-
Energy is the ability to alter a state or produce a change.
-
The joule |(\text{J})| is the measurement unit of energy.
Energy can be manifested naturally or artificially. It is involved in our most trivial daily activities. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be transformed from one form to another or transferred from one medium to another.
The law of conservation of energy indicates, nothing is lost, nothing is created, everything is transformed.
The following table presents the different forms of energy and examples of the energy sources associated with each one.
|
Form of energy |
Description |
Energy sources associated with the form of energy |
|---|---|---|
|
Energy contained in the chemical bonds between the atoms of the substance’s molecules |
|
|
|
Energy contained in objects due to their movement, position, or deformation |
|
|
|
Energy carried by an electromagnetic wave |
|
|
|
Energy contained in a substance due to the agitation of its particles |
|
|
|
Energy contained in the nucleus of atoms due to the bonds between protons and neutrons |
|
When we analyse a technical object or a technological system, identifying the energy forms and transformations helps to better understand the way it functions.
Some textbooks describe electrical energy as a separate form of energy. In this concept sheet, electrical energy is considered part of mechanical energy, since it is associated with the movement of electrons.
Chemical energy is contained in the chemical bonds between a substance’s atoms.
During the chemical transformation of a substance, the bonds between the substance’s atoms are broken to form new substances, the products. When the reaction releases energy, some of the chemical energy of the reactants is released in another form, usually thermal and/or radiant energy, but also in mechanical form (i.e., sound waves or electrical energy).
Food, coal, and biogas are examples of substances that contain accessible chemical energy.
The foods we eat are made up of numerous substances such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. The nutrients’ chemical bonds contain the chemical energy our cells need.

Timolina, Shutterstock.com
Coal comes from the decomposition of plant matter. The chemical bonds in coal contain the energy necessary to be used as fuel.

Patty Chan, Shutterstock.com
Some biogas comes from the methane in cattle manure. The chemical bonds of the gases contain the energy needed to be used as fuel.

Fabian Faber, Shutterstock.com
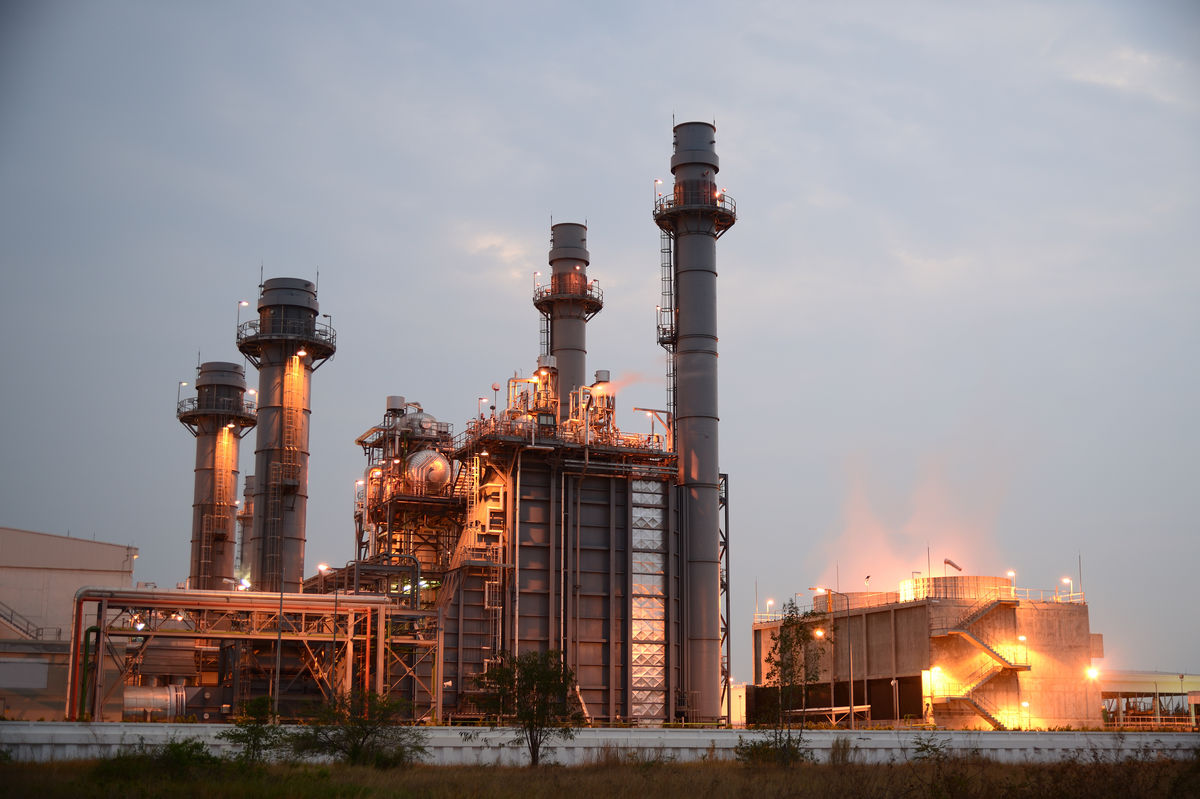
A thermal power station is a complex technological system where the chemical energy of coal or natural gas (fossil fuel) is transformed into electricity for human activities.
Harnessing the chemical energy of fossil fuels has an environmental impact.

