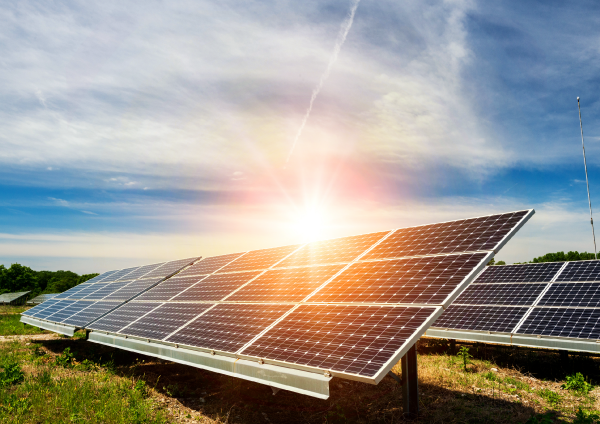
Solar radiation is the light emitted by the Sun.
Some solar radiation reaches the Earth and is used as an energy resource.
|
Origin |
Form of Energy |
|---|---|
|
Radiant energy, light or solar energy |
Note: Some textbooks categorize solar radiation as an energy resource originating from the atmosphere.
Energy obtained from solar radiation is mainly used to generate electricity using photovoltaic panels, often called solar panels.
The consumption of solar energy has a negative impact on the environment. For example:
-
The manufacturing of photovoltaic panels (or solar panels) requires the extraction and transformation of minerals. Industrial development projects, such as mines and ore processing plants, and their processes contributes to:
-
wildlife displacement and deforestation, leading to the loss of biodiversity
-
destruction of bedrock
-
heavy machinery use causing soil compaction
-
heavy machinery use causing a release of greenhouse gasses due to fuel combustion
-
large quantities of clean water use
-
chemical use increases the risk of groundwater contamination.
-
-
To generate a significant amount of electricity, multiple solar panels have to be installed creating a solar farm (also known as a solar park). Solar farms generally require a large amount of land unoccupied by trees which further contributes to deforestation and wildlife displacement.
-
The batteries in the photovoltaic panels contain heavy metals. When they end up in a landfill, there is a risk of groundwater contamination. This is why there are processes for recycling photovoltaic panels and measures for properly disposing of end-of-life batteries.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Passive heating in a house or another building also relies on solar radiation as an energy resource. It relies on the building’s position, the shape of the roof, and the strategic placement of the windows.
In the winter, when the Sun is low in the sky, the amount of solar radiation that enters a house is maximized by large windows on the south side of the building. In the summer, when the Sun is higher in the sky, an eave (an overhanging roof edge) blocks some of the solar radiation from entering the house to keep it cool.

-
Hydroelectricity is electricity generated using hydraulic energy.
-
Hydraulic energy is the mechanical energy of moving water.
Here are the main hydroelectricity resources.
A hydroelectric dam is a structure that generates electricity by retaining and controlling the flow of water.
|
Origin |
Form of Energy |
|---|---|
|
Mechanical energy or hydraulic energy |
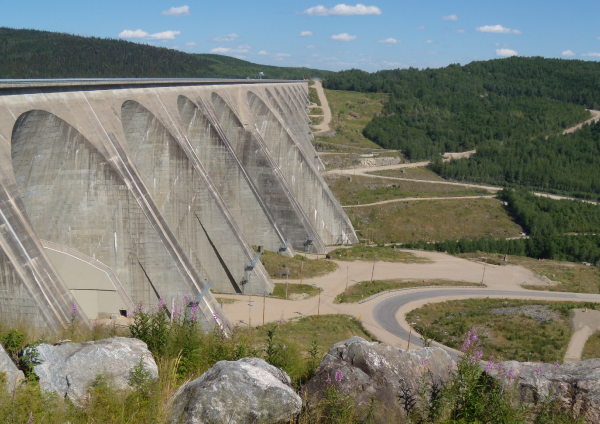

Simon J. Ouellet, Shutterstock.com
River diversion is the main negative environmental impact of exploiting hydroelectricity using dams. It contributes to:
-
wildlife displacement leading to the loss of biodiversity
-
drying up and/or flooding of different areas in a watershed
-
decomposition of flooded plant matter causing the release of heavy metals into the water and their subsequent introduction into the food chain.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
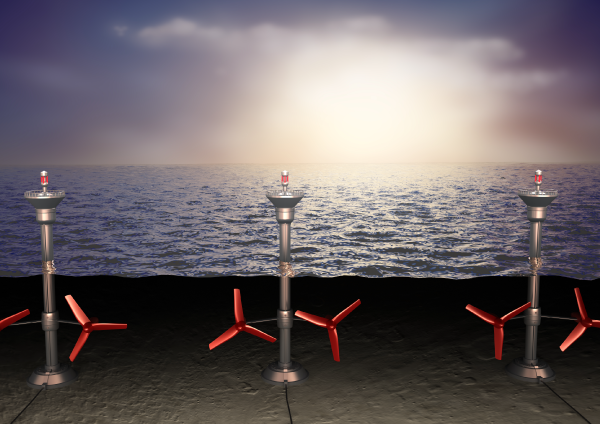
Ocean currents, or oceanic circulation, are the movement of water in the ocean across the planet.
