A diagram is the simplified representation of an object or a system to explain how it works.
Just like manufacturing drawings, diagrams are a form of graphical language used in technical drawings. On the other hand, unlike manufacturing drawings which reproduce the general appearance of an object with precision, other diagrams are simplified drawings of an object or a system, which provide information about how it works or how it is built.
The three main types of diagrams used in technology are the design plan, the technical diagram and the circuit diagram. Each serves a specific function, which is summarized in the table below.
|
Type of diagram |
Function |
|---|---|
|
Indicates the forces and motions involved in the operation of the object. |
|
|
Indicates how to construct the object to ensure its operation. |
|
|
Indicates the connection of the components of an electrical circuit to ensure its operation. |
Although a diagram is a simplified graphical representation, it must still meet certain standards. The following are some of the standards.
-
Laying out: Lines must be clean and legible. They are made by hand with technical drawing instruments or on the computer.
-
Colour: It is possible to add colour to a diagram to distinguish the parts of an object or to distinguish the materials used during construction.
-
Representation: The object is illustrated in two dimensions on a diagram. It is possible to represent it with multiple views, as in a multiview projection. Cross-sectional views can also be used to highlight specific details.
-
Proportions: The measurements of the pieces do not have to be exact or to scale, but they must comply with the proportions of the object studied.
-
Dimensioning: dimensioning is optional on a diagram. If used, it must follow the same rules as in the manufacturing drawings.
Symbols used in mechanical and electrical engineering are standardized representations found in diagrams to indicate certain specifications related to the operation and construction of an object.
To visualize an object and its operation more clearly, symbols are added to a diagram. The symbols are standardized to ensure clear communication between the different parties involved in the manufacture or analysis of an object. In fact, these symbols are a part of an international language of graphical symbols, as are basic lines in technical drawing.
Since each type of diagram has its own purpose, different symbols are used in each one.
The following elements can be illustrated using symbols:
-
Constraints
-
Types of motion
-
Motion transmission systems
-
Motion transformation systems
-
Mechanical links and guiding controls
The design plan and the construction diagram are two types of diagrams used in mechanical engineering. The following symbols can be found in these diagrams.
Constraints
Constraint symbols are used to represent the effects of forces acting on an object. They are usually found in the design plan.
|
Compression |
Tension |
Torsion |
Deflexion (Bending) |
Shearing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
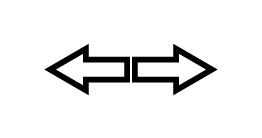 |
 |
 |
 |
Types of motion
Symbols representing mechanical motions are also included in the design plan to illustrate the types of motion that can be carried out by parts of an object. They are usually found in the design plan.
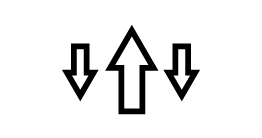
|
Unidirectional rectilinear translation |
Bidirectional rectilinear translation |
Unidirectional rotation |
Bidirectional rotation |
Unidirectional helical motion |
Bidirectional helical motion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Motion Transmission Systems
Some technological objects have motion transmission systems. To indicate them, the following standardized symbols are used. They are usually found in a design plan.
|
Friction gears |
Pulleys and belt |
Gear train |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
|
Chain and sprockets |
Worm and worm gear |
|
 |
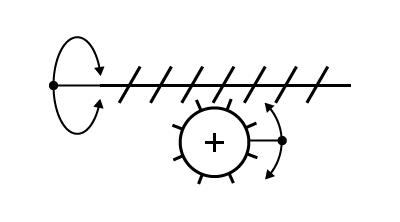 |
|
Motion Transformation Systems
Some technological objects have motion transformation systems. The systems are indicated by the following standardized symbols. We usually find them in a design plan.
|
Screw gear |
Connecting rod and crank |
Rack and pinion |
|---|---|---|
 |
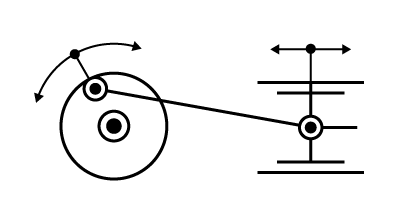 |
 |
|
Worm and rack |
Cam and roller |
|
 |
 |
|
Mechanical links and guides
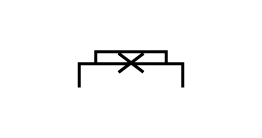
The link symbols enable you to visualize the interlocking or the links that unite the parts. Guiding symbols are used to design the trajectory of moving parts. They are usually found in the construction diagram.
|
Complete link |
Complete flat link |
Translational guiding control |
Rotational guiding control |
Rotational and translational guiding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
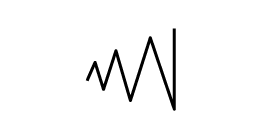
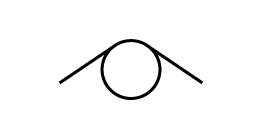
Depending on the characteristics of the links, they can be rigid or flexible. A flexible link is often associated with springs. The following symbols are used to represent the different types of springs. They are usually found in a construction diagram.
|
Compression spring |
Tension spring |
Conical spring |
Torsion spring |
Angular tension spring |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
The circuit diagram is used to represent the connection of the components of an electrical circuit. Standard symbols are used to illustrate each electrical component. On this type of diagram, it is also possible to show the value of certain parameters, such as voltage, current intensity, and resistance.
Here is a list of the most commonly used symbols in a circuit diagram.
|
Ammeter |
Voltmeter |
Bulb |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
|
Resistor |
Cell or battery |
Open switch |
 |
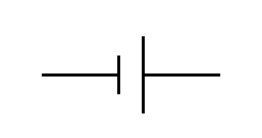 |
 |
Consult the concept sheet on electrical circuits and their symbols to access the complete list of standardized symbols used in electrical engineering.