Lovely Bird, Shutterstock.com
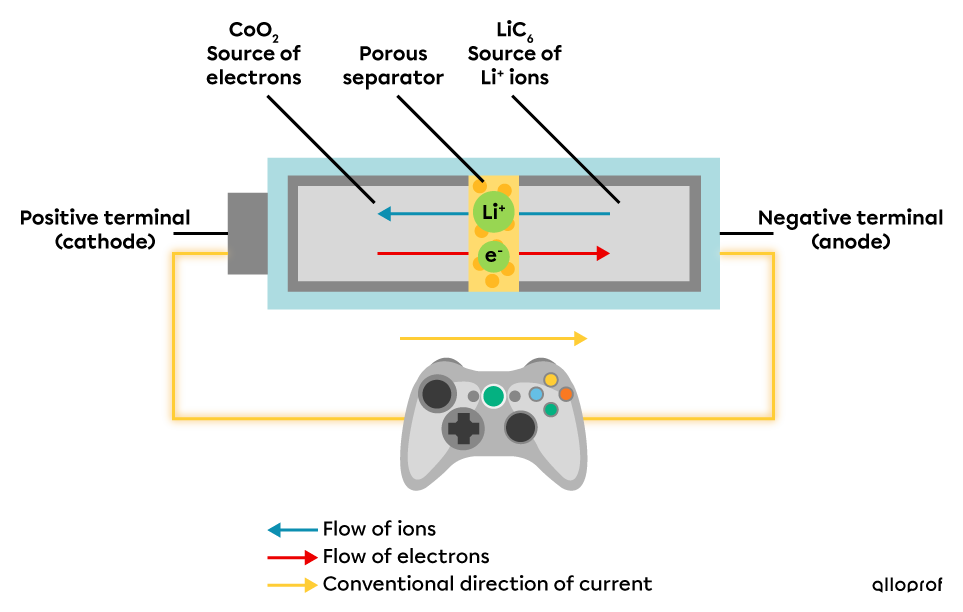
In a lithium ion battery, the chemical bonds of lithium-graphite |(\text{LiC}_6)| and a cobalt oxide |(\text{CoO}_2)| are broken down by an oxidation-reduction reaction. The reaction releases positive ions |(\text{Li}^+)| and electrons |(\text{e}^-).| Positive lithium ions |(\text{Li}^+)| pass through a porous separator and the electrons |(\text{e}^-)| move in the opposite direction. The movement of electrons generates an electric current.
Through the process, chemical energy is transformed into electrical energy.
Mechanical energy is associated with the movement, position, or deformation of an object.
When the shape, position, or movement of an object is changed, its mechanical energy tends to be transferred to another object or transformed into another form of energy.
The following situations are examples of mechanical energy.
The movement of a car is associated with mechanical energy. The energy varies according to the speed of the car.

irin-k, Shutterstock.com
A person standing on a diving board is associated with mechanical energy. The energy varies depending on the position of the person relative to the ground.

sirtravelalot, Shutterstock.com
A child jumping on a trampoline is associated with mechanical energy, because the child is moving up and down.
Between jumps, the trampoline fabric stretches, and then returns to its original shape. The elastic deformation of the trampoline is also associated with mechanical energy.

Martin Novak, Shutterstock.com
Electrical energy is mechanical energy. It is associated with the movement of electrons.
In the context of energy transformation, electrical energy is considered a separate form of energy from mechanical energy.
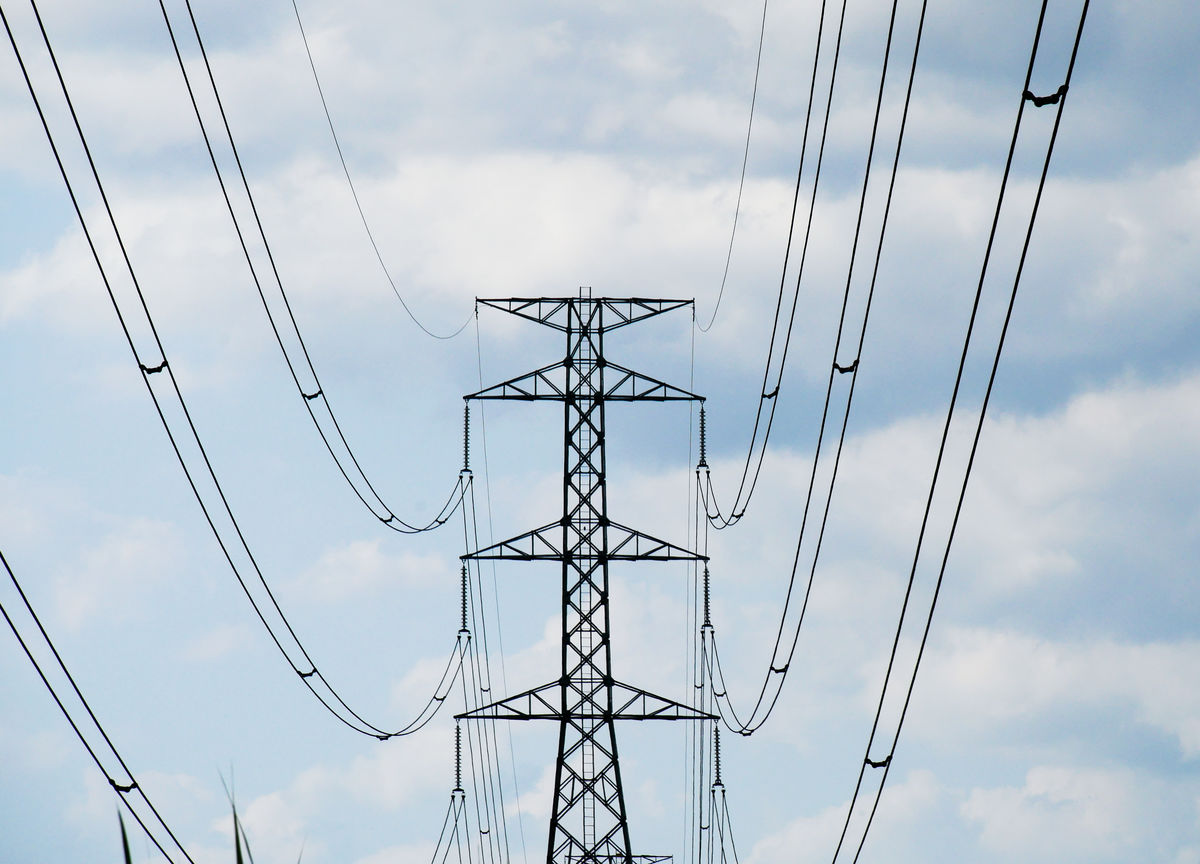