|
Origin |
Form of Energy |
|---|---|
|
Mechanical energy, hydraulic energy or marine energy |
Energy obtained from the ocean currents is mainly used to generate electricity using underwater turbines.
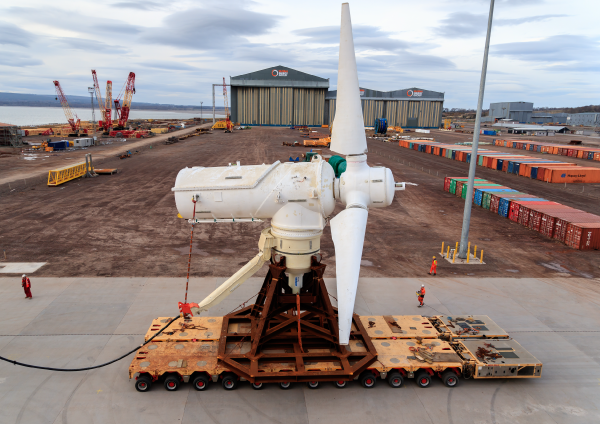

Arild Lilleboe, Shutterstock.com
The impact of marine energy is still under study, therefore, the impact of consumption on the environment is still unknown. However, it is possible it disrupts marine ecosystems, especially in the benthic zones.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
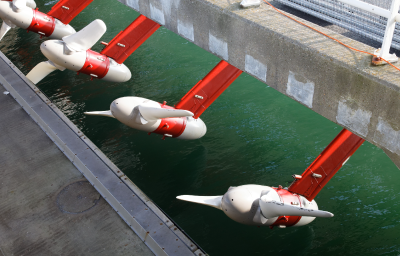
Tides are periodic variations in the sea and ocean level. Tides are caused by the gravitational force of the Moon and, to a lesser extent, the Sun.
|
Origin |
Form of Energy |
|---|---|
|
Mechanical energy, hydraulic energy or tidal energy |
Tidal energy is mainly used to generate electricity using tidal power plants.
The use of tidal energy to generate electricity disrupts neritic, or coastal, ecosystems. The installation of tidal infrastructure tends to separate and transform the ecosystems upstream and downstream from the power plant. Overtime, the separation leads to the loss of biodiversity.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Fossil fuels are fuels high in carbon |(\text{C})| and hydrogen |(\text{H})| that can be extracted from the Earth’s crust. Fossil fuels form when organic matter decomposes very slowly over the course of millions of years.
|
Origin |
Form of Energy |
|---|---|
|
Chemical energy or fossil fuel energy |
Here are the main fossil fuels.
The consumption of fossil fuels has an impact on the environment. For example:
-
The combustion of fossil fuels emits greenhouse gasses which contribute to the intensification of the greenhouse effect and the disruption of the carbon cycle.
-
The combustion of fossil fuels emits sulfur oxides |(\text{SO}_x)| and nitrogen oxides |(\text{NO}_x)| into the atmosphere. These gasses contribute to acid rain.
-
Industrial development projects, such as coal mines, installation of oil and natural gas drilling rigs, and their processes contribute to:
-
wildlife displacement and deforestation, leading to the loss of biodiversity
-
destruction of bedrock
-
heavy machinery use causing soil compaction
-
heavy machinery use causing a release of greenhouse gasses due to fuel combustion
-
use of large quantities of clean water
-
chemical use that increase the risk of groundwater, surface water and ocean water contamination
-
fuel spills that contaminate groundwater, surface water and the oceans.