PhotoAdventure Studio, Shutterstock.com
Hydraulic energy is mechanical energy. It is associated with the movement of water.
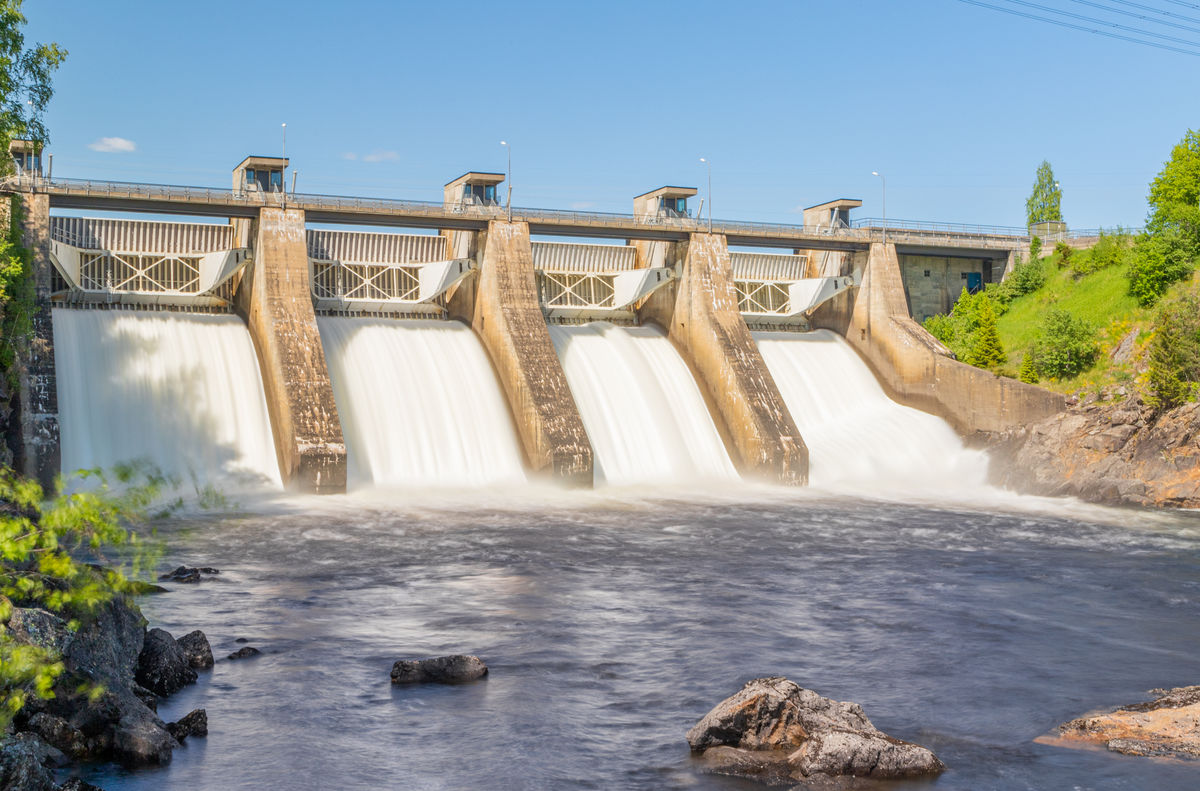

SorbyPhoto, Shutterstock.com
Wind energy is mechanical energy. It is associated with the movement of air masses.

Jesus Keller, Shutterstock.com
A hydroelectric dam is a complex technological system where the mechanical energy associated with the movement of water (hydraulic energy) is transformed into electricity for human activities.
Exploiting hydraulic energy has an impact on the environment.
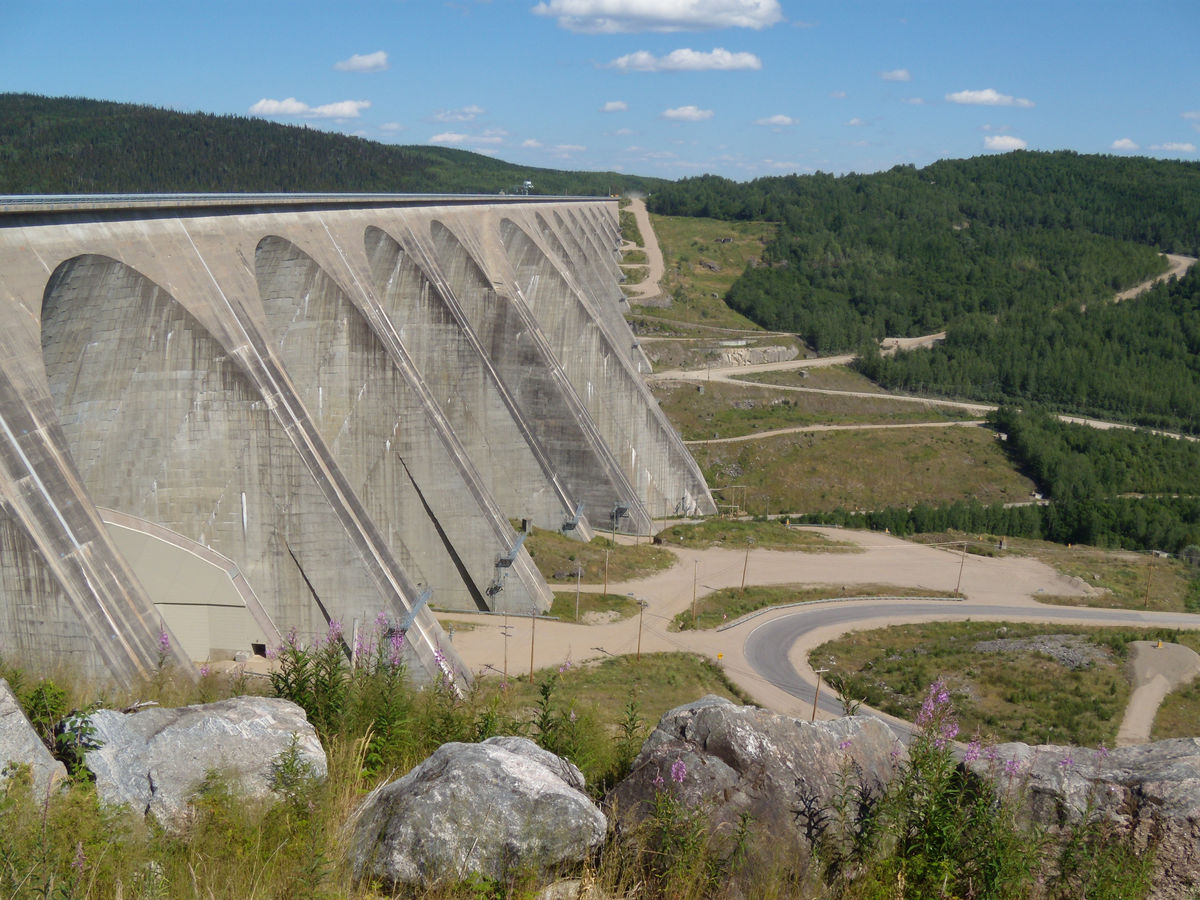

Simon J. Ouellet, Shutterstock.com
Gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy are also types of mechanical energy. They are concepts covered in Secondary IV Environmental Science and Technology (EST). Mechanical energy is covered in more detail in the Physics program in Secondary V.
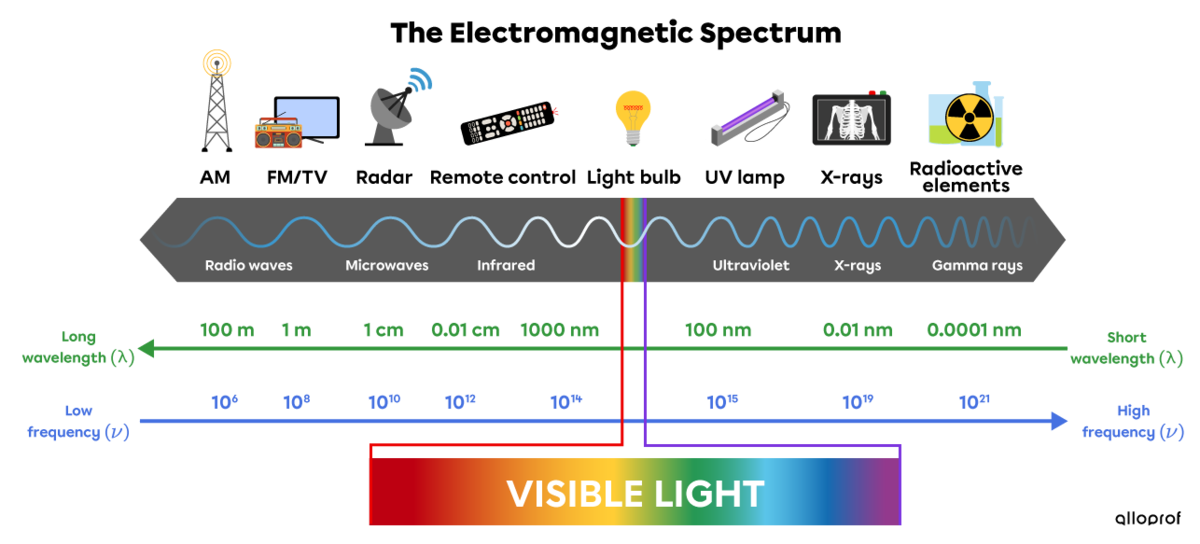
Radiant energy is carried by waves in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Electromagnetic waves, either from the sun or from a microwave oven, carry radiant energy. The electromagnetic spectrum presents and classifies all electromagnetic waves according to the energy they carry.
Waves on the right of the electromagnetic spectrum carry more radiant energy than waves on the left. For example, X- rays carry a large amount of radiant energy compared to radio waves which carry very little.
The following situations are examples of radiant energy.
A sunburn is the body's response to radiant energy transported by the ultraviolet rays emitted by the Sun.
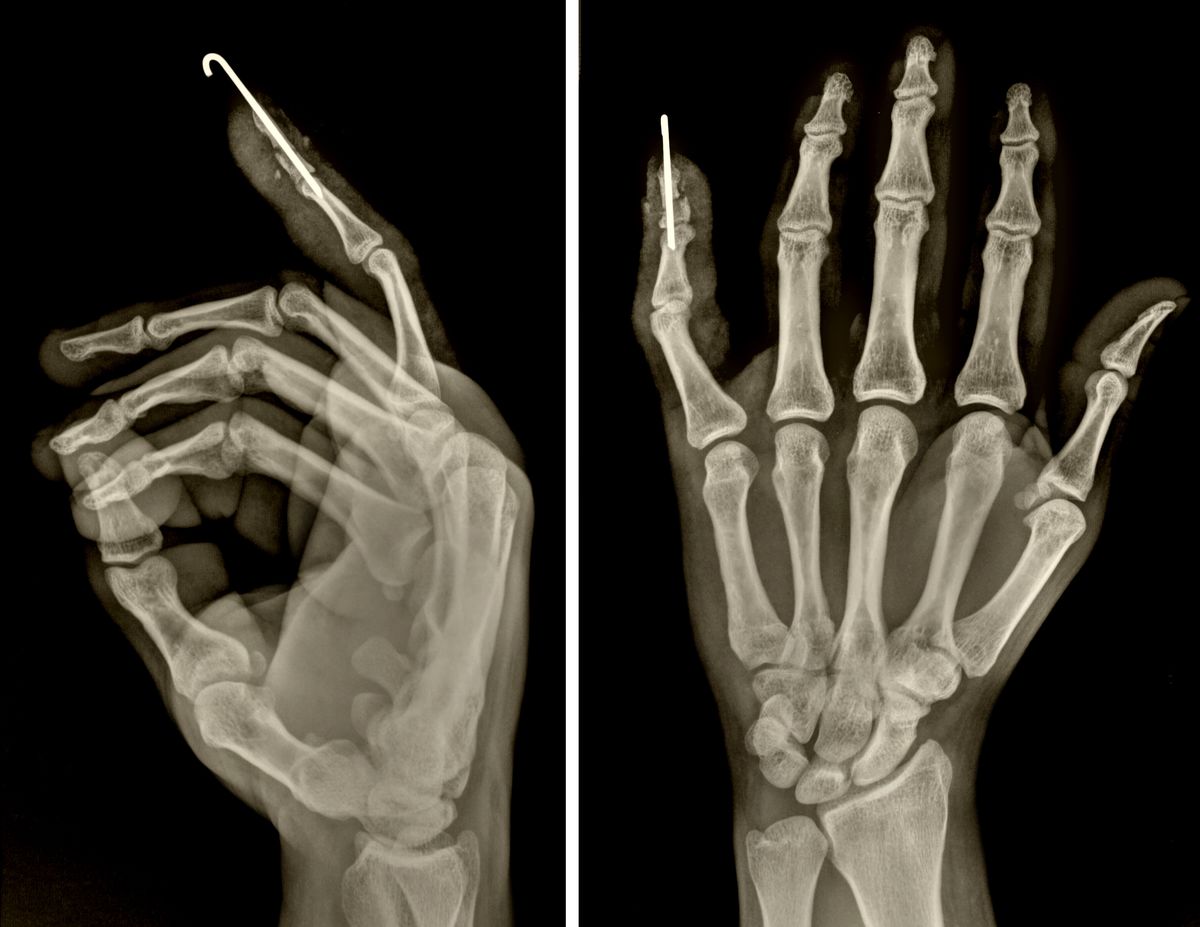
Radiography uses the radiant energy of X-rays to create an image of bones.
pakirri, Shutterstock.com
The microwave oven uses radiant microwave energy to heat food.
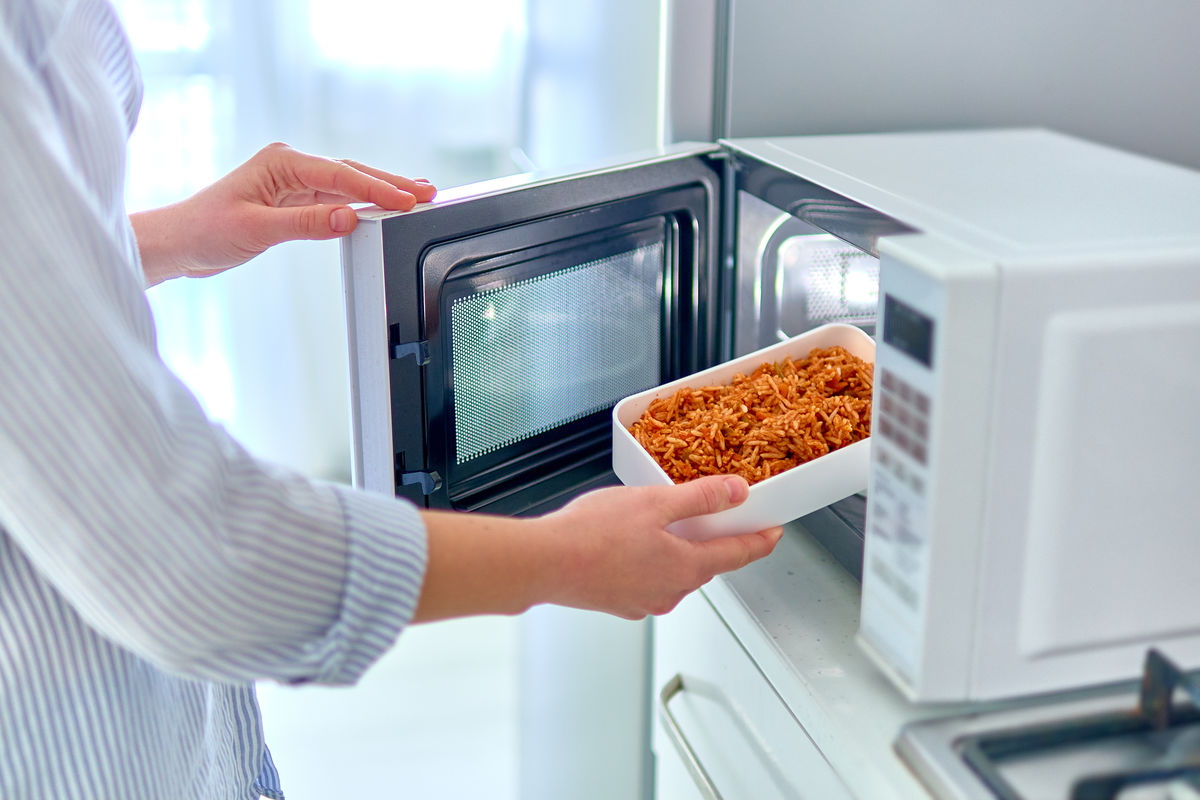