-
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Coal is a carbon-rich ore |(\text{C})| formed by the decomposition of organic matter, primarily plant-based matter accumulated at the bottom of shallow lakes.
Energy obtained from coal is mainly used to generate electricity at coal-fired power stations.
Oil, sometimes called crude oil or petroleum, is a mineral oil formed by the decomposition of organic matter, primarily matter accumulated at the bottom of the ocean, such as plankton.
Energy derived from oil is mainly used to produce fuel used in the transportation industry.
Natural gas is a gaseous mixture, mostly composed of methane |(\text{CH}_4)| formed by the methanation of animals and plants buried in sedimentary rock.
Energy obtained from natural gas is mainly used in building heating systems.
Uranium is a metal with multiple isotopes, found in the Earth's crust and with varying nuclear stability.
|
Origin |
Form of Energy |
|---|---|
Uranium isotopes are used to initiate nuclear fission reactions and release large amounts of energy.
Nuclear energy is mainly used to generate electricity at nuclear power plants.
Uranium is sometimes categorized as nuclear fuel because it releases a lot of energy. However, uranium is not involved in a combustion reaction at a nuclear power plant. In a chemical sense, uranium cannot be used as fuel in the triangle of fire.
The consumption of uranium has a negative impact on the environment. For example:
-
Industrial development projects, such as mines and ore processing plants, and their processes contribute to:
-
displacement of wildlife and deforestation, leading to the loss of biodiversity
-
destruction of bedrock
-
heavy machinery use causing soil compaction
-
heavy machinery use causing a release of greenhouse gasses due to fuel combustion
-
use of large quantities of clean water
-
chemical use that increase the risk of groundwater, surface water and ocean water contamination
-
-
The discharge of hot water by the nuclear power plant accelerates the eutrophication of rivers.
-
The disposal of radioactive waste poses a risk of groundwater contamination. The risk is considered low when the storage of radioactive waste is adequate.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
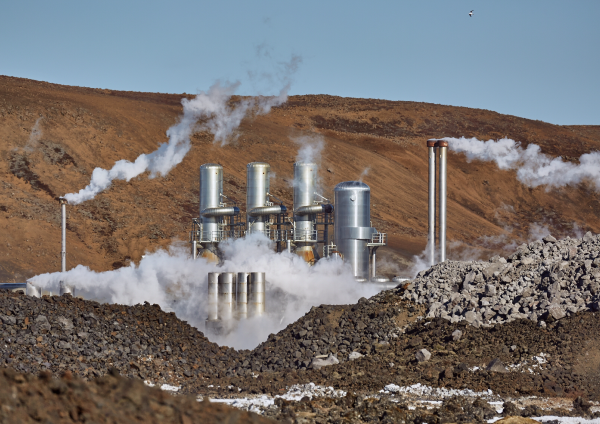
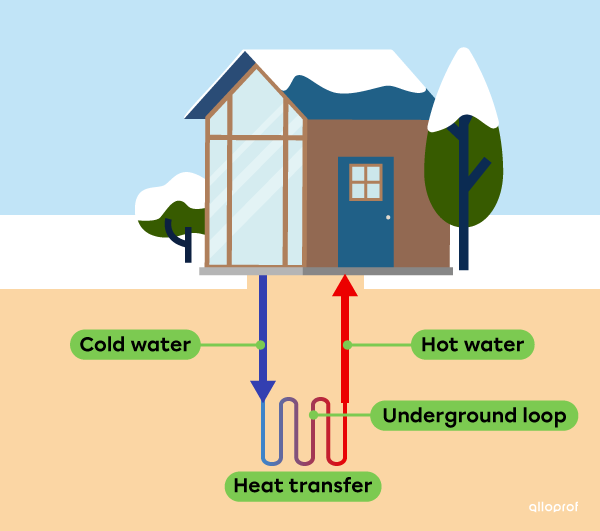
Geothermal energy is the thermal energy of the Earth’s core.
|
Origin |
Form of Energy |
|---|---|
|
Thermal energy or geothermal energy |
Geothermal energy of the Earth’s core is mainly used to generate electricity at geothermal power plants.
The use of geothermal energy to generate electricity has little impact on the environment.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Building heating systems that make use of geothermal energy do not require the heat of the Earth’s core to be transformed into electricity. Geothermal heat is used directly by heating up either water or air pipes.