goffkein.pro, Shutterstock.com
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) emit radiant energy in the form of visible light to illuminate a room.

LariBat, Shutterstock.com
A photovoltaic panel is a technological system where the radiant energy of the sun is transformed into electricity for human activities.
The exploitation of solar energy has an impact on the environment.
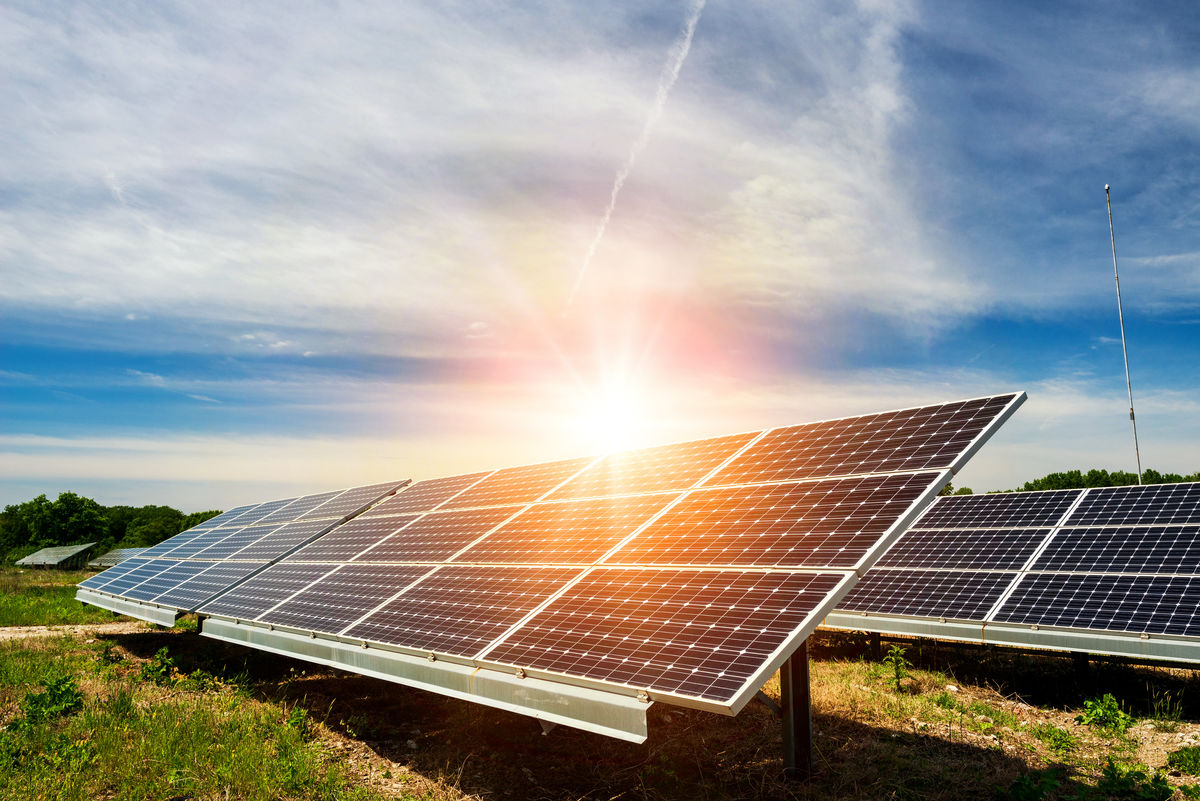

Diyana Dimitrova, Shutterstock.com
Thermal energy is associated with the agitation of a substance’s particles.
The thermal energy of a substance varies according to the temperature, quantity, and nature of the particles.
According to the particle model, particles are continuously in motion. When a substance receives heat, its particles become more agitated, which increases the thermal energy of the substance.
The following situations are examples of thermal energy.
The phase change from liquid to water steam is due to an input of thermal energy, causing the water particles to become more agitated.
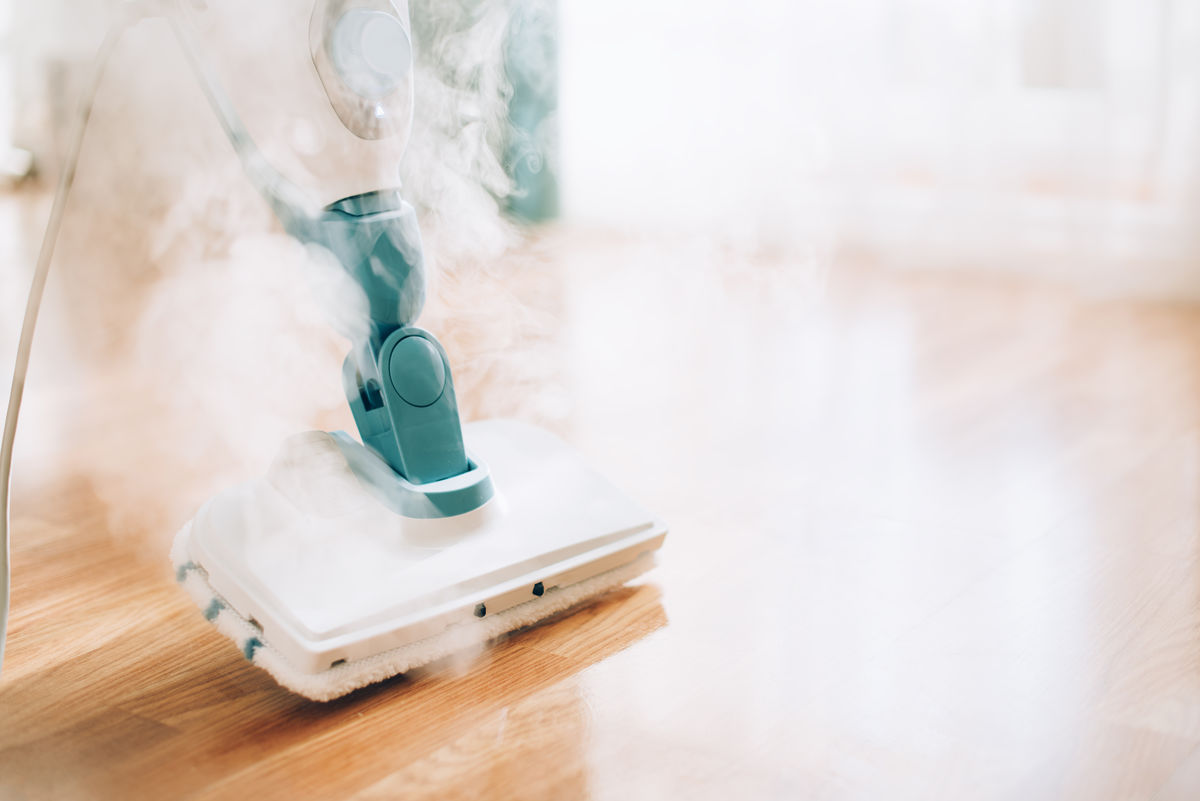

j.chizhe, Shutterstock.com
Initiating the combustion of a candle requires a sufficient supply of thermal energy.
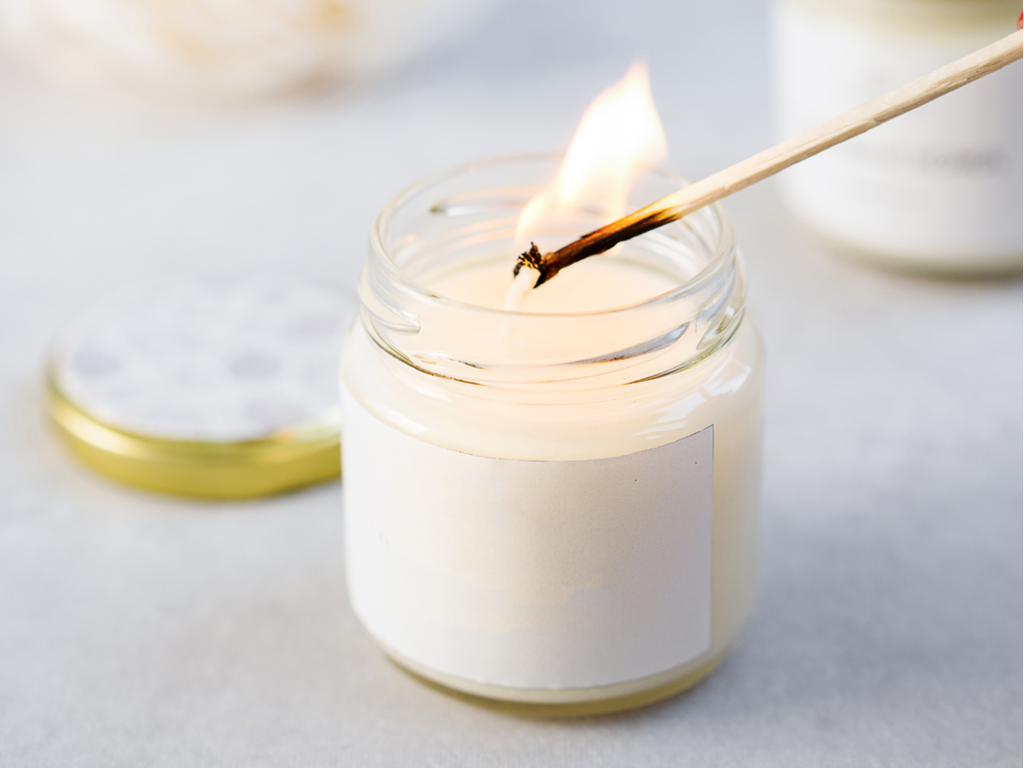

LNataly, Shutterstock.com
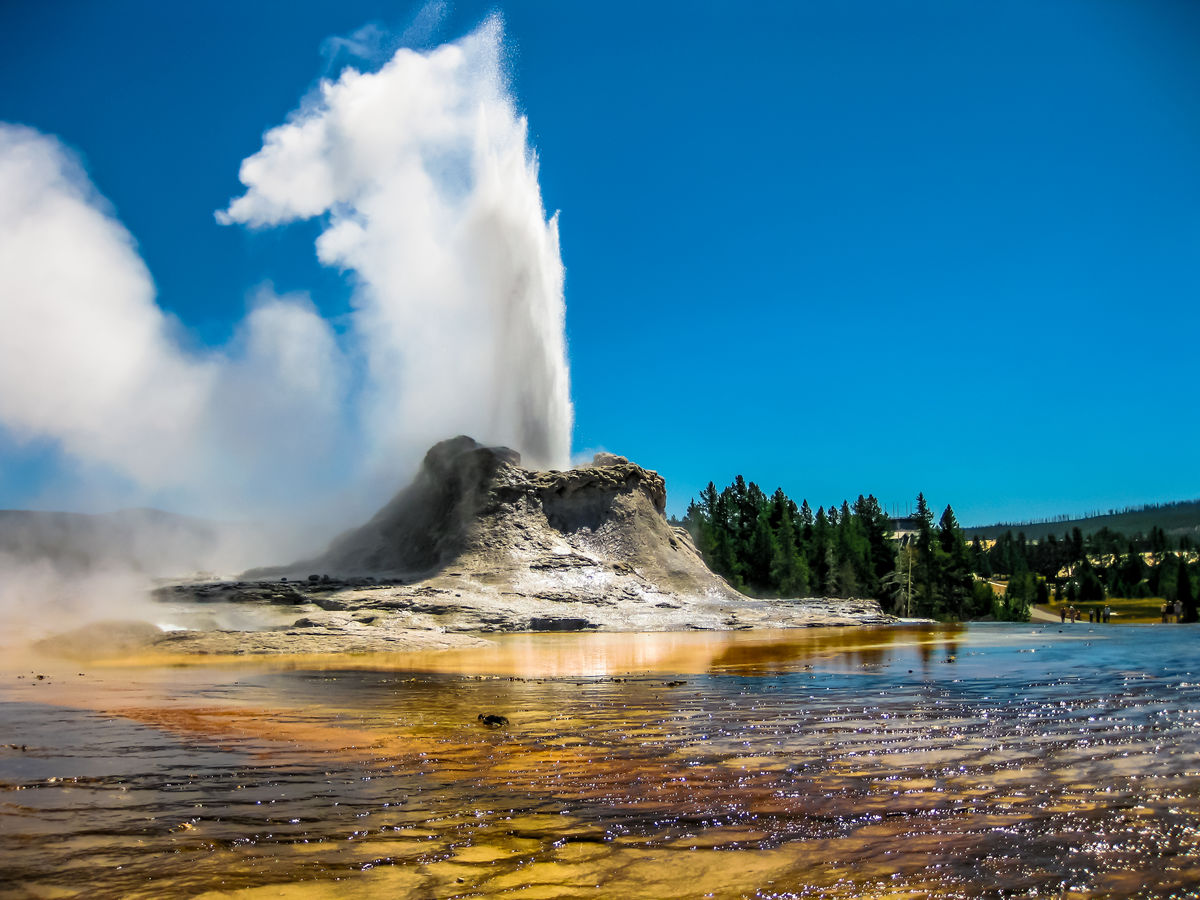

Benny Marty, Shutterstock.com
A geothermal power station is a complex technological system where thermal energy from the Earth's mantle is transformed into electricity for human activities.
In some cases, geothermal energy does not transform thermal energy. Instead, heat from the ground is transferred and used directly as a heating source for buildings.
Exploiting thermal energy from the ground has an impact on the environment.
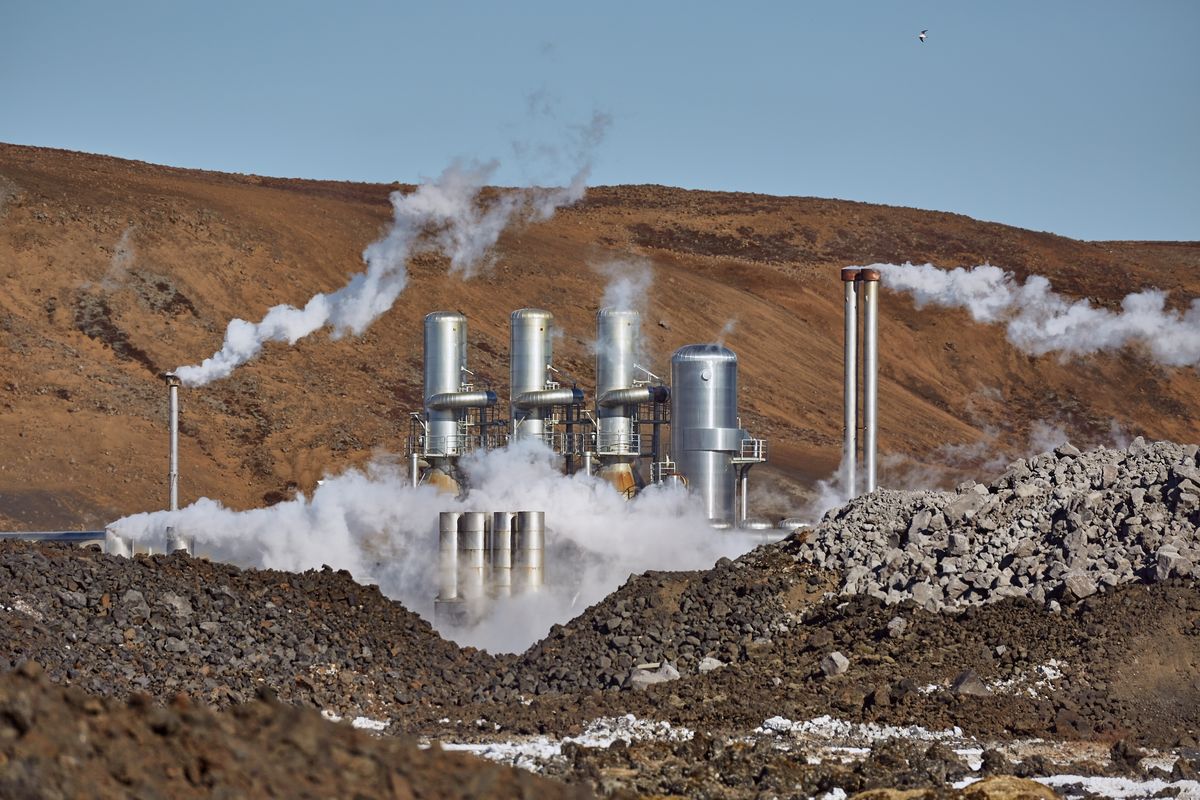

Gudella, Shutterstock.com
To validate your understanding of thermal energy in an interactive way, consult the following MiniRécup:

The following situations are examples of nuclear energy.
The formation of stars similar to the sun results from nuclear fusion. Hydrogen atoms combine to form helium atoms.
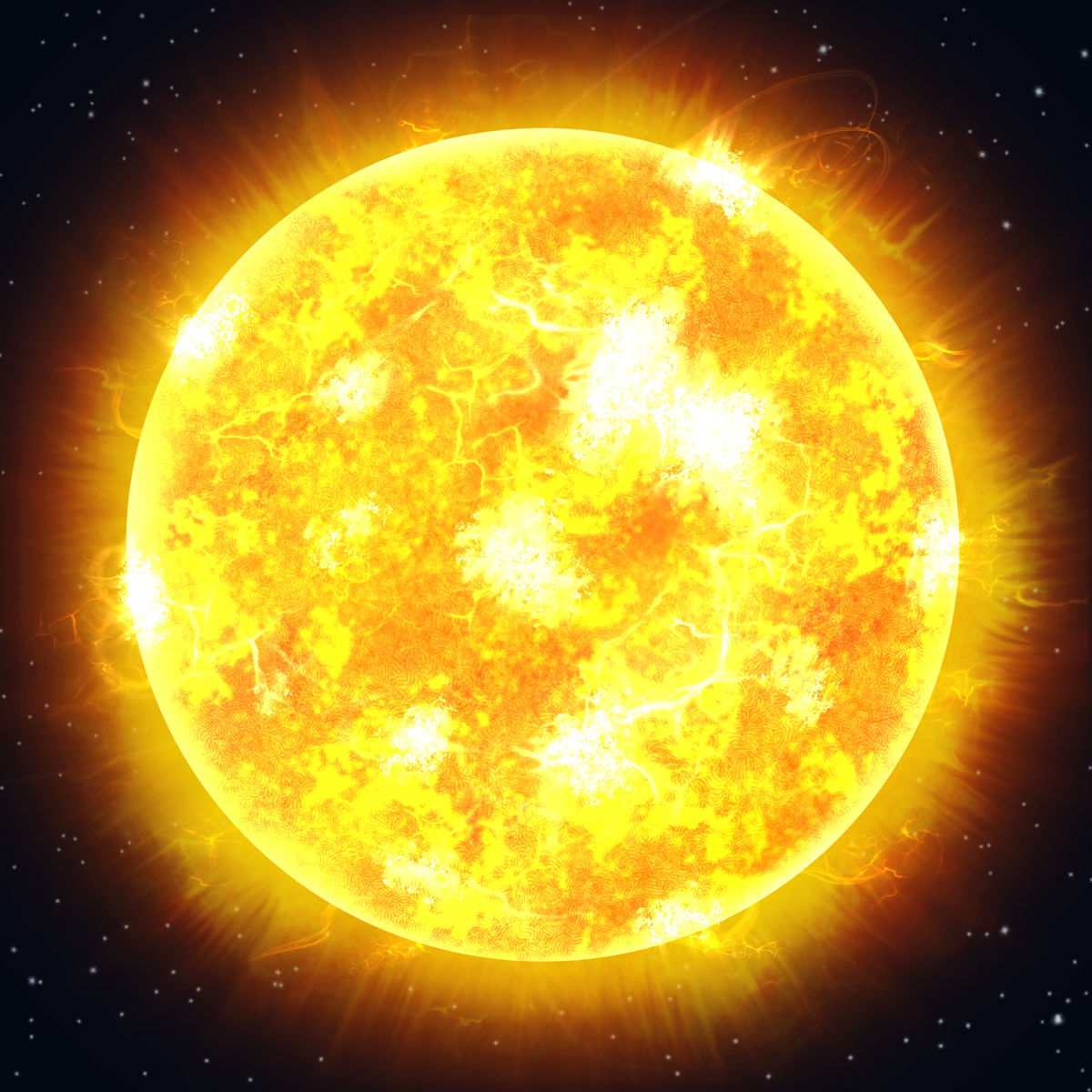

Flameheart, Shutterstock.com
The nuclear energy contained in uranium is transformed by the nuclear fission of its atoms. A huge amount of thermal energy is released by the nuclear reaction.
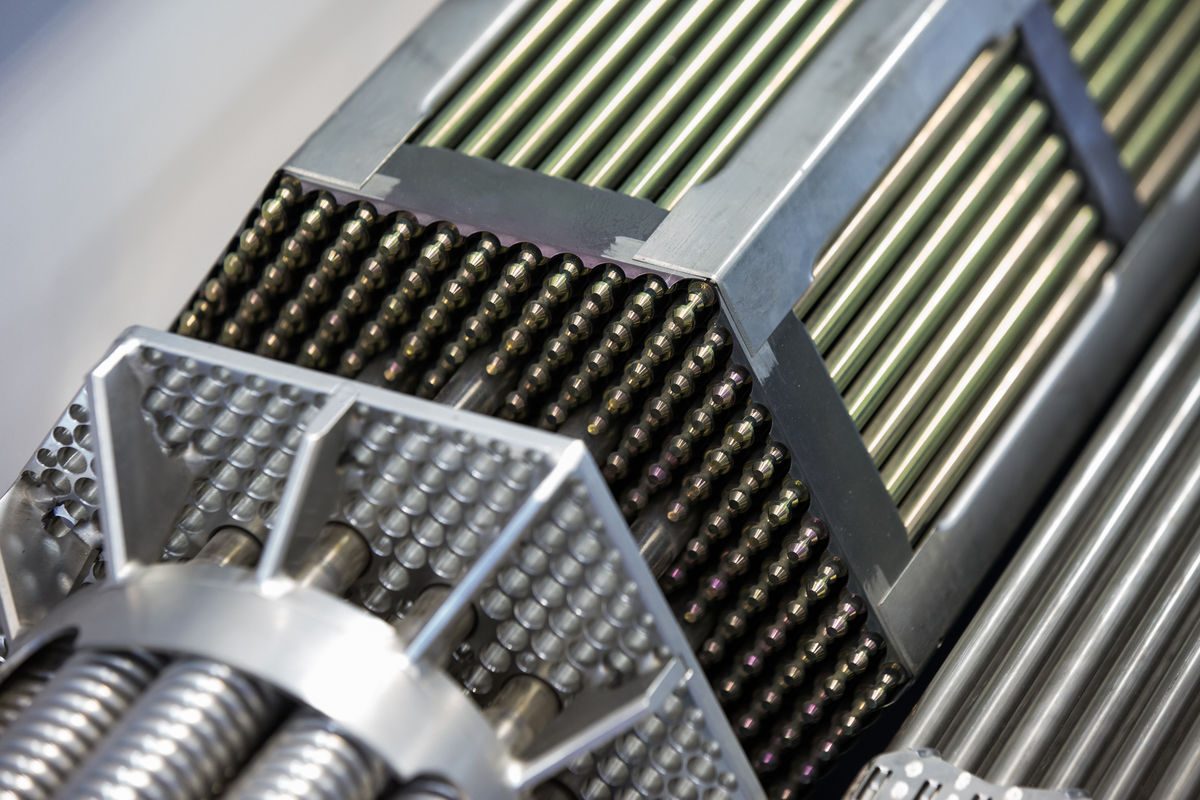
Parilov, Shutterstock.com
A nuclear power plant is a complex technological system where nuclear energy from uranium is transformed into electricity for human activities.
Exploiting nuclear energy from uranium has an impact on the environment.
